leflunomide
Leflunomide is an immunosuppressant medication used to treat active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is an autoimmune disease where the body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage.
Leflunomide is a disease modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) that modulates the immune system, reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression. It is a prodrug that is converted to its active metabolite A77 1726 (M1) in the body.
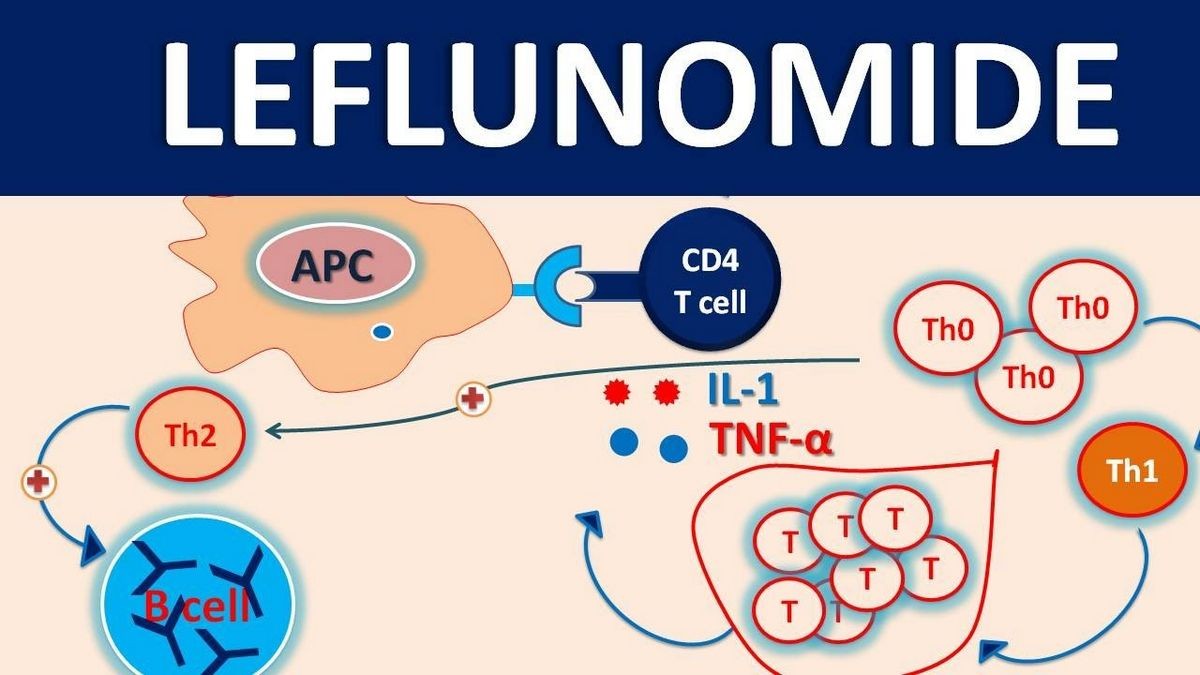
Inflammation in active RA is characterized by high T-lymphocyte (T-cell) activity. Activated T-cells have a higher requirement of pyrimidine nucleotide than resting T-cells. Pyrimidine nucleotide is essential for T-cells to grow and proliferate. Leflunomide affects activated T-cells more because resting T-cells use the salvage pathway to meet their pyrimidine requirement.
Leflunomide prevents the expansion of activated autoimmune lymphocytes by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, an enzyme necessary for de novo synthesis of pyrimidine. By inhibiting pyrimidine synthesis, leflunomide arrests the cell cycle progression of activated T-cells, controlling T-cell mediated inflammation.
Leflunomide is used for:
- BK virus in kidney transplant recipients
- Cytomegalovirus disease in transplant recipients resistant to standard antivirals, as an adjunct therapy
Warnings
- Do not use in patients hypersensitive to leflunomide or any of its components.
- Do not use leflunomide in pregnant women, as it may cause fetal harm.
- Do not initiate leflunomide therapy in women of reproductive potential without first excluding pregnancy.
- Advise women of child-bearing potential to use effective contraception during therapy. Do not use leflunomide in women who do not use reliable methods of contraception.
- Advise women to avoid pregnancy until they complete accelerated drug elimination procedure with cholestyramine, and leflunomide levels are verified to be undetectable.
- If pregnancy occurs during therapy, inform the patient of the potential hazards to the fetus.
- Using leflunomide concurrently with other medications that can damage the liver increases the risk for liver injury.
