Contents
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Fatty acids consist of chains of carbon atoms linked together by chemical bonds. On one end of the carbon chain is a methyl group, and on the other end is a carboxyl group. These chemical bonds determine if a fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids can also vary in length, with short chain fatty acids having fewer than 6 carbons, and long chain fatty acids having 12 or more carbons.
Fatty acids serve as energy for the body and as building blocks for cell membranes. Any unused fatty acids are converted into triglycerides and stored in the body as fat tissue.
Saturated fatty acids contain only single bonds. Foods high in saturated fats include lard, butter, whole milk, cream, eggs, red meat, chocolate, and solid shortenings. An excessive intake of saturated fat can raise blood cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one double bond. Foods high in monounsaturated fat include avocados, nuts, and olive, peanut, and canola oils. Increasing consumption of monounsaturated fats can lower LDL cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease, especially when used to replace saturated fats and refined sugars.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids contain more than one double bond. Foods high in polyunsaturated fats include vegetable oils, corn, sunflower, and soy.
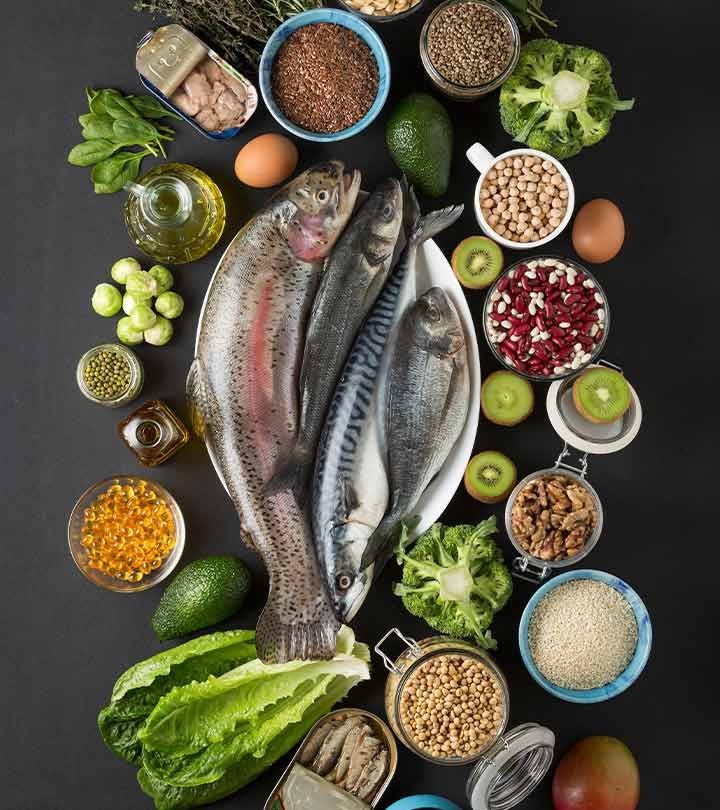
Omega-3 fatty acids are a class of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids with a double bond in the third carbon position. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, halibut, sardines, albacore, trout, herring, walnut, flaxseed oil, and canola oil. Other sources include shrimp, clams, light chunk tuna, catfish, cod, and spinach.
Omega-6 fatty acids are a class of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids with a double bond in the sixth carbon position. Foods rich in omega-6 fatty acids include corn, safflower, sunflower, soybean, and cottonseed oil.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are also known as n-3 and n-6 fatty acids, respectively.
Trans fatty acids, also known as trans fats, are made through hydrogenation. They increase the risk of heart disease and are found in vegetable shortenings, margarines, commercial pastries, fried foods, crackers, cookies, and snack foods.
What are the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids?
Scientific evidence suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death and improve blood lipid levels, potentially decreasing the risk of heart disease.
QUESTION
What foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids?
- Eat whole, natural, and fresh foods.
- Eat five to ten servings of fruits and vegetables daily, and include more peas, beans, and nuts in your diet.
- Increase omega-3 fatty acid intake by consuming more fish, walnuts, flaxseed oil, and green leafy vegetables. Examples of meeting the recommended intake include eating 2 portions of salmon per week or taking a daily 1 gram omega-3 fatty acid supplement.
- Drink water, tea, non-fat dairy, and red wine in moderation.
- Choose lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, and lean cuts of red meat.
- Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fat intake by avoiding fried foods, hard margarine, commercial baked goods, packaged and processed snack foods, high-fat dairy, and processed meats.
- Limit glycemic foods made with sugar and white flour, as they can increase blood sugar levels and insulin release.
- Exercise regularly.
Has science proven the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids?
Animal studies
In studies involving animals, omega-3 fatty acids were found to prevent ventricular fibrillation in experimentally induced heart attacks. Scientists suspect that omega-3 fatty acids may prevent ventricular fibrillation in humans, which is the leading cause of sudden death among heart attack victims.
Evidence from observational studies: Two large, long-term observational studies, the Nurses’ Health Study and the Physician’s Health Study, have shown a relationship between fish oil and omega-3 fatty acid intake and the risk of heart disease and sudden cardiac death.
The Physician’s Health Study found that men who consumed one or more fish meals per week had a 50% lower risk of sudden cardiac death compared to men who rarely ate fish.
The Nurses’ Health Study found that women who ate fish once a week had a 29% lower risk of coronary heart disease compared to those who rarely ate fish. Women who ate fish five times a week had a 34% reduction in the risk of coronary heart disease and a 45% reduction in the risk of death from heart disease.
Controlled Studies: Two controlled studies, the GISSI-Prevention trial and the Lyon Diet Heart Study, have also been conducted on omega-3 fatty acids and fish oil.
The GISSI-Prevention trial found that omega-3 fatty acids reduced death rates from coronary heart disease, particularly sudden cardiac death, compared to vitamin E and control groups.
The Lyon Diet Heart Study found that a Mediterranean diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids significantly reduced the risk of sudden cardiac death and repeat heart attacks compared to a Western diet.
Though the GISSI-Prevention trial focused on preventing sudden cardiac death and the Lyon Diet Heart Study examined the recurrence of heart attacks, both studies support the cardiovascular benefits of omega-3 fatty acids.