Contents
guarana
Guarana is the South American name for Paullinia cupana, a climbing liana vine belonging to the family of soap tree plants, native to the Amazon.
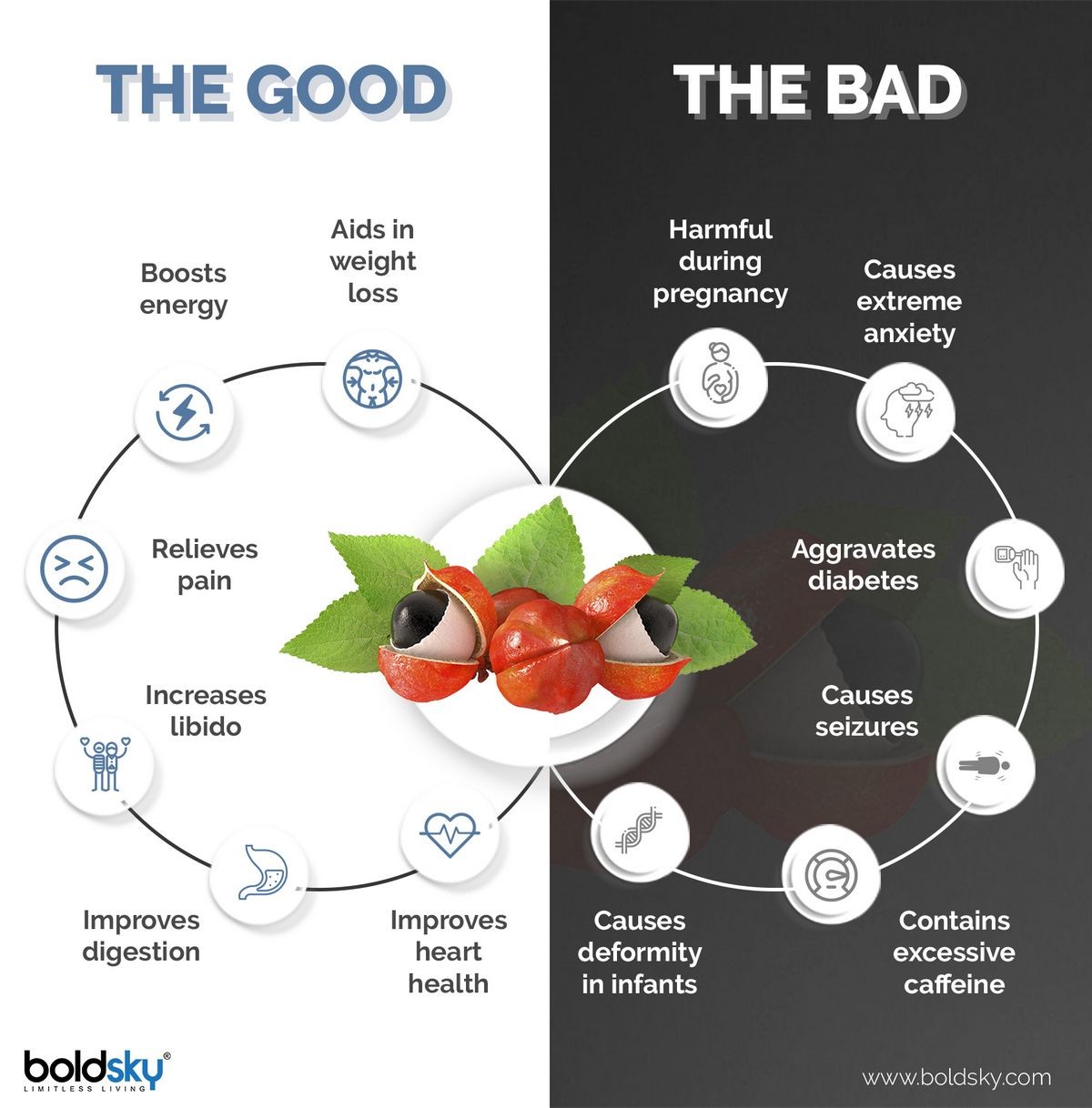
Guarana seeds, dried and powdered, are used as a dietary supplement for weight loss, to enhance athletic performance, as a stimulant similar to coffee, and for many other purposes. Guarana is available over the counter (OTC) as a powder, tablet, or capsule. It is also an ingredient of many nutritional supplements and energy drinks and bars.
Guarana is primarily used for its stimulant effect of guaranine, a chemical identical to caffeine. It also contains other therapeutic substances including theobromine, theophylline, proanthocyanidins, catechin, epicatechin, tannins, saponins, starches, and minerals. These chemicals in guarana are believed to have muscle-relaxing, antioxidant, and general health-promoting properties.
