How Long Can You Live With Cirrhosis?
The life expectancy of people with liver cirrhosis is typically predicted through the following variables.
Life expectancy in liver cirrhosis is highly influenced by the level of liver damage. Most studies have reported that liver cirrhosis is associated with a reduced life expectancy.
The life expectancy of people with liver cirrhosis is usually predicted through the below variables:
- Percentage of cirrhosis
- Responsiveness to treatment
- Degree of liver reserve
- Age
- Underlying medical conditions
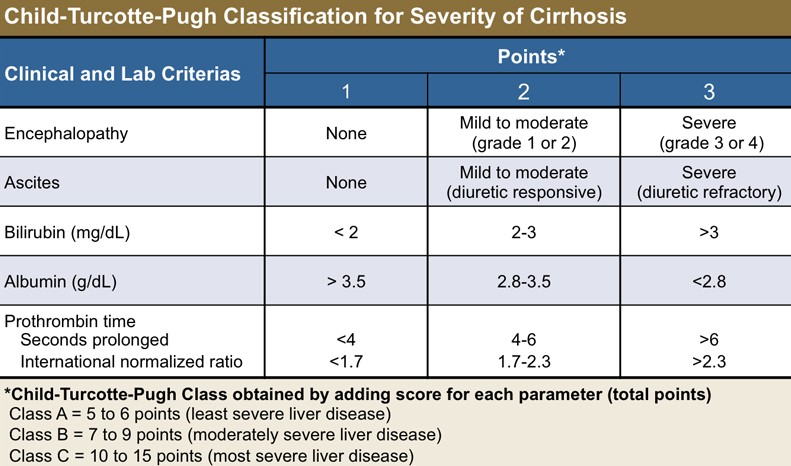
Cirrhosis is commonly classified into three types based on the Child-Pugh score. This score is used to determine the person’s mortality.
The person is categorized as follows based on this score:
- People with cirrhosis in Class A have the best prognosis, with a life expectancy of 15 to 20 years.
- People with cirrhosis in Class B are still healthy, with a life expectancy of 6 to 10 years. As a result, these people have plenty of time to seek sophisticated therapy alternatives such as a liver transplant.
- People with cirrhosis in Class C have the worst prognosis, with a life expectancy ranging from one to three years.
People in classes A and B (Child-Pugh score) have a good chance of extending their lives by using numerous therapeutic choices. Unfortunately, it is not easy to detect people in these stages. However, early detection remains a critical goal for improved life expectancy in people with liver cirrhosis.
How do doctors diagnose liver cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is usually strongly suspected based on the following:
- Symptoms
- Physical examination results
- History of cirrhosis risk factors (such as prolonged alcohol usage)
During a physical examination, a clinician may observe symptoms of cirrhosis such as:
- An enlarged spleen (liver is not enlarged)
- A swollen abdomen (showing ascites)
- Jaundice
- A rash that indicates skin bleeding
Doctors will then conduct tests to rule out any other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
- Laboratory tests:
- Because these tests are somewhat insensitive and the liver may operate for a long period despite injury, the results are frequently normal.
- A complete blood count is performed to detect anemia and other blood abnormalities.
- Blood tests are performed to rule out hepatitis and other potential causes.
- A liver function test may be used. This test evaluates enzyme and protein levels that reflect how effectively the liver is functioning. When the findings of this test are deemed abnormal, it can suggest liver disease.
- Imaging tests can identify advanced cirrhosis but often do not identify early cirrhosis. Doctors may use ultrasound scan, fibroscan, computed tomography (CT) scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to check for stages of liver cirrhosis.
- If the diagnosis is still questionable, a liver biopsy (the removal of a tissue sample for evaluation under a microscope) is frequently performed to confirm it.
- A biopsy and, in certain cases, blood testing can assist doctors in determining the cause and stage of cirrhosis.
- If cirrhosis is diagnosed, ultrasonography is performed every six months to screen for liver cancer.
- If ultrasonography reveals anomalies that could indicate malignancy, doctors will perform an MRI or a CT scan after injecting a chemical that can be seen on an MRI or X-rays (contrast agent).
- When cirrhosis is verified, an upper digestive tract endoscopy (insertion of a flexible viewing tube) is performed to look for varices. This examination is performed every two to three years. If varices are found, it is done more frequently.
- Blood tests to evaluate the liver are performed regularly.
QUESTION
What is compensated and decompensated liver cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a significant liver condition that causes delayed, degenerative damage and is classified into two categories.
