Contents
- 1 What Are the 5 Main Functions of the Muscular System?
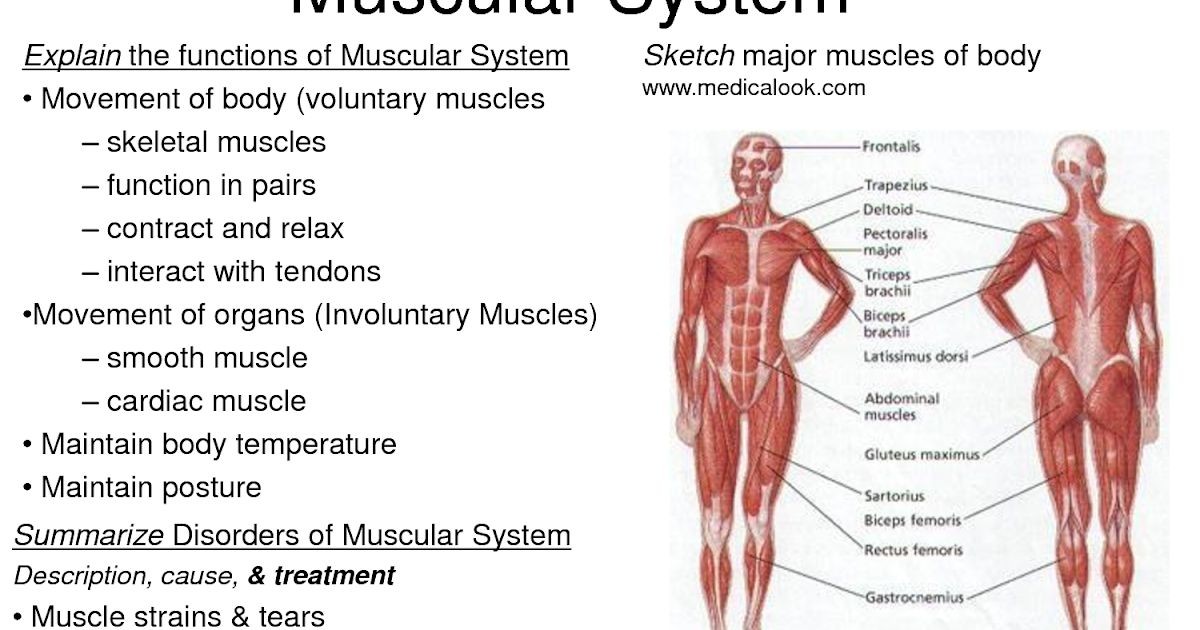
What Are the 5 Main Functions of the Muscular System?
The muscular system is a machine that converts food’s chemical energy into mechanical energy. The 5 main functions of the muscular system are movement, support, protection, heat generation, and blood circulation.
1. Movement
- Skeletal muscles pull on bones, causing joint movements.
- Skeletal muscles pull on facial soft tissues, causing expressions.
- Respiratory muscles enable breathing.
2. Support
- Body wall muscles support internal organs.
- As these muscles lose tone, internal organs may bulge outward with aging.
3. Protection
- Skeletal muscles cushion the body’s internal organs from external force.
4. Heat generation
- Heat is a byproduct of muscle metabolism, which helps maintain body temperature.
- Shivering generates heat to warm the body.
5. Blood circulation
- Cardiac muscles aid the heart’s pumping action, facilitating blood circulation.
What are the types of muscles in the muscular system?
The muscular system consists of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles:
- Skeletal muscles: These muscles create body movement and constitute about 40% of body weight.
- Smooth muscles: These involuntary muscles line blood vessels and viscera.
- Cardiac muscles: These muscles contract and expand the heart properly.
What are the functions of skeletal muscle fibers?
Skeletal muscle fibers are categorized into two types: slow-twitch fiber and fast-twitch fiber, performing different functions:
Slow-twitch fibers
- Contract at a slow rate.
- Play a vital role in endurance activities like cross-country races.
Fast-twitch fibers
- Contract at a fast rate.
- Produce explosive power and fast repetitive contractions.
- Mainly used in high-speed activities like sprints and weightlifting.
- Play a vital role in anaerobic activities.
QUESTION
What foods are good for the muscular system?
Nutrient-rich food is important for the muscular system. Foods that contribute to a strong muscular system include:
- Meat, poultry, milk, eggs, and seafood: These contain essential amino acids. Dairy products also strengthen bones and muscles.
- Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables: These contribute to a healthy muscular and skeletal system by providing carbohydrates, antioxidants, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Healthy fats: These prevent inflammation and function as a reserve fuel source.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These lower the risk of irregular heartbeats and prevent plaque accumulation.
What is an oblique muscle?
The oblique muscles consist of external oblique muscles and internal oblique muscles. They form a firm wall in the abdomen, supporting the spine and internal organs and maintaining an erect posture for protection.
Abdominal muscles work together to produce spine movements and compress the abdominal viscera. The oblique muscles, along with the transversus abdominis muscle, make up the three muscle layers surrounding the abdominal wall.
Clicking Submit means you agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that you may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
What is the external oblique muscle?
The external oblique muscle is located on both sides of the trunk. It contributes to various trunk movements, such as twisting, pulling the chest downwards, and rotating the spine. Strain, injury, or trauma to the muscle can be debilitating.
The external abdominal oblique muscle has different functions based on unilateral or bilateral contraction:
- Unilateral contraction, in synergy with the internal oblique muscle, rotates the trunk to the opposite side.
- Working with back muscles, it helps bend the trunk sideways.
- Bilateral contraction leads to the forward flexion of the trunk and increases the tone of the abdominal wall and intra-abdominal pressure during activities like exhalation and childbirth.
What is the internal oblique muscle?
The internal oblique muscle is a broad, thin muscular sheet deep to the external oblique muscle. It has multiple sites of origin and is divided into anterior, posterior, and lateral fibers. This muscle opposes the diaphragm during exhalation, rotates and bends the trunk sideways, and helps maintain normal abdominal wall tension.
Along with other abdominal wall muscles, the internal abdominal oblique muscle plays a protective and supportive role. Bilateral contraction of this muscle increases intra-abdominal pressure and aids in functions like forced expiration, urination, defecation, and prevention of abdominal hernias.
From
Healthy Resources
- 7 Germy Places You Probably Touch Every Day
- BMI Calculator: What Your Numbers Mean
- Myelofibrosis: Active Role in Your Health