Contents
Nitrofurantoin vs. Amoxicillin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by bacteria such as E. Coli, Enterococcus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter cystitis, and Staphylococcus aureus. It interferes with the production of bacterial proteins, DNA, and cell walls. Bacteria cannot survive or multiply without a cell wall or DNA.
Nitrofurantoin is available in three forms: Furadantin (microcrystalline form), Macrodantin (macrocrystalline form), and Macrobid (sustained release macrocrystalline form). The macrocrystalline form is absorbed more slowly than the microcrystalline form and is suitable for individuals who cannot tolerate the microcrystalline form.
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic, which belongs to the same drug class as ampicillin, piperacillin, ticarcillin, and others. Penicillin-type antibiotics prevent bacteria from multiplying by inhibiting the formation of bacterial cell walls. Bacteria need a cell wall to survive and protect themselves from the environment.
Amoxicillin is effective against many bacteria, including H. influenzae, N. gonorrhoea, E. coli, Pneumococci, Streptococci, and certain strains of Staphylococci. It is used to treat infections of the middle ear, tonsils, throat, larynx (laryngitis), bronchi (bronchitis), lungs (pneumonia), urinary tract, skin, and gonorrhea.
Side effects of nitrofurantoin and amoxicillin
Nitrofurantoin side effects
Common side effects of nitrofurantoin include stomach upset, which can be minimized by taking a lower dose or consuming it with food or milk. Possible serious side effects include lung injury, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, cough, peripheral neuropathy (tingling in the extremities), reduced red blood cell count (hemolytic anemia), and liver damage leading to jaundice or fatal hepatitis. Nitrofurantoin can also cause urine to change color to a dark yellow or brown.
Amoxicillin side effects
Side effects of amoxicillin include rash, itching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rare but serious reactions such as seizures, severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), and low platelet or red blood cell count. It can also encourage overgrowth of bacteria like Clostridium difficile in the colon, causing inflammation of the colon (pseudomembranous colitis).
Dosage of nitrofurantoin and amoxicillin
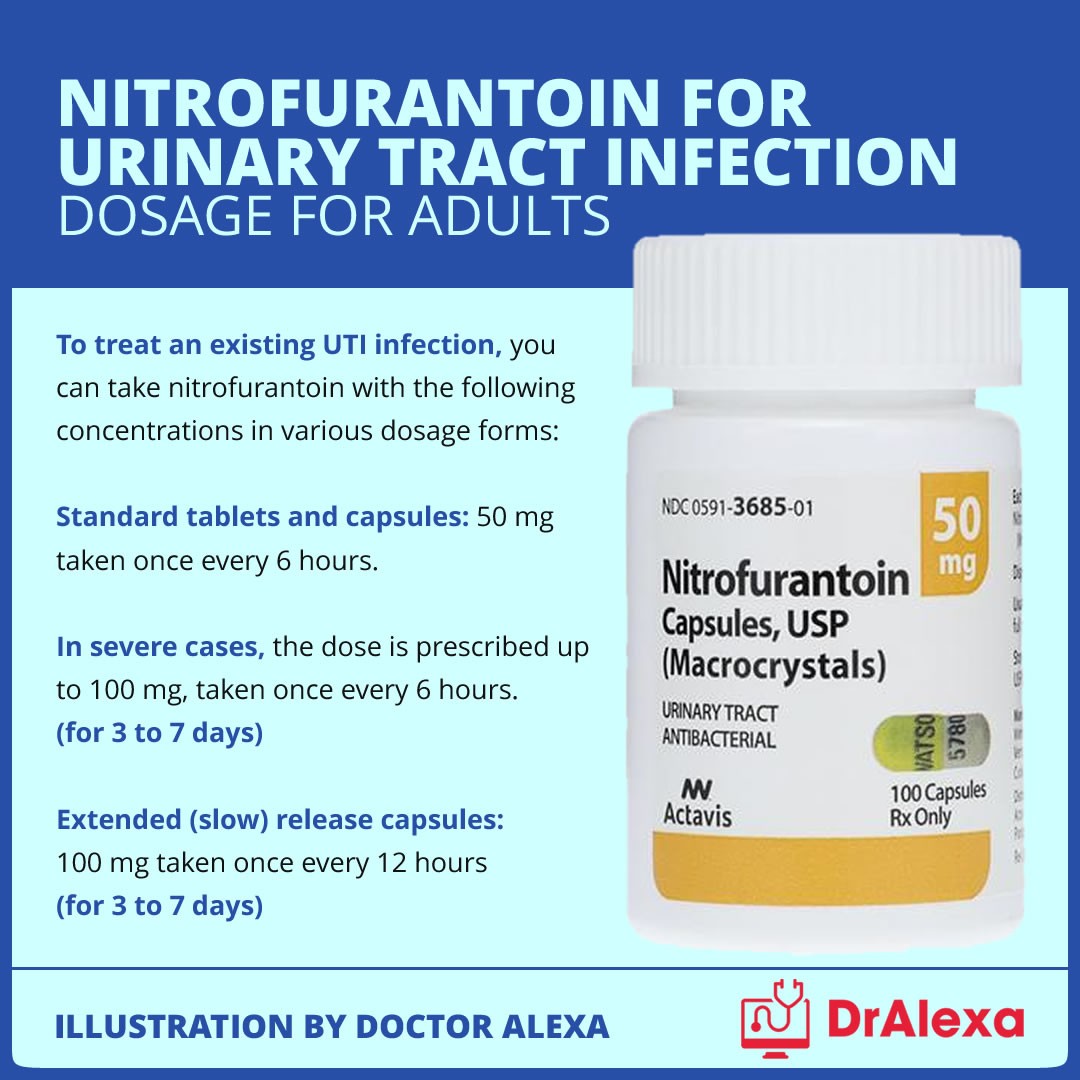
Nitrofurantoin dosage
- The recommended adult dose for treating UTIs is 50-100 mg 4 times daily (Macrodantin, Furadantin) or 100 mg every 12 hours (Macrobid) for 7 days or for 3 days after obtaining sterile urine.
