Contents
Sickle Cell Disease (Sickle Cell Anemia)
Sickle cell anemia is a blood disorder caused by abnormal hemoglobin in red blood cells. The abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become distorted and fragile, leading to anemia. Additionally, these irregular cells can block blood vessels and cause damage and pain.
Sickle cell anemia is a common inherited blood disorder that primarily affects Africans and African Americans. In the United States, it is estimated that 90,000 to 100,000 Americans have sickle cell anemia. It is particularly prevalent among African Americans, with one in 500 births being affected.
Causes of sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia occurs when red blood cells sickle due to low oxygen levels, increased acidity, or low blood volume. Factors such as tissue injury, dehydration, and anesthesia can promote sickling. Organs that have lower oxygen levels or acidities, or high metabolic rates, are more susceptible to sickle cell anemia-related damage.
QUESTION
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia result from the blockage of blood flow by sickled red blood cells, leading to tissue damage and impaired oxygen supply. The severity and frequency of symptoms depend on the involvement of organs.
The major symptoms of sickle cell anemia include fatigue, anemia, pain, swelling and inflammation of the hands and/or feet, bacterial infections, pooling of blood in the spleen and liver congestion, lung and heart injury, leg ulcers, bone infarcts, and eye damage.
Additional symptoms, occurring at different ages, may include fever, abdominal pain, bacterial infections, painful swellings of the hands and feet, and splenic sequestration in infants and younger children. Leg ulcers, aseptic necrosis, and eye damage are more common in adolescents and young adults. Adults typically experience intermittent pain episodes due to organ injury.
Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia can be identified through microscopic examination of the blood, which reveals sickle-shaped red blood cells. Other tests, such as sickle prep and solubility tests, can detect abnormal hemoglobin S. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is used to confirm the disease by quantifying the types of hemoglobin present. Prenatal diagnosis can be done through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
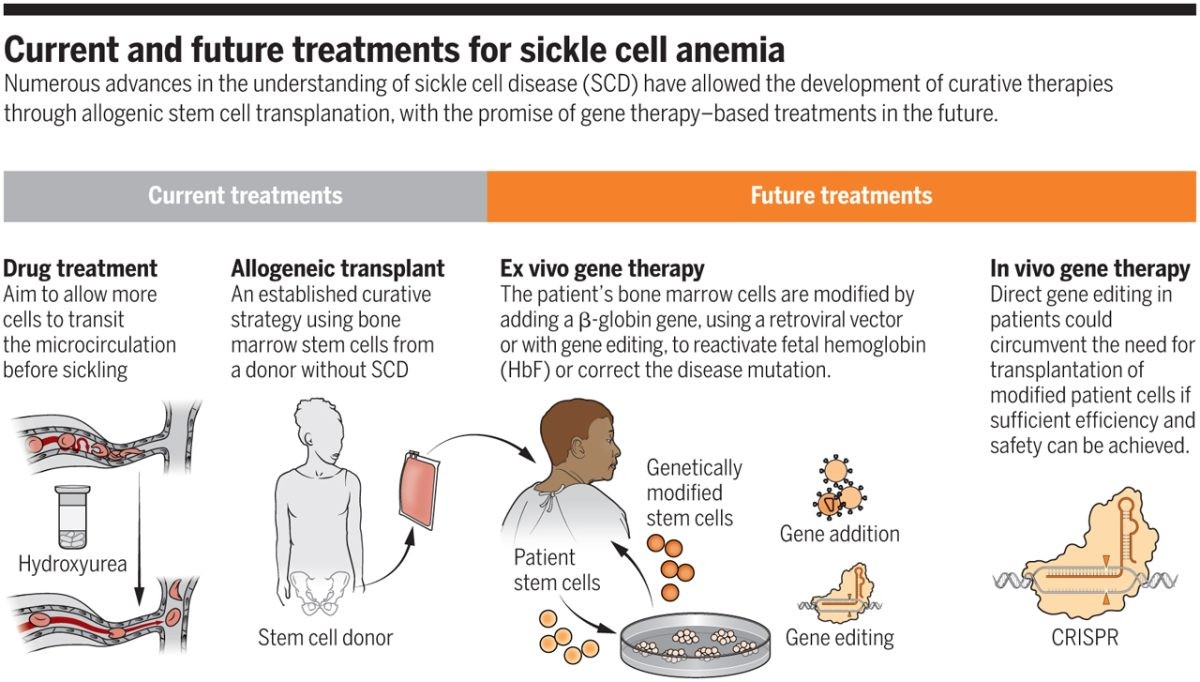
Treatments for sickle cell anemia
Fatigue is a common symptom in people with sickle cell anemia, and treatment usually involves managing chronic anemia by monitoring blood hemoglobin levels. Severe drops in hemoglobin may require blood transfusions. Pain crises caused by impaired blood circulation can be managed with analgesics and increased fluid intake. Hydroxyurea is used to increase fetal hemoglobin levels and reduce pain. Swelling and inflammation in the hands and feet can be treated with anti-inflammatory medications.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.


