Myelodysplastic or Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (Leukemia Types)
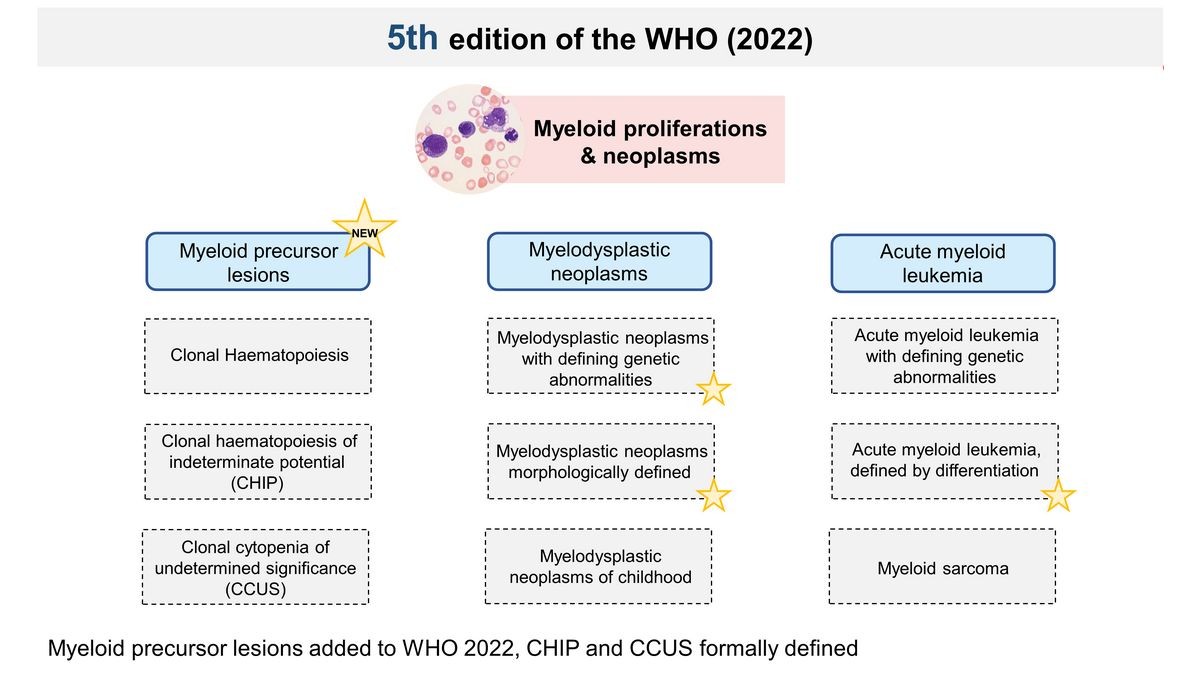
Myelodysplastic syndrome is characterized by the production of abnormal blood cells in the bone marrow.
Both myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) are different types of blood disorders. MDS is a group of disorders that affect the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, whereas MPN is a group of disorders that affect the show as well as the function of blood cells.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the incidence of MDS/MPN varies greatly. It can range from approximately 3 per 100,000 people older than 60 years annually for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia to as few as 0.13 per 100,000 children younger than 14 years annually for juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia.
What are 3 types of myelodysplastic or myeloproliferative neoplasms?
Three main types of myelodysplastic syndromes/myeloproliferative neoplasms are as follows:
1. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML)
It is a rare cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow. It is characterized by the abnormal production of a type of white blood cell called monocytes and other abnormal cells in the blood.
It is more common in older adults, with the average age at diagnosis being about 70 years. The exact cause of CMML is not known, but it is thought to be related to genetic abnormalities that affect the production and function of blood cells. There are no known ways to prevent CMML, and the condition is usually diagnosed through a combination of blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging tests.
CMML can progress to acute myeloid leukemia and may affect other organs, such as the liver and spleen. Symptoms of CMML may include fatigue, weakness, anemia, bruising or bleeding easily, and infections. Treatment options may include medications to control the production of abnormal cells, blood transfusions, and bone marrow transplantation.
Several genetic abnormalities have been associated with CMML, such as:
- Somatic mutations: These are changes in the DNA of certain cells that occur after a person is born. Some of the most common somatic mutations in CMML include changes in the TP53, NRAS, and TET2 genes.
- Chromosomal translocations: These are changes in which pieces of chromosomes are swapped or rearranged. A common chromosomal translocation in CMML involves the RAS oncogene located on chromosome 3.
- Monosomy 7: This is a condition in which a person is missing one copy of chromosome 7. Monosomy 7 is found in about 50 percent of people with CMML.
- Tetrasomy 8: This is a condition in which a person has four copies of chromosome 8 instead of the normal two copies. Tetrasomy 8 is found in about 15 percent of people with CMML.
Not all people with CMML have these genetic abnormalities, and the specific genetic changes present can vary. Further research is required to understand the role of genetics in CMML.
JMML is a rare cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow. It is mostly diagnosed in children younger than four years and is characterized by the abnormal production of certain types of blood cells, including monocytes.
JMML can affect other organs, such as the liver and spleen. Symptoms of JMML may include fever, fatigue, easy bruising or bleeding, and infections. JMML requires prompt medical treatment.
Treatment options may include chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, and medications to control the production of abnormal cells. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of a successful outcome.
The exact cause of JMML is not fully understood yet. However, it is thought to be related to genetic abnormalities that affect the production and function of blood cells.
Several genetic abnormalities have been associated with JMML, including mutations in the CBL gene and other genes involved in signaling pathways that control cell growth and division, such as the NRAS and PTPN11 genes.
3. Atypical chronic myelogenous leukemia (aCML)
It is a rare subtype of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) that has features different from those of classic CML. aCML is less common than classic CML and is a slow-growing condition. However, aCML can progress to blast crisis if left untreated.
Symptoms of aCML may include fatigue, weakness, anemia, and infections. Treatment options may include medications (such as imatinib) to control the production of abnormal cells and bone marrow transplantation.
The exact cause of aCML is not fully understood. However, it is thought to be related to genetic abnormalities that affect the production and function of blood cells.
aCML is caused by a genetic abnormality called the Philadelphia chromosome, which results from a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22. This translocation leads to the production of a fusion protein called BCR-ABL, which promotes the abnormal growth and division of white blood cells. Philadelphia chromosome may not be present in all people with aCML, and other genetic changes may be involved.
QUESTION
What is myelodysplastic syndrome?
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), sometimes called myelodysplastic leukemia, is characterized by the production of abnormal blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to a decrease in healthy blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Symptoms of MDS may include fatigue, shortness of breath, easy bruising or bleeding, and an increased risk of infections.
A variety of factors, including exposure to certain chemicals, radiation therapy, certain medications, genetic mutation, or other medical conditions can cause MDS. Treatment for MDS may include medications to help the bone marrow produce normal blood cells, blood transfusions, and other supportive therapies. In advanced cases, a bone marrow transplant may be necessary.
What are myeloproliferative neoplasms?
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of disorders that affect the production and function of blood cells. MPN is characterized by the overproduction of specific blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets, leading to an increase in their number in the bloodstream. This can cause various symptoms, such as fatigue, bone pain, and an increased risk of blood clots.
The symptoms can vary depending on the type of MPN and the specific blood cells affected.
Some common symptoms of MPN may include:
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Shortness of breath
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Treatment for MPN may include medications to reduce the production of abnormal blood cells, blood transfusions, and other supportive therapies. A bone marrow transplant may be an option in the advanced stages.