Compensated cirrhosis
- People may experience no symptoms at all.
- People with compensated cirrhosis may go years without realizing their liver is scarred because although the liver is severely damaged, it can still perform its functions.
- Liver function tests, however, are abnormal.
However, if cirrhosis is not recognized and treated, pressure in the portal vein increases, leading to complications. Few remaining healthy liver cells get overwhelmed. Then, people may notice symptoms such as:
- Low energy
- Poor appetite
- Weight and muscle loss
- Depressed mood
- Itching
- Loss of sexual function
Decompensated cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis can lead to serious consequences as it advances, which can be related to portal hypertension or the liver’s inability to perform its functions.
Compensated cirrhosis occurs when the liver can withstand damage while still performing essential tasks. In compensated cirrhosis, life expectancy is high. The liver is unable to perform its functions correctly in decompensated cirrhosis. People with decompensated cirrhosis have substantial consequences that might lead to a short life expectancy after diagnosis.
How is cirrhosis managed?
A healthy liver can mend minor damage without affecting the person’s life expectancy. However, liver cirrhosis causes so much damage that there aren’t enough antioxidants remaining to battle the free radicals. As a result, scar tissue forms on the liver, preventing it from working correctly.
The problem with cirrhosis is that it is typically asymptomatic; a person may not notice any symptoms until the disease has progressed to its most severe stage.
The following are some of the most frequent strategies to manage liver cirrhosis:
- Lifestyle changes: There are numerous things you may take to improve your health and lower your risk of experiencing more problems.
- Reduce weight
- Limit and avoid alcohol, especially if your cirrhosis is caused by it
- Never take medicines without prescription
- People with cirrhosis frequently have malnutrition. They should eat a well-balanced diet to receive the most nutrients.
- Doctors may recommend such people lower salt consumption to help reduce the risk of swelling.
- People with cirrhosis may require specific protein content (consult with your hepatologist) and calories in their diet .
- Healthy snacks in between meals are essential and should contain protein. It is beneficial to consume three or four meals per day.
- Depending on your cause and complications, doctors may order the following:
- Diuretics (water pills) to get rid of fluid buildup
- Vitamin K or blood products to prevent excess bleeding
- Medicines for mental confusion
- Antibiotics for infections
- High blood pressure tablets
- Anti-itching creams
- Endoscopic treatments for esophageal vein enlargement (varices)
- Fluid removal from the abdomen (paracentesis)
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt implantation to restore blood flow in the liver
- If your liver is scarred, it may cease to function entirely. In this circumstance, a liver transplant is your only option.
- This is significant surgery to remove the diseased liver and replace it with a healthy one.
- However, the waiting time for liver transplants is usually high.
What are the major complications of cirrhosis?
The most common major complications of cirrhosis include:
- Ascites and pleural effusion: Fluid buildup in your abdomen and chest
- Variceal bleeding: Bleeding inside the body from the swollen veins
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Confusion related to cirrhosis
People with severe cirrhosis have difficulty eliminating toxins, resulting in toxin accumulation in the blood, which can impair mental function, cause personality changes, and possibly lead to coma.
Toxin buildup in the brain might manifest itself in the following ways:
- Neglect of personal appearance
- Unresponsiveness
- Forgetfulness and mood changes
- Concentration problems or changes in sleeping habits
Cirrhosis impairs the usual cleansing process. Thus, medications are not properly filtered, resulting in increased sensitivity to drugs and their negative effects.
Other issues that can occur in the latter stages of cirrhosis include:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin
- Gallstones: The digestive fluid produced by the liver reaches the gallbladder, leading to gallstones
Further information
- Cirrhosis is persistent and usually progressive, but the rate at which it progresses is frequently unpredictable.
- Cirrhosis of the liver is a major health issue that is sometimes underestimated. Its prevalence is increasing because of excessive alcohol consumption and viral etiology.
- Cirrhosis of the liver that causes liver damage can be prevented if detected early (in some circumstances).
- Excessive alcohol use must be reduced, and antiviral treatments for hepatitis B show promising outcomes.
- Although liver transplantation has increased the life expectancy of individuals with liver cirrhosis, it has limitations.
- Cirrhosis is the 11th leading cause of death in the United States. Almost half of these are related to drinking. Cirrhosis kills approximately 25,000 people each year.
- Eating a well-balanced diet, receiving regular body checkups, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption are the best ways to prevent liver cirrhosis.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.


