Contents
- 1 Birth Control Options
- 1.0.1 How long does it take for birth control to work?
- 1.0.2 Can you get pregnant on birth control?
- 1.0.3 What are the different types of birth control available?
- 1.0.4 Hormonal birth control (birth control pills) types and side effects
- 1.0.5 Barrier methods of birth control (including condoms) types and side effects
- 1.0.6 Surgical sterilization (tubal ligation or vasectomy) side effects and risks
- 1.0.7 From
- 1.0.8 Natural birth control methods
- 1.0.9 Emergency contraception types and side effects
- 1.0.10 IUDs (intrauterine devices) side effects
Birth Control Options
Birth control prevents pregnancy in various ways.
- Hormonal birth control prevents ovulation to make a woman temporarily infertile.
- Barrier methods prevent sperm from reaching an egg.
- Barrier methods include:
- diaphragms,
- condoms, and
- cervical caps.
How long does it take for birth control to work?
- Some birth control methods start working with the first use, like barrier methods.
- Hormonal methods like pills, implants, or patches may not work immediately.
- Their effectiveness depends on the time in a woman’s monthly cycle when she starts using contraception.
- Women are sometimes advised to use an alternate method of contraception for the first week after starting the pill or hormonal contraception.
Can you get pregnant on birth control?
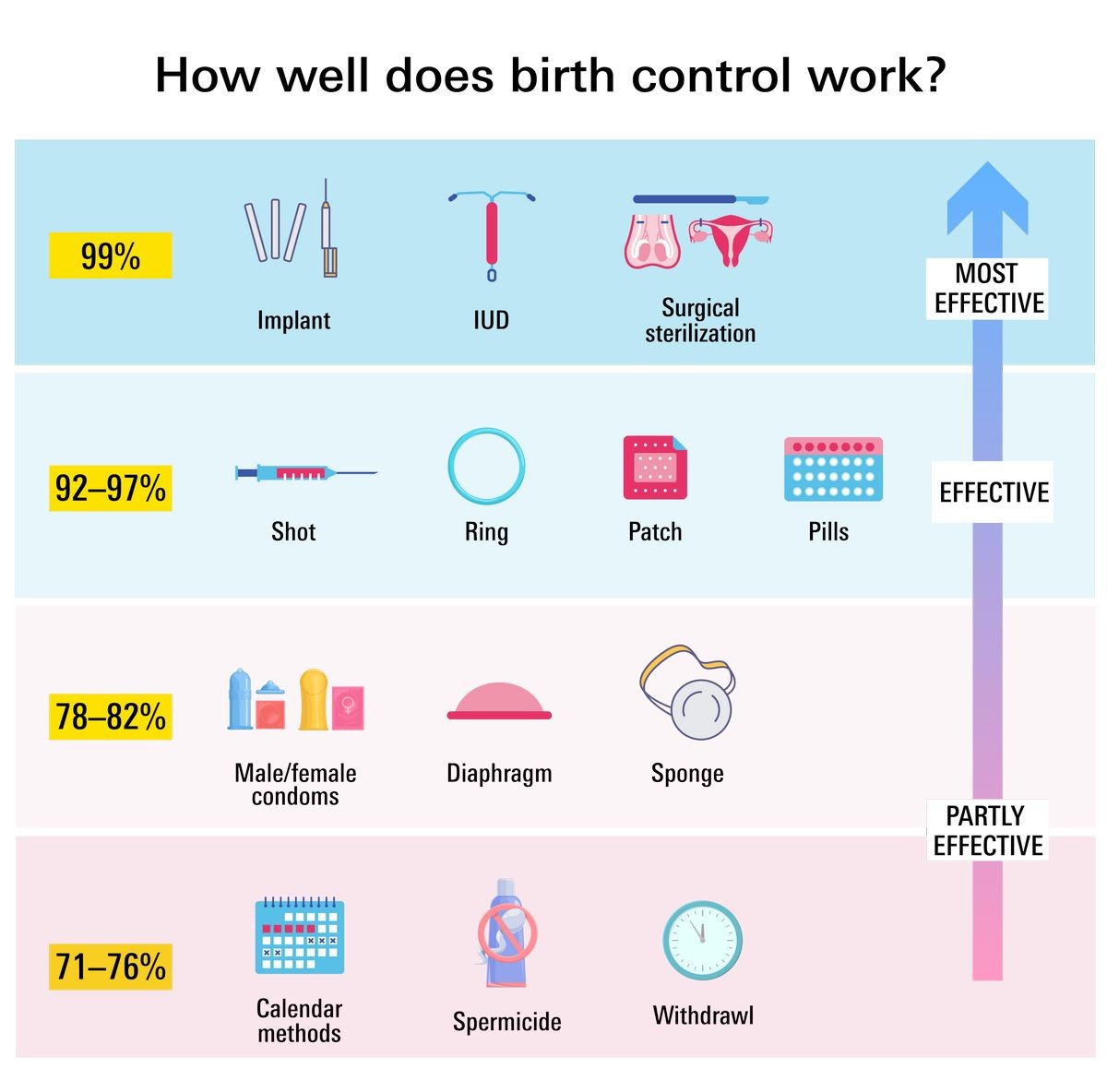
No form of birth control is 100% effective, so it is possible to get pregnant while using most types. However, many types of birth control, when used correctly, are highly effective. For example, the birth control pill is over 99% effective when taken correctly. It is important to have a basic understanding of how birth control works and how to use it correctly to prevent failure. Not fully following or understanding instructions and advantages and disadvantages of certain methods contribute to the failure of birth control methods.
