Contents
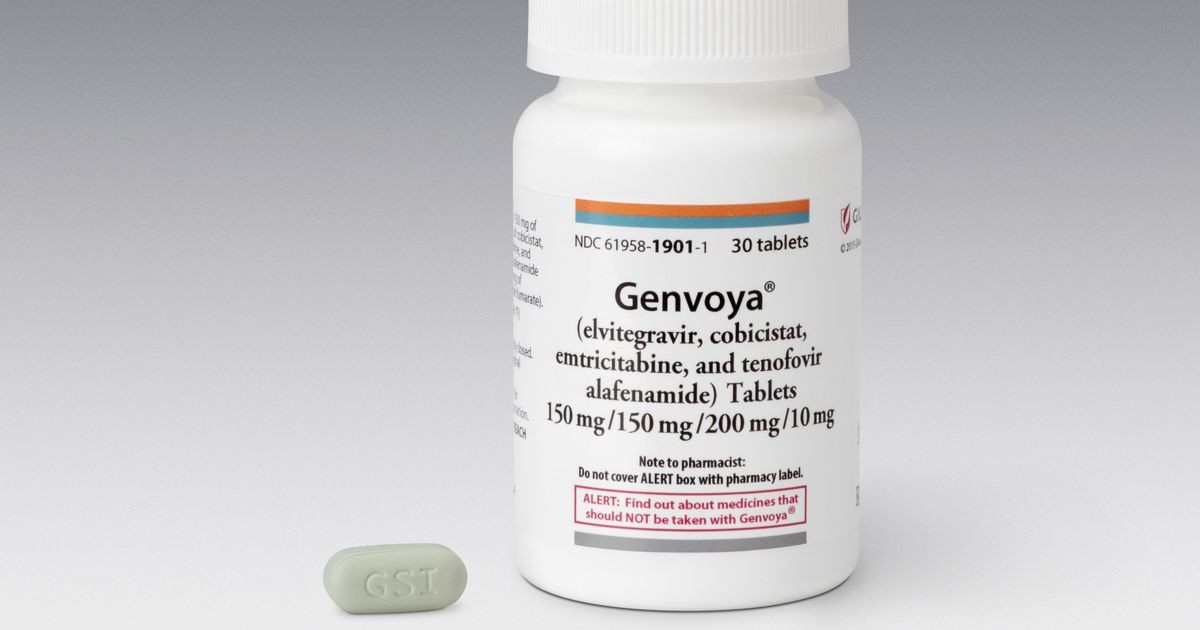
Genvoya
Genvoya is a prescription medicine used to treat HIV-1 in adults and children weighing at least 55 pounds (25 kg). It can be used in two cases:
- For individuals who haven’t received HIV-1 medicines before
- To replace current anti-HIV-1 medicines if certain requirements are met
HIV-1 is the virus causing AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
Genvoya contains elvitegravir, cobicistat, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide.
Side Effects of Genvoya
WARNING
POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of Genvoya. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue Genvoya. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
Genvoya can cause serious side effects including:
- Worsening of Hepatitis B infection: If you have HBV infection and take Genvoya, your HBV may worsen (flare-up) if you stop taking Genvoya. Do not run out of Genvoya. Refill your prescription or talk to your healthcare provider before your Genvoya is all gone. Do not stop taking Genvoya without first talking to your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider needs to check your health often and do blood tests regularly for several months after you stop taking Genvoya. Inform your healthcare provider about any new or unusual symptoms that occur after you stop taking Genvoya.
Other Side Effects of Genvoya
Genvoya may cause serious side effects including:
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome): Your immune system may become stronger and start fighting previously hidden infections. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience new symptoms after starting Genvoya.
- New or worse kidney problems, including kidney failure: Your kidneys should be regularly checked through blood and urine tests during Genvoya treatment. Your healthcare provider may advise you to discontinue Genvoya if new or worsening kidney problems occur.
- Too much lactic acid in your blood (lactic acidosis): Too much lactic acid can be a rare but serious medical emergency leading to death. Seek immediate medical attention if you experiencesymptoms such as unusual weakness, muscle pain, shortness of breath, stomach pain with nausea and vomiting, cold or blue hands and feet, dizziness or lightheadedness, or fast or abnormal heartbeat.
- Severe liver problems: In rare cases, Genvoya can cause severe liver problems leading to death. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, light-colored stools, loss of appetite, nausea, or stomach pain.
The most common side effect of Genvoya is nausea.
These are not all the possible side effects of Genvoya.
Contact your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You can report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Recommended Dosage for Genvoya
- Take Genvoya as directed by your healthcare provider. It should be taken alone for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
- Take Genvoya once daily with food.
- If you are on dialysis, take your daily dose of Genvoya after dialysis.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking Genvoya without consulting your healthcare provider. You should remain under a healthcare provider’s care during treatment with Genvoya.
- If you need to take an indigestion medicine (antacid) containing aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, or calcium carbonate during Genvoya treatment, take it at least 2 hours before or after taking Genvoya.
- Do not miss a dose of Genvoya.
- When your Genvoya supply is running low, obtain more from your healthcare provider or pharmacy. This is crucial as stopping the medication, even for a short period, can lead to increased viral levels and development of drug-resistant strains.
- If you take too much Genvoya, seek immediate medical attention or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Additional Information about Genvoya
The safety and effectiveness of Genvoya in children weighing less than 55 pounds (25 kg) have not been established.
Do not take Genvoya if you also take medication containing:
- Alfuzosin hydrochloride
- Carbamazepine
- Cisapride
- Ergot-containing medicines, including:
- Dihydroergotamine mesylate
- Ergotamine tartrate
- Methylergonovine maleate
- Lomitapide
- Lovastatin
- Lurasidone
- Midazolam (oral)
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Pimozide
- Rifampin
- Sildenafil (for pulmonary arterial hypertension)
- Simvastatin
- Triazolam
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) or products containing St. John’s wort.
What to Tell Your Healthcare Provider
Prior to taking Genvoya, inform your healthcare provider of all your medical conditions, including:
- Liver problems, including hepatitis B infection
- Kidney problems
- Pregnancy or a plan to become pregnant. The safety of Genvoya during pregnancy is unknown. Genvoya should not be used while pregnant, as you may not have sufficient Genvoya in your body during pregnancy. Notify your healthcare provider if you become pregnant during Genvoya treatment. Your healthcare provider may prescribe different medicines in such cases.
- Pregnancy Registry: There is a registry for individuals taking antiretroviral medicines during pregnancy. Its purpose is to collect information about the health of both you and your baby. Discuss with your healthcare provider how you can participate in this registry.
Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Some medications may interact with Genvoya. Keep a list of your medications and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when starting a new medicine.
- You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with Genvoya.
- Do not start a new medicine without consulting your healthcare provider. They can advise you on the safety of taking Genvoya with other medications.
Summary
Genvoya is a prescription medicine used to treat HIV-1 in adults and children. The most common side effect is nausea. Serious side effects may include changes in the immune system, kidney problems, lactic acidosis, and severe liver problems.