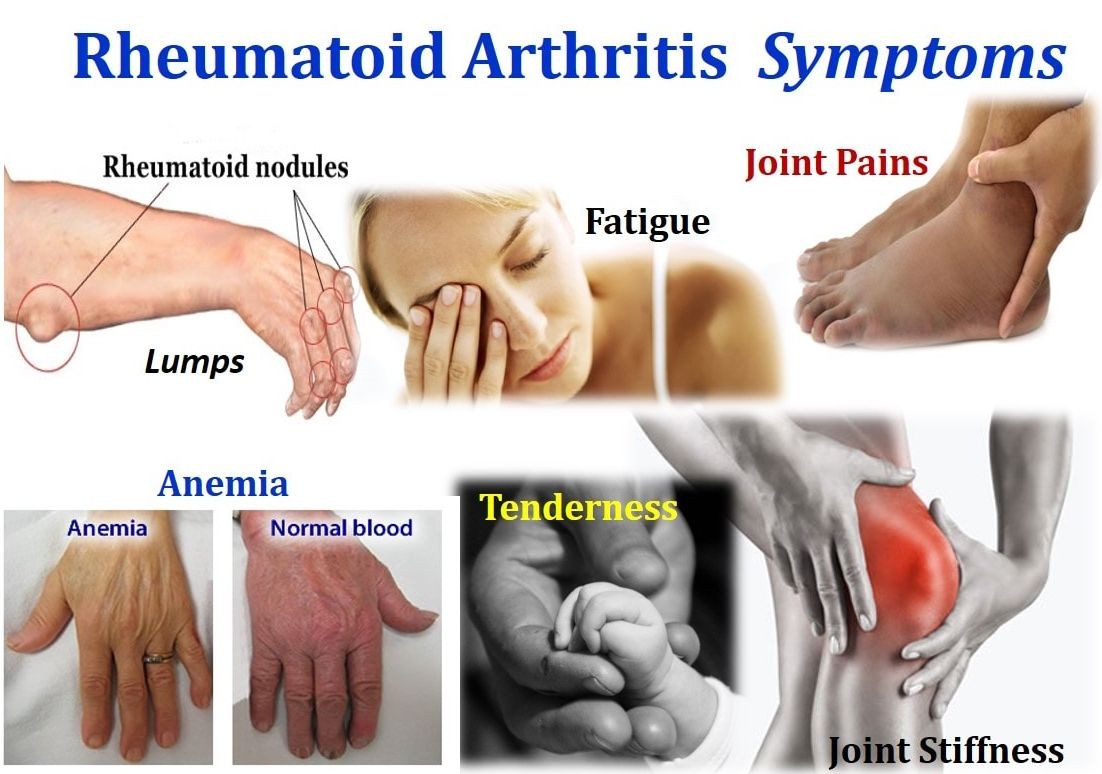
Contents
- 1 Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Caused by Stress?
- 1.0.1 Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect Mental Health?
- 1.0.2 How Can Patients Cope with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- 1.0.3 Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause IBD?
- 1.0.4 How Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect the Digestive Tract?
- 1.0.5 Side Effects of RA Medications on Digestive System
- 1.0.6 How to Alleviate Gastrointestinal Problems in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Caused by Stress?
Research suggests that stress can cause and contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) along with other conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
RA, a chronic inflammatory joint condition and autoimmune disease, is triggered by stress. This sets off the immune system’s inflammatory response, releasing cytokines that can worsen the severity of RA in some patients.
- Greater stress exposure leads to increased inflammation, triggering RA flares.
While there is no definitive cure for RA, treatment can temporarily alleviate symptoms, providing a period of symptom-free remission followed by flare-ups.
Studies indicate that RA and IBD can coexist in some individuals, as both are autoimmune conditions.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect Mental Health?
Long-term symptoms of RA, such as constant joint pain and poor sleep, create a cycle that contributes to stress, anxiety, and depression.