QUESTION
What are the different types of birth control available?
Types of birth control methods include options that prevent sperm from reaching an egg, methods that prevent ovulation, and methods that prevent implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus. Permanent methods (surgical sterilization) are also available for those who no longer desire to have children.
Types of birth control
Hormonal methods include:
- Birth control pills
- Hormonal patches
- Birth control implants
- Vaginal ring
Barrier methods include:
- Diaphragms
- Condoms
- Cervical caps
- Spermicides
Natural methods include:
- Ovulation test kits
- Cervical mucus examination
- Tracking menstrual cycles (rhythm method)
Other options include:
- Intrauterine devices
- Emergency contraception "morning after" pills
Surgical sterilization methods include:
- Tubal ligation ("tubes tied")
- Vasectomy
Hormonal birth control (birth control pills) types and side effects
Hormonal birth control uses hormones to prevent ovulation in women. Besides oral contraceptive pills, alternatives include the vaginal ring, hormone patches, and progestin injections (birth control shot).
Common side effects of birth control pills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight gain
- Skin discoloration
- Acne
- Bleeding between periods or spotting
- Mood swings
- Change in menstrual flow
- Breast swelling or tenderness
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of these complications. Women over 35 who are heavy smokers (>15 cigarettes/day) are at the highest risk. Health-care professionals usually recommend quitting smoking when using birth control pills.
Barrier methods of birth control (including condoms) types and side effects
Barrier methods prevent fertilization by creating a physical block or killing sperm cells. Examples include the diaphragm, condoms, and cervical cap or shield.
Contraceptive sponges contain spermicidal cream to kill sperm, and there are other spermicides available. Spermicides may be used along with barrier methods for greater effectiveness.
Side effects of barrier methods of birth control
Side effects can include:
- An increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) with a diaphragm and spermicide.
- A diaphragm or cervical cap left in for more than 24 hours increases the risk of toxic shock syndrome.
- Some people may have allergies to the chemicals used in spermicide products, leading to irritation of the vagina or penis.
One advantage of barrier methods is that they can decrease the risk of sexually transmitted diseases (especially properly used condoms). However, no method eliminates this risk.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Surgical sterilization (tubal ligation or vasectomy) side effects and risks
Surgical sterilization is a permanent form of birth control for women (tubal ligation) and men (vasectomy). Sterilization implants, which consist of a small coil inserted into the fallopian tubes to block them, are a newer form of permanent birth control for women that avoids surgical procedures like tubal ligation.
What are the risks of a vasectomy or tubal ligation?
Although women who have had tubal ligation do not experience side effects after recovery, any surgery carries a small risk of infection, bleeding, or complications from anesthesia.
Vasectomy is associated with small risks from the procedure, as well as swelling and pain in the days following it. For a period after vasectomy, a man can still be fertile, so it is typically recommended to use a barrier method or other form of birth control for 10-12 weeks or 15 to 20 ejaculations post-procedure.
From
Women’s Health Resources
- Early Signs of Pregnancy
- Birth Control Pills: What to Consider
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Natural birth control methods
Natural methods involve tracking a woman’s menstrual cycle to determine when ovulation is likely to occur and avoiding sexual intercourse (or using barrier contraceptives) during that time. Ways to detect ovulation include measuring basal body temperature (ovulation causes a slight increase), using home ovulation test kits, and checking and recording cervical mucus consistency.
These methods tend to have lower success rates as they require discipline in recording, tracking, and interpreting results.
Emergency contraception types and side effects
Emergency contraception is used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse. Emergency hormonal contraceptives are sometimes called "morning-after" pills and must be taken within 72 hours after intercourse. Another effective method is insertion of a copper intrauterine device (IUD).
Side effects of emergency contraception (morning-after pill)
Side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Breast tenderness
- Lower abdominal pain
IUDs (intrauterine devices) side effects
IUDs create an unfavorable environment in the uterine lining that prevents the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Side effects depend on the type of IUD used:
- Copper-containing IUDs may worsen menstrual bleeding and cramps.
- Puncture or perforation of the uterus is a rare complication with all IUDs.
- IUDs that contain hormones may cause similar side effects to hormonal contraceptives, such as headaches, breast tenderness, or acne.