Contents
- 1 Osteoarthritis Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
- 1.1 What joints are most often affected by osteoarthritis?
- 1.2 What are risk factors for developing osteoarthritis?
- 1.3 What are symptoms of osteoarthritis?
- 1.4 What are home remedies that can ease osteoarthritis symptoms?
- 1.5 What medications are used to treat osteoarthritis?
- 1.6 Types of surgery used to treat osteoarthritis include…
- 1.7 What is the best exercise for osteoarthritis?
- 1.8 What are the best foods to eat for osteoarthritis?
- 1.9 What foods should I avoid if I have osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
What joints are most often affected by osteoarthritis?
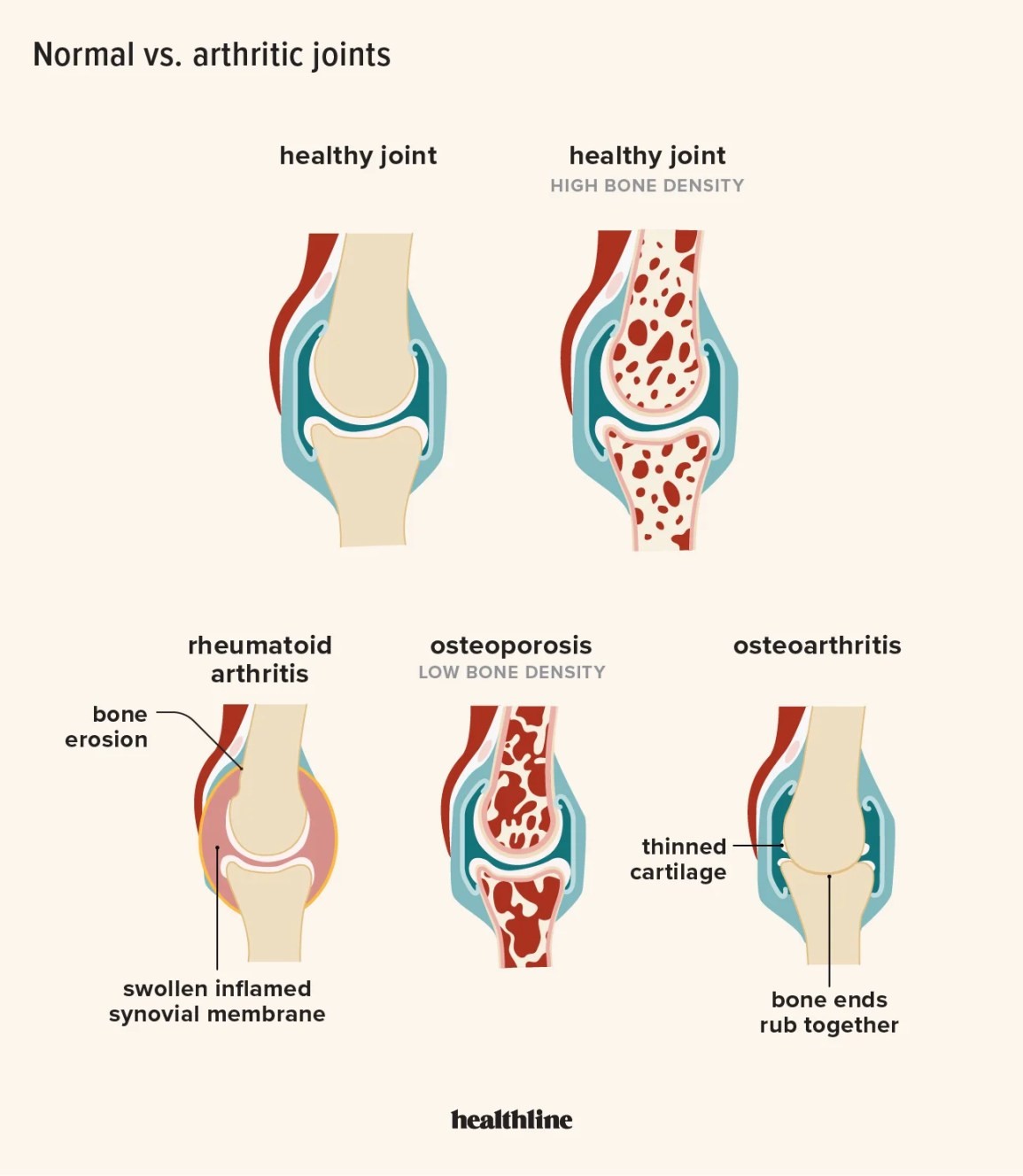
There are many types of arthritis, or conditions involving joint inflammation. Osteoarthritis (OA) commonly affects the hands, fingers, knees, hips, and spine.
OA is the most common type, typically occurring with age. The cartilage between bones that cushions the joints breaks down, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling as the bones rub against each other.
