Contents
- 1 Invanz
- 1.0.1 Side Effects of Invanz
- 1.0.2 Dosage for Invanz
- 1.0.3 Drug Interactions with Invanz
- 1.0.4 Safety of Invanz during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- 1.0.5 Summary
Invanz
Invanz is a prescription medicine used to treat various bacterial infections in the skin, lungs, stomach, pelvis, and urinary tract. It may be used alone or with other medications.
Invanz belongs to the class of drugs called Carbapenems.
The safety and effectiveness of Invanz in children younger than 3 months of age is unknown.
Side Effects of Invanz
Invanz may cause serious side effects, including:
- Severe stomach pain
- Watery or bloody diarrhea
- Tremors
- Twitching
- Rigid (very stiff) muscles
- Seizures
- Unusual changes in mood or behavior
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
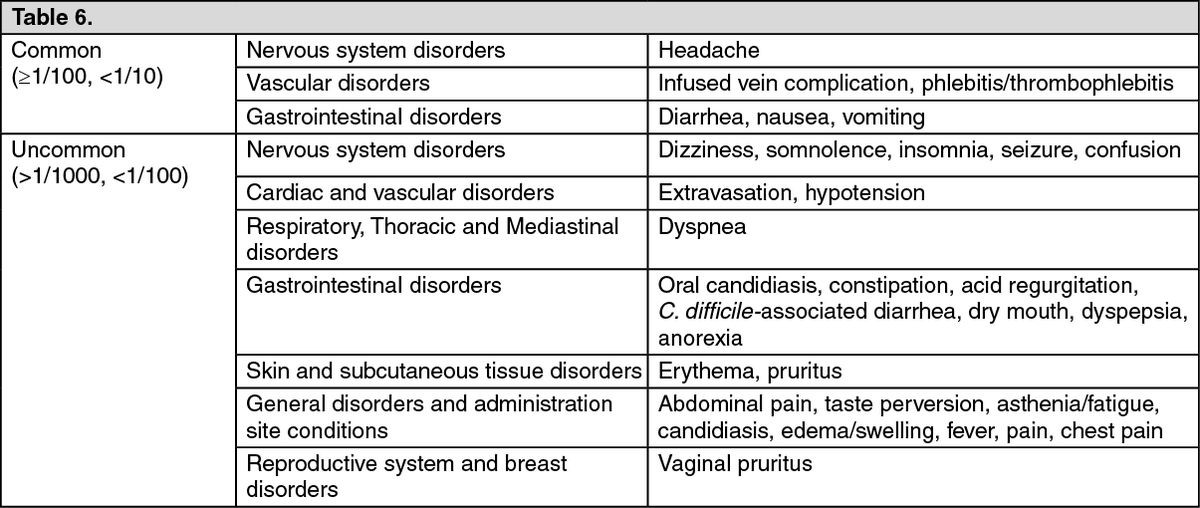
The most common side effects of Invanz include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Pain, redness, or mild swelling at the injection site
If you have a side effect that bothers you or does not go away, inform your doctor.
These are not all the possible side effects of Invanz. For more information, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Contact your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may also report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Dosage for Invanz
Instructions for Use in All Patients
For Intravenous or Intramuscular Use
DO NOT MIX OR CO-INFUSE Invanz WITH OTHER MEDICATIONS. DO NOT USE DILUENTS CONTAINING DEXTROSE (α-D-GLUCOSE).
Invanz can be administered by intravenous infusion for up to 14 days or by intramuscular injection for up to 7 days. When given intravenously, it should be infused over 30 minutes.
Intramuscular administration may be used as an alternative to intravenous administration for appropriate infections.
Treatment Regimen
13 Years of Age and Older
- The dose of Invanz in patients 13 years of age and older is 1 gram (g) once daily.
3 Months to 12 Years of Age
- The dose of Invanz in patients 3 months to 12 years of age is 15 mg/kg twice daily (not to exceed 1 g/day).
- Table 1 presents treatment guidelines for Invanz.
