Contents
- 1 Metronidazole vs. Vancomycin
Metronidazole vs. Vancomycin
Metronidazole is an antibiotic used to treat Clostridium difficile diarrhea, amebic liver abscess, amebic dysentery, bacterial vaginosis, trichomonas vaginal infections, carriers of trichomonas who do not have symptoms of infection, Giardia infections of the small intestine, abscesses, Helicobacter pylori, acne rosacea, and metronidazole vaginal gel is used to treat bacterial vaginosis.
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic used for the treatment of Clostridium difficile diarrhea and staphylococcal enterocolitis. Vancomycin is only effective against gram-positive bacteria.
What are the side effects of metronidazole and vancomycin?
Metronidazole
Flagyl is a useful antibiotic and is generally well tolerated with appropriate use.
The most common and minor side effects include:
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- A metallic taste
- Rarely a rash
- Abdominal cramps
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Dark-colored urine
- Metallic taste in mouth
- Weight loss (anorexia)
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Furry tongue
- Rash
- Nasal congestion
- Flushing
- Vaginal dryness
Side effects that are uncomfortable, but may become serious include:
- Brain disease
- Fevers
- Mouth sores
- Pain with urination
- Prickling or tingling sensations that may become permanent
- Cystitis
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Decrease of libido
- Proctitis
- Stomitis
- Glossitis
Serious side effects of Flagyl are rare and the drug should be stopped if these symptoms appear:
- Seizures
- Damage of nerves resulting in numbness and tingling of extremities
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Encephalopathy
- Aseptic meningitis
- Asceptic meningitis
- Colon cancer in people with Crohn’s disease
Vancomycin
The most common side effects associated with oral vancomycin treatment are:
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Low potassium levels in the blood
Less common side effects are:
- Peripheral edema (swelling of the feet and/or legs)
- Tiredness
- Fever
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Gas
- Vomiting
- Urinary tract infection
- Back pain
Rare but serious side effects are:
- Kidney failure
- A decrease in platelets
- Hearing problems
- Vasculitis
QUESTION
What is the dosage of metronidazole vs. vancomycin?
Metronidazole
- Metronidazole may be taken orally with or without food.
- In the hospital, metronidazole can be administered intravenously to treat serious infections.
- The liver is primarily responsible for eliminating metronidazole from the body, and doses may need to be reduced in patients with liver disease and abnormal liver function.
Various metronidazole regimens are used. Some examples are listed below.
- Amebic dysentery: 750 mg orally 3 times daily for 5-10 days
- Amebic liver abscess: 500-750 mg orally three times daily for 5-10 days
- Anaerobic infections: 7.5 mg/kg orally or by injection every 6 hours for 7 to 10 days not to exceed 4 grams daily.
- Bacterial vaginosis: 750 mg (extended release tablets) once daily for 7 days or 500 mg twice daily for 7 days or 2 g single dose or one applicator-full of 0.75% vaginal gel, once or twice daily for 5 days.
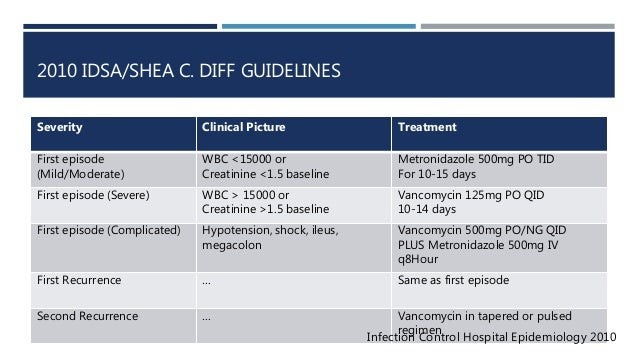
- Clostridium difficile infection: 250-500 mg orally 4 times daily or 500-750 orally 3 times daily
- Giardia: 250 mg orally three times daily for 5 days Helicobacter pylori: 800-1500 mg orally daily for several days in combination with other drugs.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): 500 mg orally twice daily for 14 days in combination with other drugs.
- Trichomoniasis: 2 g single dose or 1 g twice
- Rosacea: apply topical gel 0.75-1% once daily
Vancomycin
Adults
- C. difficile-associated diarrhea: The recommended dose is 125 mg administered orally 4 times daily for 10 days.
- Staphylococcal enterocolitis: Total daily dosage is 500 mg to 2 g administered orally in 3 or 4 divided doses for 7 to 10 days.
Pediatric Patients (less than 18 years of age)
For both C. difficile associated diarrhea and staphylococcal enterocolitis, the usual daily dosage of Vancomycin is 40 mg/kg in 3 or 4 divided doses for 7 to 10 days. The total daily dosage should not exceed 2 g.
What drugs interact with metronidazole and vancomycin?
Metronidazole
- Alcohol should be avoided because metronidazole and alcohol together can cause severe nausea, vomiting, cramps, flushing, and headache.
- Metronidazole can increase the blood thinning effects of warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) and increase the risk of bleeding by reducing the breakdown of warfarin.
- Cimetidine (Tagamet) increases blood levels of metronidazole while cholestyramine (Questran, Questran Light) reduces blood levels of metronidazole by reducing its absorption.
- Metronidazole should not be combined with amprenavir (Agenerase) for treating human immunodeficiency disease (HIV) because amprenavir contains propylene glycol.
- Metronidazole blocks the breakdown of propylene glycol in the liver leading to accumulation in blood. Accumulation of propylene glycol could cause seizures, increased heart rate, and lead to kidney failure.
- Metronidazole increases the blood levels of carbamazepine (Tegretol, Tegretol XR, Equetro, Carbatrol), lithium (Eskalith, Lithobid) and cyclosporine though unknown mechanisms. Serious reactions may occur if these drugs are taken with metronidazole.
Vancomycin
No drug interaction studies have been conducted for oral vancomycin.
Are metronidazole and vancomycin safe to use while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Metronidazole
- Metronidazole is not used in early pregnancy because of potential adverse effects on the fetus.
- Metronidazole is excreted in breast milk. Females who are nursing, because of potential adverse effects on the newborn, should not use metronidazole.
Vancomycin
Use of vancomycin in pregnancy has not been adequately evaluated. Due to the lack of safety data, vancomycin should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed. Oral vancomycin is classified as FDA pregnancy risk category B. This designation indicates animal studies have shown no harm to the fetus, but adequate safety studies on pregnant women do not exist.
Vancomycin is excreted in human milk after intravenous administration. However, oral administration of vancomycin does not result in significant levels of the drug in the blood, and it is not known if vancomycin is excreted in breast milk after oral administration. Due to the lack of safety data, oral vancomycin should be used cautiously in nursing mothers.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Summary
Metronidazole is an antibiotic used to treat Clostridium difficile diarrhea, amebic liver abscess, amebic dysentery, bacterial vaginosis, trichomonas vaginal infections, carriers of trichomonas who do not have symptoms of infection, Giardia infections of the small intestine, abscesses, acne rosacea, and metronidazole vaginal gel is used to treat bacterial vaginosis. Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic used for the treatment of Clostridium difficile diarrhea and staphylococcal enterocolitis.
Overall, the text has been carefully reviewed for redundancy and unnecessary phrasing. The information has been condensed without losing its original meaning, resulting in a concise and impactful text. The HTML markup has been preserved exactly as in the original.