Contents
- 1 bumetanide
- 1.0.1 What are the side effects of bumetanide?
- 1.0.2 What is the dosage for bumetanide?
- 1.0.3 Which drugs or supplements interact with bumetanide?
- 1.0.4 Is bumetanide safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
- 1.0.5 What else should I know about bumetanide?
- 1.0.6 Summary
- 1.0.7 Related Disease Conditions
- 1.1 High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
- 1.2 Cirrhosis (Liver)
- 1.3 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- 1.4 Edema (Pitting)
- 1.5 Pulmonary Edema
- 1.6 Things to Know About High Blood Pressure Treatment
bumetanide
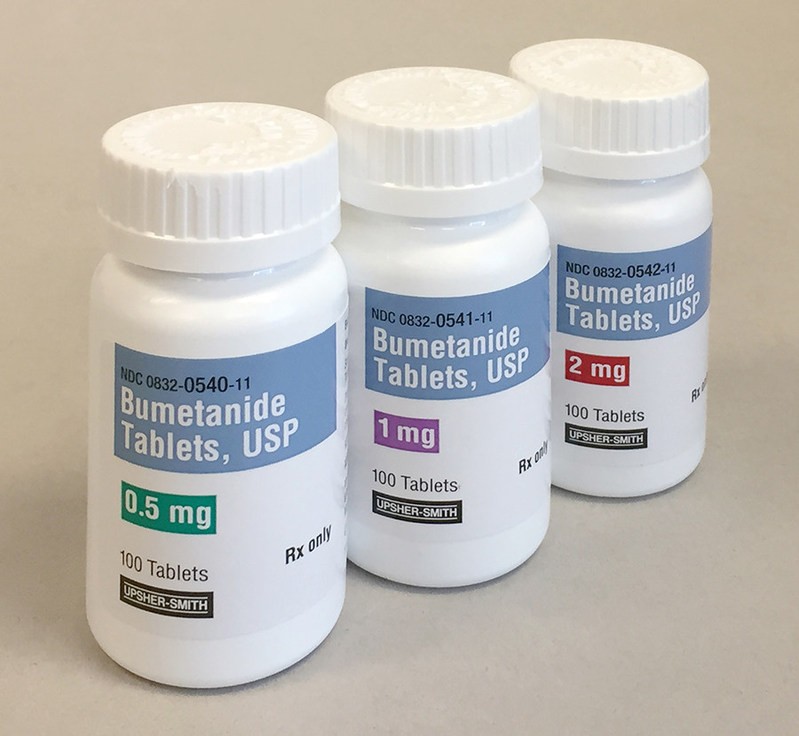
Bumetanide is a potent diuretic that increases urine output by preventing the kidney from retaining fluid. It blocks the reabsorption of sodium and fluid from the kidney’s tubules. Bumetanide belongs to a class of diuretics called "loop" diuretics, which also includes furosemide (Lasix) and torsemide (Demadex). One mg of bumetanide is roughly equivalent to 10-20 mg of torsemide and 40 mg of furosemide. The potent diuretic effect of bumetanide can cause the loss of large amounts of body water, leading to dehydration and electrolyte loss (sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium). Medical supervision is necessary during treatment. Bumetanide was FDA-approved in 1983.
Is bumetanide available as a generic drug?
Do I need a prescription for bumetanide?
What are the side effects of bumetanide?
Potent diuretics like bumetanide can cause low blood levels of potassium, magnesium, sodium, and calcium, as well as fluid losses leading to dehydration.
- dry mouth,
- thirst,
- weakness,
- drowsiness,
- reduced kidney function,
- heart arrhythmias,
- muscle aches and pains,
- nausea, and
- vomiting.
Toxicity to the inner ear, in the form of tinnitus and hearing loss, has been associated with loop diuretics. High plasma levels of bumetanide are toxic to the inner ear of animals. These effects on the inner ear are more common with intravenous use. High uric acid concentrations in the blood, leading to attacks of gouty arthritis, may occur during diuretic therapy.