Hands Hips Both hands and hips Shoulders
What are risk factors for developing osteoarthritis?
- Age over 55
- Gender – women are 2-3 times more likely to develop OA
- Obesity
- Occupations requiring frequent squatting and kneeling, such as dock work, shipyard work, carpentry, construction, farm work, and cotton processing
- Prolonged standing or walking several miles each day
- Sports such as wrestling, boxing, pitching in baseball, cycling, parachuting, gymnastics, soccer, and football
High blood pressure Weight loss Age over 55 Steroid use
What are symptoms of osteoarthritis?
OA symptoms typically occur in hands, fingers, knees, hips, and spine. Joints of the elbow, wrist, and ankle are rarely affected.
- Joint pain worsening with activity, relieved by rest; severe cases may have pain at rest
- Morning joint stiffness resolving within 30 minutes of waking
- Joint swelling (effusion) from excess fluid accumulation
- Crackling or grating sensation in the joints (crepitus)
- Bony outgrowths called osteophytes or bone spurs, enlarging over time and felt under the skin near joints
Joint pain Joint stiffness Joint swelling All of the above
What are home remedies that can ease osteoarthritis symptoms?
- Weight loss lowers the risk of worsening OA and decreases pain
- Physical therapy and exercise programs improve flexibility, strengthen the muscles around joints, decrease pain, and improve joint function
- Orthoses help keep joints aligned to reduce symptoms and maintain function
- Splints immobilize joints to reduce pain and inflammation
- Assistive devices such as canes, walkers, electric-powered seat lifts, raised toilet seats, and tub and shower bars reduce joint stress and ease daily tasks
- Arthritis education and support help patients self-manage their condition
- Psychosocial support such as informal support networks or formal OA support groups benefit patients
- Glucosamine and chondroitin are dietary supplements that may reduce pain with few side effects; consult your doctor before using any nutritional supplements
Weight loss Shoe inserts Fish oil Acupuncture
What medications are used to treat osteoarthritis?
- Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) applied to the skin over the joint; tried before oral NSAIDs
- Topical capsaicin, derived from hot chili pepper, helps with hand and knee OA
- Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain and reduce inflammation, available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription
- Steroid injections occasionally recommended for significant pain unresponsive to weight loss, exercise, and other medications
- Acetaminophen offers minimal benefits but is usually not significantly effective for OA pain relief
- Hyaluronate injections not generally recommended due to lack of evidence and high cost
- Opioids (narcotic pain relievers) not recommended for long-term use due to equal effectiveness as other pain medications, high risk of side effects, and potential for abuse and addiction
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Hyaluronate injections Narcotic pain medications
Types of surgery used to treat osteoarthritis include…
- Realignment of chronically misaligned bones and other joint structures instead of joint replacement, for younger and more active patients
- Fusion surgery permanently fuses two or more bones at a joint; used when joint replacement is not appropriate for badly damaged joints
- Joint replacement surgery replaces a damaged joint with an artificial (prosthetic) joint; for pain relief that limits everyday activities and an active lifestyle
Realignment Fusion Replacement All of the above
What is the best exercise for osteoarthritis?
- Strength exercises using free weights, weight machines, or body weight
- Low-impact endurance exercises such as swimming and cycling
- Yoga or tai chi
Yoga Running Basketball Boxing
What are the best foods to eat for osteoarthritis?
- Calcium and vitamin D-rich foods, like leafy green vegetables
- Broccoli, containing a compound called sulforaphane that may slow OA progression
- Green tea, containing antioxidants that reduce inflammation and slow cartilage destruction
- Citrus fruits, full of vitamin C
- Bell peppers, containing antioxidants that prevent joint deterioration
- Pineapples and pomegranates, with anti-inflammatory effects
- Garlic, containing the compound diallyl disulphine that limits cartilage-damaging enzymes
- Oils with omega-3 fatty acids, such as extra virgin olive oil, avocado, safflower, and walnut oils
Citrus fruits Meat Bread Cookies
What foods should I avoid if I have osteoarthritis?
- Wheat products like pasta and refined grain products (prefer whole grains)
- Fried foods that raise cholesterol and contribute to inflammation and pain
- Foods with omega-6 fatty acids like red meat and egg yolks
- Salt causing water retention and inflammation
- Sugary snacks that worsen inflammation
Refined wheat Fried foods Salt All of the above
Images provided by:
1. iStockPhoto
2. iStockPhoto
3. iStockPhoto
4. iStockPhoto
5. iStockPhoto
6. iStockPhoto
7. iStockPhoto
8. iStockPhoto
9. iStockPhoto
Arthritis Research Institute of America. Foods That Osteoarthritis Sufferers Should Avoid.
This tool does not provide medical advice. See additional information:
THIS TOOL DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE. It is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MedicineNet Site. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your doctor or dial 911.
© 1996-2024 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved.
© 1996-2024 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved.