Contents
- 1 guaifenesin
- 1.0.1 What are the side effects of guaifenesin?
- 1.0.2 What is the dosage for guaifenesin?
- 1.0.3 Which drugs or supplements interact with guaifenesin?
- 1.0.4 Is guaifenesin safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
- 1.0.5 What else should I know about guaifenesin?
- 1.0.6 Summary
- 1.0.7 Related Disease Conditions
- 1.1 Cough: 19 Tips on How to Stop a Cough
- 1.2 What Is Mucus?
- 1.3 Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
- 1.4 Upper Respiratory Infection (URI)
- 1.5 Chronic Rhinitis and Post-Nasal Drip
- 1.6 Common Cold
- 1.7 Pneumonia
- 1.8 Chronic Cough
- 1.9 Acute Bronchitis
- 1.10 Can I Get Any STDs Through Clothing?
- 1.11 Chronic Bronchitis
- 1.12 Asthma Over-the-Counter Treatment
- 1.13 Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
guaifenesin
Guaifenesin treats coughs associated with colds and minor upper respiratory tract infections in individuals 12 years and older.
What brand names are available for guaifenesin?
Diabetic Tussin, Geri-Tussin, Robitussin, Fenesin IR, Mucinex, Mucosa, Mucus Relief, Mucus ER
Is guaifenesin available as a generic drug?
Do I need a prescription for guaifenesin?
What are the side effects of guaifenesin?
Side effects of guaifenesin are uncommon, but can include:
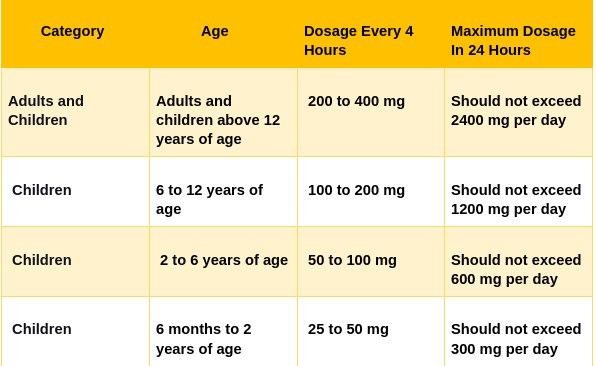
What is the dosage for guaifenesin?
Guaifenesin may be taken with or without food. The tablets should be taken whole and should not be crushed, chewed, or broken. The recommended dose is 600-1200 every 12h hours up to a maximum of 2.4 g per day. Patients should consult a healthcare professional if symptoms last more than 7 days.
Which drugs or supplements interact with guaifenesin?
There are no known drug interactions with guaifenesin.
QUESTION
Is guaifenesin safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
Although one analysis found a correlation between guaifenesin use in the first trimester of pregnancy and an increased risk of hernia in the fetus, others found no increased risk of fetal malformations. Thus, guaifenesin should be used in pregnancy only if the physician feels that the potential benefits outweigh the potential and unknown risks.
It is not known if guaifenesin is secreted into breast milk.
What else should I know about guaifenesin?
What preparations of guaifenesin are available?
Tablet (extended-release): 600, and 1200 mg
How should I keep guaifenesin stored?
Tablets, capsules, and syrup should be stored below 30 C (86 F). The liquid should not be refrigerated.
Summary
Guaifenesin (Humibid, Humibid LA, Robitussin, Organidin NR, Fenesin, Mucosa, Mucus Relief, Mucus ER, Mucinex) is an expectorant medication used for the treatment of cough due to colds or minor upper respiratory tract infections. Side effects and pregnancy efficacy should be reviewed before taking this medication.
Related Disease Conditions
Cough: 19 Tips on How to Stop a Cough
Coughing is a reflex that helps a person clear their airways of irritants. There are many causes of an excessive or severe cough including irritants like cigarette and secondhand smoke, pollution, air fresheners, medications like beta blockers and ACE inhibitors, the common cold, GERD, lung cancer, and heart disease. Natural and home remedies to help cure and soothe a cough include staying hydrated, gargle salt water, use cough drops or lozenges, use herbs and supplements like ginger, mint, licorice, and slippery elm, and don’t smoke. Over-the-counter products (OTC) to cure and soothe a cough include cough suppressants and expectorants, and anti-reflux drugs. Prescription drugs that help cure a cough include narcotic medications, antibiotics, inhaled steroids, and anti-reflux drugs like proton pump inhibitors or PPIs, for example, omeprazole (Prilosec), rabeprazole (Aciphex), and pantoprazole (Protonix).
What Is Mucus?
Mucus is a normal substance produced by lining tissues in the body. Excess mucus or mucus that is yellow, green, brown, or bloody may indicate a problem. Mucus production may increase when allergies, a cold, flu, cough, or sore throat are present. Antihistamines and cold and flu medications may help alleviate excess mucus. A neti pot may be used to decrease nasal congestion and clear mucus.
Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Sinus infection (sinusitis) is caused by allergies, infection, and chemicals or other irritants of sinuses. Signs and symptoms include headache, fever, and facial tenderness, pressure, or pain. Treatments of sinus infections are generally with antibiotics and at times, home remedies.
Upper Respiratory Infection (URI)
An upper respiratory infection is a contagious infection of the structures of the upper respiratory tract, which includes the sinuses, nasal passages, pharynx, and larynx. Common causes of an upper respiratory infection include bacteria and viruses such as rhinoviruses, group A streptococci, influenza, respiratory syncytial, whooping cough, diphtheria, and Epstein-Barr. Examples of symptoms of upper respiratory infection include sneezing, sore throat, cough, fever, and nasal congestion. Treatment of upper respiratory infections is based on the cause. Generally, viral infections are treated symptomatically with over-the-counter (OTC) medication and home remedies.
Chronic Rhinitis and Post-Nasal Drip
Chronic rhinitis (non-allergic rhinitis) causes a runny nose, sneezing, nasal itching, and congestion. Post-nasal drip is drainage of mucus from the sinuses into the throat. Treatment includes over-the-counter (OTC) medications.
Common Cold
The common cold (viral upper respiratory tract infection) is a contagious illness that may be caused by various viruses. Symptoms include a stuffy nose, headache, cough, sore throat, and maybe a fever. Antibiotics have no effect upon the common cold, and there is no evidence that zinc and vitamin C are effective treatments.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses. Symptoms and signs include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chills. Antibiotics treat pneumonia, and the choice of the antibiotic depends upon the cause of the infection.
Chronic Cough
Chronic cough is a cough that does not go away and is generally a symptom of another disorder such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, sinus infection, cigarette smoking, GERD, postnasal drip, bronchitis, pneumonia, medications, and less frequently tumors or other lung disease. Chronic cough treatment is based on the cause but may be soothed with natural and home remedies.
Acute Bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the airways in the lung. Acute bronchitis is short in duration (10-20 days) in comparison with chronic bronchitis, which lasts for months to years. Causes of acute bronchitis include viruses and bacteria, which means it can be contagious. Acute bronchitis caused by environmental factors such as pollution or cigarette smoke is not contagious. Common symptoms of acute bronchitis include nasal congestion, cough, headache, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Acute bronchitis in children also includes a runny nose, fever, and chest pain. Treatment for acute bronchitis is over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, cough suppressants (although not recommended in children), and rest. Infrequently antibiotics may be prescribed to treat acute bronchitis.
Can I Get Any STDs Through Clothing?
Most sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) cannot be transmitted through clothing. Some such as pubic lice, scabies, and molluscum contagiosum can be transmitted by sharing clothes with an infected person.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a cough that occurs daily with the production of sputum that lasts for at least 3 months, 2 years in a row. Causes of chronic bronchitis include cigarette smoking, inhaled irritants, and underlying disease processes (such as asthma or congestive heart failure). Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, and wheezing. Treatments include bronchodilators and steroids. Complications of chronic bronchitis include COPD and emphysema.
Asthma Over-the-Counter Treatment
Patients who have infrequent, mild bouts of asthma attacks may use over-the-counter (OTC) medications to treat their asthma symptoms. OTC asthma medicines are limited to epinephrine and ephedrine. These OTC drugs are best used with the guidance of a physician, as there may be side effects, and the drugs may not be very effective.
Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
Before treating a cold, the flu, or allergies with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, it’s important to know what’s causing the symptoms, which symptoms one wishes to relieve, and the active ingredients in the OTC product. Taking products that only contain the medications needed for relieving your symptoms prevents ingestion of unnecessary medications and reduces the chances of side effects.
Before treating a cold, the flu, or allergies with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, it’s important to know what’s causing the symptoms, which symptoms one wishes to relieve, and the active ingredients in the OTC product. Taking products that only contain the medications needed for relieving your symptoms prevents ingestion of unnecessary medications and reduces the chances of side effects.