Table 1: Treatment Guidelines for Adults and Pediatric Patients with Normal Renal Function* and Body Weight
| Infection† | Daily Dose (IV or IM) Adults and Pediatric Patients 13 years of age and older | Daily Dose (IV or IM) Pediatric Patients 3 months to 12 years of age | Recommended Duration of Total Antimicrobial Treatment |
| Complicated intra-abdominal infections | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ | 5 to 14 days |
| Complicated skin and skin structure infections including diabetic foot infection# | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ | 7 to 14 days¶ |
| Community acquired pneumonia | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ | 10 to 14 days# |
| Complicated urinary tract infections including pyelonephritis | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ | 10 to 14 days# |
| Acute pelvic infections including postpartum endomyometritis septic abortion and post-surgical gynecologic infections | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ | 3 to 10 days |
| * defined as creatinine clearance>90 mL/min/1.73 m² † due to the designated pathogens ‡ not to exceed 1 g/day § Invanz has not been studied in diabetic foot infections with concomitant osteomyelitis. ¶ adult patients with diabetic foot infections received up to 28 days of treatment (parenteral or parenteral plus oral switch therapy) # duration includes a possible switch to an appropriate oral therapy, after at least 3 days of parenteral therapy, once clinical improvement has been demonstrated. |
|||
Prophylactic Regimen in Adults
- Table 2 presents prophylaxis guidelines for Invanz.
Table 2: Prophylaxis Guidelines for Adults
| Indication | Daily Dose (IV) Adults | Recommended Duration of Total Antimicrobial Treatment |
| Prophylaxis of surgical site infection following elective colorectal surgery | 1 g | Single intravenous dose given 1 hour prior to surgical incision |
Patients with Renal Impairment
- Invanz can be used for the treatment of infections in adult patients with renal impairment. No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with a creatinine clearance >30 mL/min/1.73 m².
- Adult patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min/1.73 m²) and end-stage renal disease (creatinine clearance ≤10 mL/min/1.73 m²) should receive 500 mg daily.
- A supplementary dose of 150 mg is recommended if ertapenem is administered within 6 hours prior to hemodialysis. There are no data in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
Patients on Hemodialysis
- When adult patients on hemodialysis receive the recommended daily dose of 500 mg of Invanz within 6 hours prior to hemodialysis, a supplementary dose of 150 mg is recommended following the hemodialysis session. If Invanz is given at least 6 hours prior to hemodialysis, no supplementary dose is needed.
- There are no data in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis or hemofiltration. There are no data in pediatric patients on hemodialysis.
- When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
Males: (weight in kg) x (140 – age in years) / (72) x serum creatinine (mg/100 mL)
Females: (0.85) x (value calculated for males)
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- No dose adjustment recommendations can be made in patients with hepatic impairment.
QUESTION
Drug Interactions with Invanz
Probenecid
- Probenecid interferes with the active tubular secretion of ertapenem, resulting in increased plasma concentrations of ertapenem. Co-administration is not recommended.
Valproic Acid
- Co-administration of carbapenems, including ertapenem, with valproic acid or divalproex sodium can reduce valproic acid concentrations.
- Reduced valproic acid concentrations may be below the therapeutic range, increasing the risk of breakthrough seizures.
- The mechanism of this interaction is unknown, but in vitro and animal studies suggest that carbapenems may inhibit the hydrolysis of valproic acid’s glucuronide metabolite, decreasing serum concentrations of valproic acid.
Safety of Invanz during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Available data on the use of Invanz in pregnancy are insufficient to determine any drug-associated risks for major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
- Ertapenem is present in human milk, but there are no data on its effects on the breastfed infant or milk production.
- The benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Invanz and any potential adverse effects on the infant from Invanz or the underlying maternal condition.
Summary
Invanz is a prescription medicine used to treat bacterial infections in the skin, lungs, stomach, pelvis, and urinary tract. It can be used alone or with other medications. Serious side effects include severe stomach pain, watery or bloody diarrhea, tremors, twitching, rigid muscles, seizures, and unusual changes in mood or behavior.