- Do not use leflunomide in patients with pre-existing liver disease and elevation of liver enzyme ALT two times the upper limit of normal (ULN).
- Monitor ALT levels regularly and if it increases more than 3 times ULN, interrupt therapy and investigate the probable cause. If leflunomide-induced, initiate cholestyramine or activated charcoal to accelerate elimination of leflunomide and monitor ALT level until it returns to normal range. If it is not leflunomide-induced, consider resuming therapy.
- Avoid use in patients with severe immunodeficiency, bone marrow dysplasia, or severe uncontrolled infections.
- In case of serious infection, interrupt therapy and initiate accelerated drug elimination procedure.
- Monitor complete blood counts of patients and if there are signs of bone marrow depression, discontinue treatment and initiate cholestyramine.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of leflunomide?
Common side effects of leflunomide include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Indigestion (dyspepsia)
- Abdominal pain
- Gastrointestinal pain
- Mouth ulcer
- Gum inflammation (gingivitis)
- Oral inflammation (stomatitis)
- Salivary gland enlargement
- Dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Oral Candida yeast infection (moniliasis/candidiasis)
- Gastroenteritis
- Inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis)
- Gastritis
- Colon inflammation (colitis)
- Gas (flatulence)
- Constipation
- Tarry black stools (melena)
- Loss of appetite (anorexia)
- Elevated levels of liver enzymes ALT and AST
- Gallstones (cholelithiasis)
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Rash
- Itching (pruritus)
- Eczema
- Dry skin
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Chest pain
- Chest pain related to coronary artery disease (angina pectoris)
- Palpitations
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Varicose veins
- Dilation of blood vessels (vasodilation)
- Blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis)
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Increased cough
- Bronchial inflammation (bronchitis)
- Sinus inflammation (sinusitis)
- Throat inflammation (pharyngitis)
- Nasal inflammation (rhinitis)
- Nasal bleeding (epistaxis)
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Lung disorder
- Urinary tract infection
- Bladder inflammation (cystitis)
- Albumin in urine (albuminuria)
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Urinary frequency
- Prostate disorder
- Menstrual disorder
- Vaginal candidiasis
- Migraine
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Skin tingling and numbness (paresthesia)
- Joint disorder
- Inflammation of the membrane around tendons (tenosynovitis)
- Inflammation of the connective tissue that lines joints (synovitis)
- Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints (bursitis)
- Joint pain (arthralgia)
- Joint degeneration (arthrosis)
- Bone tissue death (necrosis)
- Bone pain
- Tendon rupture
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Leg cramps
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Pelvic pain
- Weakness (asthenia)
- Flu syndrome
- Fever
- Injury accident
- Pain
- Feeling unwell (malaise)
- Hernia
- Abscess
- Cyst
- Allergic reaction
- Weight loss
- Low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia)
- High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia)
- High blood fats (hyperlipidemia)
- Increase in creatine phosphokinase
- Swelling of extremities (peripheral edema)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Low red blood cell count (anemia)
- Skin reactions including:
- Acne
- Contact dermatitis
- Fungal dermatitis
- Flat and raised skin lesions (maculopapular rash)
- Bleeding under the skin (hematoma)
- Discoloration of skin from bleeding underneath (ecchymosis)
- Skin and subcutaneous nodules
- Skin ulcers
- Skin disorders
- Nail disorders
- Herpes simplex
- Herpes zoster
- Hair discoloration
Less common and rare side effects of leflunomide include:
- Opportunistic and severe infections including sepsis
- Hypersensitivity reactions including:
- Hives (urticaria)
- Swelling under the skin and mucous membranes (angioedema)
- Severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)
- High level of eosinophils in blood (eosinophilia)
- Erythema multiforme
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis
- Severely low count of granulocyte immune cells (agranulocytosis)
- Low count of neutrophil immune cells (neutropenia)
- Low count of leukocyte immune cells (leukopenia)
- Low count of platelets (thrombocytopenia)
- Low count of all types of blood cells (pancytopenia)
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Interstitial pneumonitis
Call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or serious side effects while using this drug:
- Serious heart symptoms include fast or pounding heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness;
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, severe weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady;
- Severe nervous system reaction with very stiff muscles, high fever, sweating, confusion, fast or uneven heartbeats, tremors, and feeling like you might pass out; or
- Serious eye symptoms include blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights.
This is not a complete list of all side effects or adverse reactions that may occur from the use of this drug. Call your doctor for medical advice about serious side effects or adverse reactions. You may also report side effects or health problems to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.