- The interplay of joint pain, inadequate sleep, and stress exacerbates each symptom.
- Anxiety arises regarding future disability, pregnancy, and financial burdens associated with treatment, leading to additional stress.
Approximately one in five RA patients experiences depression due to the illness, which further worsens symptoms and leads to reduced functionality, increased pain, and more frequent doctor visits.
How Can Patients Cope with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis can cause stress, and stress can trigger joint inflammation.
To manage their RA, patients can:
- Take pain medications: Follow the doctor’s prescription for analgesics and maintain hydration.
- Use warm or cold compresses: Apply warm packs for stiffness and ice packs for inflamed joints.
- Consider massage therapy: Seeking a professional massage can alleviate pain and reduce stress and anxiety.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, Tai chi, and yoga offer stress relief.
- Seek cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps patients manage anxiety and change their perception of stressful situations, potentially reducing flares.
- Engage in regular exercise and maintain a healthy diet: These practices can decrease RA severity, strengthen joint-supporting muscles, aid weight loss, and improve overall well-being.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Weight control is crucial in managing RA, as obesity can worsen symptoms.
- Enjoy activities that bring joy: Performing activities that bring pleasure, such as watching movies, painting, walking, gardening, or indulging in relaxing baths, can help reduce stress.
- Join a support group: Seeking support from others facing similar challenges can help patients cope with stress and manage their condition.
- Listen to uplifting music, sing, or dance: Engaging with feel-good music and expressing oneself through singing and dancing can provide an emotional boost.
- Have faith in the doctor: Trusting the doctor’s expertise is crucial. Patients should communicate concerns about treatments while continuing treatment and following medical advice.
- Consider complementary and alternative therapy: Incorporating alternative treatments, such as Ayurvedic approaches, alongside conventional treatments may offer holistic benefits. Consult a doctor before trying any such methods.
- Seek appropriate medications: In cases where other measures fail to provide relief, short-term use of medications like antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs may help manage anxiety. Only use these medications under medical supervision.
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause IBD?
RA and IBD are both autoimmune conditions, and overlapping pathologies suggest that some individuals with RA may also develop IBD. However, digestive issues may occur in RA patients that are unrelated to IBD.
How Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect the Digestive Tract?
Role of Inflammation
RA and IBD can coexist due to shared chronic inflammation. Rheumatoid vasculitis, which inflames blood vessels, can affect the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and weight loss. Managing RA inflammation can alleviate these symptoms.
Role of Genes and Environment
Common genetic factors and environmental influences likely contribute to the development of both RA and IBD.
Risks of RA Medications on Digestive System
Side Effects of RA Medications on Digestive System
Medications used to treat RA may cause gastrointestinal symptoms as side effects.
Common RA medications and related side effects include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Frequent and prolonged use may lead to gastritis and peptic ulcer disease.
- Steroids: High doses over an extended period can result in gastric ulcer, gastrointestinal perforation (bleeding), and pancreatitis. Concurrent use of NSAIDs increases the risk.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Methotrexate, a DMARD, may cause diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Immunotherapy (biologics): Certain immunotherapy drugs used for RA can produce side effects like nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and, in severe cases, GI perforations and bowel obstruction.
Prioritize discussing the potential risks and benefits of these medications with your doctor during the shared decision-making process.
How to Alleviate Gastrointestinal Problems in Rheumatoid Arthritis
To alleviate GI symptoms in RA, it is crucial to follow the doctor’s instructions for managing arthritis. Inform your doctor about any new GI symptoms after starting medications. They may adjust your medication, prescribe proton-pump inhibitors to reduce nausea, or suggest dietary modifications to minimize GI complaints.
Sources:
Medscape Medical Reference
Arthritis Foundation: How Stress Affects Arthritis
Frontiers in Neuroscience: The Interplay Between Stress, Inflammation, and Emotional Attention: Relevance for Depression


