rifampin/isoniazid/pyrazinamide – oral, Rifater
WARNING: Isoniazid can rarely cause severe liver disease, especially in individuals aged 35 or older, those who consume alcohol or use illegal drugs, or those with pre-existing liver problems. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of liver disease, such as nausea/vomiting, stomach/abdominal pain, weakness/tiredness, dark urine, or yellowing of the eyes/skin. In addition, regular liver function tests should be conducted while taking this medication. Attend all medical and laboratory appointments.
USES: This product treats lung tuberculosis (TB) and contains three antibiotics: rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide. Rifampin is a rifamycin antibiotic that stops bacterial growth. It only treats bacterial infections, not viral infections like the common cold or flu. Misuse of antibiotics can result in decreased effectiveness.
HOW TO USE: Take this medication by mouth one hour before or two hours after a meal, usually once daily or as directed by your doctor. Use a full glass of water (8 ounces/240 milliliters) unless instructed otherwise. Take it at the same time each day to maintain a constant level in the body. Continue taking this medication and other TB medications until the full prescribed amount is finished, even if symptoms disappear. Stopping the medication prematurely or skipping doses can allow bacteria to continue growing and make the infection more difficult to treat. Your doctor may also advise taking vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) to prevent certain side effects from isoniazid. Avoid foods containing tyramine/histamine (such as cheese, red wine, certain types of fish) as they may interact with isoniazid and cause increased blood pressure, flushing, headache, dizziness, or fast heartbeat. Follow any special diet recommended by your doctor. Contact your doctor if your condition persists or worsens.
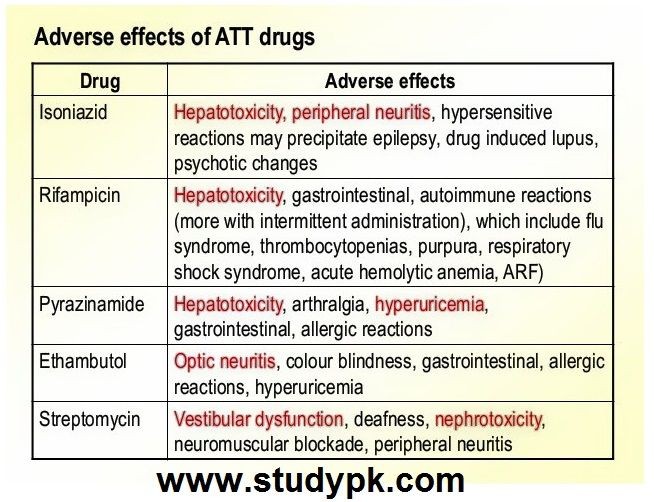
SIDE EFFECTS: Nausea/vomiting, upset stomach, heartburn, mild muscle/joint pain, or headache may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, notify your doctor or pharmacist promptly. This medication may cause reddish-colored urine, sweat, saliva, or tears. This is harmless and will subside after discontinuation. However, dentures and contact lenses may become permanently stained. Inform your doctor if you experience unlikely but serious side effects, such as numbness/tingling of arms/legs or painful/swollen joints. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience rare but serious side effects, such as changes in urine amount, increased thirst/urination, bloody urine, vision changes, rapid heartbeat, easy bruising/bleeding, signs of a new infection (e.g., fever, persistent sore throat), mental/mood changes (e.g., confusion, psychosis), or seizures. This medication may rarely cause a severe intestinal condition (Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea) due to resistant bacteria. Do not use anti-diarrhea products or narcotic pain medications if you experience persistent diarrhea, abdominal/stomach pain/cramping, or blood/mucus in the stool. Severe allergic reactions to this drug are rare, but seek immediate medical attention if you notice symptoms like rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. This is not a complete list of potential side effects. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you experience any additional effects.
PRECAUTIONS: Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, or other rifamycins (e.g., rifabutin, rifapentine), as this medication may contain inactive ingredients that can cause allergic reactions or other complications. Share your medical history, particularly if you have previously experienced severe reactions to isoniazid, liver disease, kidney disease, alcohol use, HIV infection, diabetes, gout, high uric acid levels, numbness/tingling of arms/legs (peripheral neuropathy), recent childbirth, or a certain blood disorder (porphyria). Before undergoing surgery, disclose all the products you use to your doctor or dentist. Alcohol use can increase the risk of liver disease. Avoid alcoholic beverages while taking this medication. This product may diminish the effectiveness of hormonal birth control methods such as pills, patches, or rings. Discuss with your doctor or pharmacist whether you should use additional reliable birth control methods. Also, inform your doctor if you experience any breakthrough bleeding or spotting, as this may indicate reduced birth control efficacy. This medication may interfere with certain laboratory tests, potentially yielding false results. Make sure all medical professionals are aware of your use of this drug.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: The effects of certain drugs may change if they are taken alongside other drugs or herbal products. This can increase the risk of serious side effects or render medications less effective. Inform your doctor or pharmacist about all the products you use, including prescription drugs, non-prescription drugs, and herbal products, before beginning treatment with this medication. To facilitate the best care, ensure that your doctor and pharmacist are aware of all the products you use by notifying them before starting treatment. Some products that may interact with this drug include acetaminophen, carbamazepine, disulfiram, MAO inhibitors, SSRI antidepressants, valproic acid, cyclosporine, digoxin, phenytoin, ranolazine, tacrolimus, theophylline, certain anti-infectives, azole antifungals, "blood thinners," calcium channel blockers, HIV NNRTIs, and HIV protease inhibitors, among others. Rifampin can accelerate the elimination of other medications from the body, potentially impacting their efficacy. Examples of impacted drugs include cyclosporine, digoxin, nimodipine, phenytoin, ranolazine, tacrolimus, theophylline, certain anti-infectives, azole antifungals, "blood thinners," calcium channel blockers, HIV NNRTIs, and HIV protease inhibitors. This medication may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control. Discuss with your doctor or pharmacist whether you should use additional reliable birth control methods. This medication may interfere with specific laboratory tests, potentially yielding false results. Notify laboratory personnel and all your doctors that you are using this drug. This is not an exhaustive list of potential drug interactions. Keep a comprehensive list of all the products you use and share it with your doctor and pharmacist to minimize the risk of medication problems.
OVERDOSE: If overdose is suspected, contact a poison control center or emergency room immediately. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canadian residents should call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include severe stomach/abdominal pain, unusual tiredness/weakness, yellowing eyes/skin, vision changes, slow/shallow breathing, or severe drowsiness.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others. Regular laboratory and/or medical tests (e.g., sputum test, kidney/liver function, bilirubin levels, uric acid levels, complete blood count) should be conducted periodically to monitor progress and check for side effects. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: To receive maximum benefit, it is important to take each scheduled dose of this medication as directed. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose and return to your regular dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature between 59-86 degrees F (15-30 degrees C) away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medicines out of reach of children and pets. Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly dispose of this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for more details on safe product disposal.
Information last revised March 2013. Copyright(c) 2013 First Databank, Inc.
Related Disease Conditions
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Symptoms include bloody sputum, fever, cough, weight loss, and chest pain. Treatment depends on the type of TB infection.


