Contents
- 1 Microscopic Colitis
- 1.0.1 What are the types of colitis?
- 1.0.2 What causes microscopic colitis?
- 1.0.3 What are the signs and symptoms of microscopic colitis?
- 1.0.4 Microscopic colitis vs. irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- 1.0.5 What procedures and tests diagnose microscopic colitis?
- 1.0.6 What is the treatment for microscopic colitis?
- 1.0.7 Can microscopic colitis be cured?
- 1.0.8 Can microscopic colitis be prevented?
Microscopic Colitis
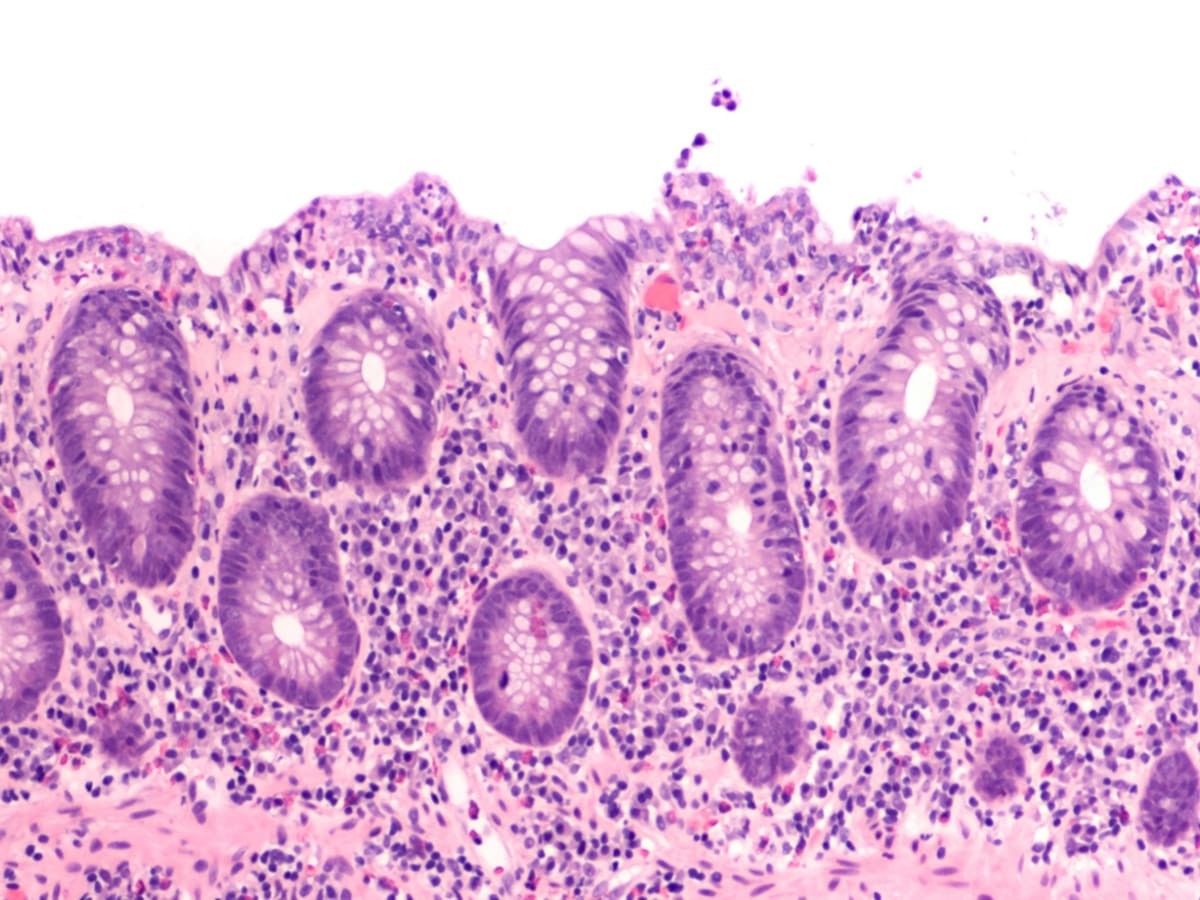
Microscopic colitis refers to inflammation of the colon that is only visible under a microscope. The appearance of the colon lining is normal during colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy.