- Nitrofurantoin can be taken with or without meals. Taking it with meals increases absorption.
- The suspension can be mixed with water, milk, juice, or infant formula.
- It is also used once a day (or twice daily in some children) to prevent UTIs.
- It should not be used in individuals with poor kidney function.
Amoxicillin dosage
- For most infections in adults, the dose of amoxicillin is 250-875 mg every 8-12 hours, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- For the treatment of gonorrhea, a single dose of 3 g is given.
- For most infections in children, the dose ranges from 25-45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8-12 hours, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
- Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food.
Drug interactions of nitrofurantoin and amoxicillin
Nitrofurantoin drug interactions
- High doses of probenecid or sulfinpyrazone can partially block the kidneys’ elimination of nitrofurantoin, increasing its blood concentrations and the risk of toxicity.
- An antacid containing magnesium trisilicate may decrease the absorption of nitrofurantoin, reducing its effectiveness.
- Nitrofurantoin may reduce the activity of live tuberculosis vaccine (BCG vaccine) and live typhoid vaccine. It should not be combined with quinolone antibiotics.
Amoxicillin drug interactions
- Amoxicillin is rarely associated with significant drug interactions.
Safety of nitrofurantoin and amoxicillin during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Nitrofurantoin
- Nitrofurantoin is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy, although it should not be used near the time of delivery (38-42 weeks gestation) due to its potential to damage the red blood cells of newborns and cause anemia.
- Nitrofurantoin is distributed into breast milk and should be used cautiously by breastfeeding women.
Amoxicillin
- Penicillins are generally considered safe for use by pregnant women who are not allergic to penicillin.
- Amoxicillin is excreted in breast milk in small amounts and may cause diarrhea or allergic responses in nursing infants. It is generally considered safe to use while breastfeeding and can be used to treat infections in newborns.
Summary
Nitrofurantoin and amoxicillin are antibiotics used to treat UTIs. Amoxicillin is also used to treat infections of the middle ear, tonsils, throat, larynx, bronchi, lungs, and skin, as well as gonorrhea. Side effects of both medications include rash, itching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.