What is the dosage for bumetanide?
The dose for most patients is 0.5 to 2 mg daily. Doses may be increased every 4 to 5 hours to a maximum of 10 mg daily. Intravenous or intramuscular injections may be used when oral administration is not possible. The IV dose is 1 mg initially followed by 0.5 to 2 mg/hour, and the IM dose is 0.5 to 10 mg daily. Dosing varies among patients and is carefully adjusted by physicians. Bumetanide may be taken with or without food.
Which drugs or supplements interact with bumetanide?
Bumetanide can cause low blood potassium, calcium, and magnesium levels, and increase the risk of toxicity from digoxin. Combining bumetanide with other diuretics can exaggerate the losses of potassium and magnesium. Bumetanide may decrease the body’s ability to eliminate lithium and can interact with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Concomitant use of bumetanide and aminoglycosides may increase the risk of hearing impairment.
Is bumetanide safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
There have been no adequate studies on the effects of bumetanide on the fetus. The potential risks and benefits must be carefully considered before prescribing it for pregnant women.
It is not known if bumetanide is excreted into breast milk. It should be used in breastfeeding women only if the potential benefits outweigh the unknown risks.
What else should I know about bumetanide?
What preparations of bumetanide are available?
Tablets: 0.5, 1, and 2 mg. Injection: 0.25 mg/ml
How should I keep bumetanide stored?
Tablets should be stored at room temperature, between 15 C – 30 C (59 F – 86 F).
Summary
Bumetanide, also known as Bumex, is a medication prescribed for the management of edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver and kidney disease, and off-label treatment for high blood pressure. Side effects, dosage, drug interactions, and pregnancy safety information should be reviewed prior to taking this medication.
Related Disease Conditions
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a disease in which pressure within the arteries of the body is elevated. About 75 million people in the US have hypertension, and only half of them are able to manage it. Many people do not know they have high blood pressure because it often has no warning signs or symptoms. Systolic and diastolic are the two readings in which blood pressure is measured. The American College of Cardiology released new guidelines for high blood pressure in 2017. The guidelines now state that normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. If either number is higher, you have high blood pressure. The American Academy of Cardiology defines high blood pressure slightly differently, considering 130/80 mmHg. or greater (either number) stage 1 hypertension, and 140/90 mmHg. or greater stage 2 hypertension. High blood pressure increases the risk of developing life-threatening diseases like stroke and heart attack. Reference: CDC. High Blood Pressure. Updated: Nov 13, 2017.
Cirrhosis (Liver)
Cirrhosis of the liver refers to a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue caused by alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C. This disease leads to abnormalities in the liver’s ability to handle toxins and blood flow, causing internal bleeding, kidney failure, mental confusion, coma, body fluid accumulation, and frequent infections. Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and survival can be up to 12 years. However, the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive heart failure (CHF) refers to a condition in which the heart loses the ability to function properly. Heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathies are just a few potential causes of congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure may include fatigue, breathlessness, palpitations, angina, and edema. Physical examination, patient history, blood tests, and imaging tests are used to diagnose congestive heart failure. Treatment of heart failure consists of lifestyle modification and taking medications to decrease fluid in the body and ease the strain on the heart. The prognosis of a patient with congestive heart failure depends on the stage of the heart failure and the overall condition of the individual.
Edema (Pitting)
Edema is swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues of the body, occurring most often in the legs, feet, ankles, or hands. Learn about different types, symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema, or fluid in the lungs, can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath. Learn about causes, diagnosis, complications, treatment, and prevention.
Things to Know About High Blood Pressure Treatment
High blood pressure (hypertension) means high pressure (tension) in the arteries. Treatment for high blood pressure includes lifestyle modifications, drugs, and medications such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers, clonidine, minoxidil, and Exforge.