Studies suggest guarana may reduce body fat percentage, lower cholesterol, and improve cognitive performance. It also appears to have some anti-bacterial and anti-fungal effects. However, more research is needed to establish all the effects of guarana. Overall, based on current studies, guarana has health-promoting properties and is safe to use in recommended doses.
Suggested uses of guarana include:
- Stimulant
- Weight loss
- Athletic performance enhancement
- Reducing mental and physical fatigue
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Astringent
- Diuretic
- Prevention of dysentery and malaria
Warnings
- Do not take guarana if you have gastric or duodenal ulcers.
- Take guarana with caution if you have any of the following conditions:
- Cardiac disease
- Irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Kidney disease
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
What are the side effects of guarana?
Common side effects of guarana include:
- Headache
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
- Delirium
- Dizziness
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Muscle spasms
- Convulsions
- Increased respiration
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Abdominal spasms (from overdose)
- Painful urination (from overdose)
- Potassium deficiency and muscle paralysis with excessive consumption
- Excessive urination (diuresis)
- Dependence
- Withdrawal symptoms with discontinuation
Call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or serious side effects while using this drug:
- Serious heart symptoms include fast or pounding heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness;
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, severe weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady;
- Severe nervous system reaction with very stiff muscles, high fever, sweating, confusion, fast or uneven heartbeats, tremors, and feeling like you might pass out; or
- Serious eye symptoms include blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights.
This is not a complete list of all side effects or adverse reactions. Call your doctor for medical advice about serious side effects or adverse reactions. You may also report side effects or health problems to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
QUESTION
What are the dosages of guarana?
There aren’t any standard established dosages for guarana.
- Seed extract: 200-1600 mg orally once daily; no more than 3 g/day
Cognitive Enhancement
- Standardized dry extract: 150 mg orally once daily
Energy Enhancement
- 200-800 mg before breakfast or lunch orally once daily, no more than 3 g/day
Diuretic
- 486 mg orally once daily
Diarrhea or Dysentery
- 1 g orally, no more than 4 times a day
Addiction/overdose
- Guarana contains caffeine, an addictive substance that can cause dependency and withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue, lethargy, restlessness, increased appetite, sleep disorders, and unpleasant dreams, upon discontinuation.
- Guarana overdose symptoms are primarily from overdose of caffeine with similar symptoms such as headaches, tremors, nervousness, and muscle aches, although individual reactions can vary. Symptoms should resolve with discontinuation of caffeine and may be treated with symptomatic care if required.
What drugs interact with guarana?
Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, who can advise you on any possible drug interactions. Never begin taking, suddenly discontinue, or change the dosage of any medication without your doctor’s recommendation.
- Guarana has no known severe, serious, moderate, or mild interactions with other drugs.
- Mild interactions of guarana include:
- armodafinil
- caffeine
- dexmethylphenidate
- dextroamphetamine
- green tea
- lisdexamfetamine
- methamphetamine
- methylenedioxymethamphetamine
- methylphenidate
- modafinil
- phentermine
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
- yohimbine
For more information on drug interactions, visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker. It is important to always tell your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider about all prescription and over-the-counter medications you use, as well as the dosage for each, and keep a list of the information. Check with your doctor or healthcare provider if you have any questions about the medication.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- The caffeine in guarana can raise blood pressure, which can negatively affect fetal development if taken during pregnancy. Avoid all caffeinated products, including guarana, if you are pregnant.
- Caffeine is present in breastmilk, avoid use if you are a nursing mother.
What else should I know about guarana?
- Guarana supplements are possibly safe for most adults if used in recommended doses.
- Use guarana exactly as per label instructions.
- Check with your healthcare provider before taking any dietary supplement, including guarana.
- Herbal products often contain many ingredients. Check labels for the components in the guarana product you choose.
- Guarana is marketed as an herbal supplement and is not regulated by the FDA. Products may differ in formulations and strengths, and labels may not always match contents; exercise caution in choosing your product.
- Store guarana safely out of reach of children.
- In case of overdose, seek medical help or contact Poison Control.
Summary
Guarana seeds, dried and powdered, are used as a dietary supplement for weight loss, to enhance athletic performance, as a stimulant similar to coffee, and for many other purposes. Guarana is available over the counter (OTC) as a powder, tablet, or capsule. Common side effects of guarana include headache, agitation, anxiety, irritability, restlessness, nervousness, insomnia, delirium, dizziness, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), muscle spasms, convulsions, increased respiration, irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), rapid heart rate (tachycardia), high blood pressure (hypertension), high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), and others. Do not take if pregnant or breastfeeding.