The diagnosis of microscopic colitis is made when a doctor takes biopsies of the normal-appearing lining during colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy and examines them under a microscope.
There are two types of microscopic colitis:
- Lymphocytic colitis. In lymphocytic colitis, there is an accumulation of lymphocytes within the lining of the colon.
- Collagenous colitis. In collagenous colitis, there is an additional layer of collagen just below the lining.
Some experts believe that lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis represent different stages of the same disease.
What are the types of colitis?
Colitis means inflammation of the colon. The colon constitutes the last part of the digestive tract. It removes water from undigested food, stores the undigested food, and eliminates it from the body through bowel movements.
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Sometimes, rectal bleeding
There are many different types of colitis with different causes, including:
- Bacterial infectious colitis caused by bacteria
- Viral infectious colitis caused by a virus
- Radiation colitis caused by radiation treatment
- Ischemic colitis caused by an artery blockage in the colon
- Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitisare two related conditions caused by abnormalities of the immune system
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are also referred to as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Visible abnormalities of the inner lining of the colon
What causes microscopic colitis?
The cause(s) of microscopic colitis is unknown. Some experts suspect that it is an autoimmune disorder. Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for more than 6 months may also be a cause. Some other drugs have been associated with microscopic colitis as well.
The most common drugs that can cause microscopic colitis include:
- proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- lansoprazole
- omeprazole
- esomeprazole
- the Statin simvastatin
- SSRI sertraline
- P2Y12 inhibitor ticlopidine
- H2 blocker ranitidine
What are the signs and symptoms of microscopic colitis?
The primary symptom of microscopic colitis is chronic, watery diarrhea.
- People with microscopic colitis can have diarrhea for months or years before the diagnosis is made.
- Typically, the symptoms begin gradually and are intermittent.
- This chronic diarrhea is different from the acute diarrhea of infectious colitis.
- Some individuals with microscopic colitis also may experience mild abdominal cramps and pain.
- Blood in the stool is unusual for microscopic colitis.
A person should seek medical care if the diarrhea lasts for more than 2 weeks or is accompanied by symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
QUESTION
Microscopic colitis vs. irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) do not have colitis. These individuals may have symptoms that mimic colitis, but there is no inflammation of the colon in patients with IBS. The cause of symptoms in IBS is not known; it may be caused by abnormal motility of the intestinal muscles or abnormally sensitive nerves in the intestines.
What procedures and tests diagnose microscopic colitis?
The diagnosis of microscopic colitis is made by performing biopsies from different regions of the colon during colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy.
The abnormalities of the colon’s lining in microscopic colitis occur in a patchy distribution. For this reason, multiple biopsies should be taken from several different regions of the colon to accurately make a diagnosis.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy often is inadequate in diagnosing the condition because the abnormalities may be absent from the sigmoid colon.
Thus, biopsies of other regions of the colon accessible only with colonoscopy may be necessary for diagnosing microscopic colitis.
What is the treatment for microscopic colitis?
The treatment of microscopic colitis has not been standardized due to the lack of large-scale treatment trials. The following strategies may relieve diarrhea in some patients:
- Avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Trial of lactose elimination.
- Antidiarrhea agents like loperamide or bismuth subsalicylate.
- Budesonide or 5-ASA compounds.
Some doctors may use medications that suppress the immune system in severe cases.
Can microscopic colitis be cured?
The long-term prognosis of microscopic colitis is not clear. In approximately two-thirds of patients, the diarrhea resolves spontaneously after several years. The remaining one-third of patients experience persistent or intermittent diarrhea and/or abdominal pain for many years.
There is no cure for microscopic colitis.
Can microscopic colitis be prevented?
Since the cause of microscopic colitis is not known, no advice can be provided about preventing this disease.
Kroser, JA, MD, et al. Collagenous and Lymphocytic Colitis. Medscape. Updated: Jan 04, 2017.
Riddell, RH, MD, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a possible cause of collagenous colitis: a case-control study. Gut. 1992 May; 33(5): 683–686.