Contents
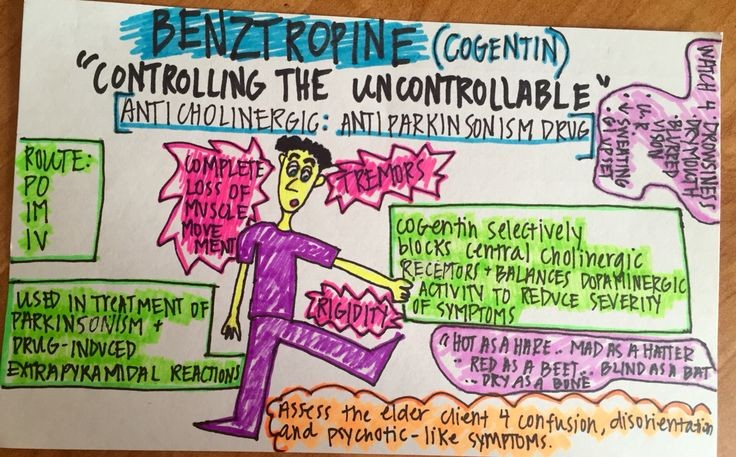
Benztropine
Benztropine is a medication used to treat all forms of Parkinson’s disease, a neurological disorder that affects movement and balance.
Benztropine also controls drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms, movement disorders resulting from antipsychotic therapy.
Benztropine is an anticholinergic agent that reduces the activity of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that makes muscles contract. Benztropine binds to muscarinic receptors in neuromuscular junctions and prevents acetylcholine from stimulating them, reducing muscle stiffness and providing symptomatic relief for Parkinson’s disease and drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms.
Benztropine cannot be used for tardive dyskinesia, a movement disorder that occurs from prolonged antipsychotic therapy. Additionally, benztropine binds to histamine receptors and inhibits the activity of histamine, but this does not have therapeutic value for Parkinson’s or extrapyramidal symptoms.
Warnings
- Do not use benztropine in patients who are hypersensitive to any of its components, pediatric patients younger than 3 years of age, or pregnant patients, as safety is not established.
- Avoid using benztropine in patients with rapid heart rate (tachycardia), gastrointestinal obstruction, or enlarged prostate (prostatic hyperplasia) and urinary stricture.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of benztropine?
Common side effects of benztropine include:
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Depression
- Memory impairment
- Nervousness
- Visual hallucinations
- Worsening of psychotic symptoms
- Toxic psychosis
- Lethargy
- Numbness of fingers
- Absence of sweating (anhidrosis)
- High body temperature (hyperthermia)
- Heatstroke
- Blurred vision
- Dilation of pupils (mydriasis)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Constipation
- Paralysis of intestinal muscles (paralytic ileus)
- Urinary retention
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Skin rash
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or serious side effects while using this drug:
- Serious heart symptoms include fast or pounding heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness.
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, severe weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady.
- Severe nervous system reaction with very stiff muscles, high fever, sweating, confusion, fast or uneven heartbeats, tremors, and feeling like you might pass out.
- Serious eye symptoms include blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights.
This is not a complete list of side effects or adverse reactions that may occur. Contact your doctor for medical advice about serious side effects or adverse reactions. You may also report side effects or health problems to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What are the dosages of benztropine?
Tablet
Injectable Solution
Adults:
- 1-2 mg/day (range, 0.5-6 mg/day) orally, intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM) at bedtime or divided every 6-12 hours; consider lower dose or 0.5 mg at bedtime in highly sensitive patients; titrate dose in 0.5-mg increments every 5-6 days (range 0.5-6 mg daily); not to exceed 6 mg/day
- 0.5-1 mg at bedtime initially; titrate dose in 0.5-mg increments every 5-6 days (range 0.5-6 mg daily; some patients may need 4-6 mg/day); not to exceed 6 mg/day
Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Disorders
- 1-2 mg IV/IM/oral every 8-12 hours; titrate gradually at 0.5 mg increments at 5-6 day intervals based on response and tolerability; not to exceed 6 mg/day; reevaluate after 1-2 weeks; may reinitiate therapy if symptoms recur
- Acute dystonia: 1-2 mg IV, then 1-2 mg oral once or twice daily for 7-28 days to prevent recurrence
Geriatric:
Parkinsonism
- 0.5 mg orally once daily or every 12 hours; titrate dose in 0.5-mg increments every 5-6 days; not to exceed 4 mg/day
Dosing Considerations
- Nonanticholinergic antiparkinson agents should be considered first for treatment of Parkinson disease.
- Not well tolerated in elderly, because of bowel, bladder, and CNS effects; avoid use if possible.
- Should not be used as prophylaxis against extrapyramidal symptoms in elderly.
Pediatric:
Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Disorders
- Children below 3 years: Not recommended
- Children above 3 years: 0.02-0.05 mg/kg IV/IM/oral once daily or every 12 hours
- Adolescents (off-label): 1-4 mg IV/IM/oral every day or every 12 hours
Overdose
- Benztropine overdose causes central nervous system (CNS) depression preceded or followed by stimulation.
- Overdose symptoms include confusion, nervousness, worsening of symptoms or toxic psychosis in psychiatric patients being treated with neuroleptic drugs, hallucinations, muscle weakness, dry mouth, dilated pupils, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, high temperature, allergic reactions, high heart rate and blood pressure, palpitations, delirium, coma, shock, convulsions, circulatory collapse, and respiratory arrest.
- Treatment is symptomatic and supportive, including:
- Physostigmine salicylate to reverse benztropine effects
- A short-acting barbiturate for CNS stimulation, but with caution to avoid subsequent depression
- Supportive measures for CNS depression
- Respiratory support in case of respiratory depression
- Intravenous fluids and medications for circulatory collapse
What drugs interact with benztropine?
Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, who can advise you on any possible drug interactions. Never begin taking, suddenly discontinue, or change the dosage of any medication without your doctor’s recommendation.
- Benztropine has no known severe interactions with other drugs.
- Serious interactions of benztropine include:
- glucagon
- glucagon intranasal
- glycopyrronium tosylate topical
- revefenacin
- secretin
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
- desipramine
- levodopa
- trazodone
The drug interactions listed above are not all of the possible interactions or adverse effects. For more information on drug interactions, visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker.
Always inform your doctor, pharmacist, or healthcare provider of all prescription and over-the-counter medications you use, including the dosage, and keep a list of the information. Consult your doctor or healthcare provider if you have any questions about the medication.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Safety of use in pregnancy is not established, avoid use.
- Two newborns developed intestinal muscle paralysis (paralytic ileus) that resolved rapidly after exposure to a combination of benztropine and chlorpromazine during the second and third trimesters and the last 6 weeks of pregnancy, respectively.
- Anticholinergic medications may suppress lactation, and it is not known if they are excreted in breast milk, avoid use.
What else should I know about benztropine?
- Take benztropine exactly as prescribed by your physician.
- Exercise caution in hot environments and during exercise as benztropine prevents sweating and may dangerously elevate body temperatures.
- Avoid engaging in hazardous tasks such as driving and operating heavy machinery as benztropine may impair mental and physical ability.
- Store safely out of reach of children.
- In case of overdose, seek medical help immediately or contact Poison Control.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Summary
Benztropine is a medication used to treat all forms of Parkinson’s disease. Common side effects include rapid heart rate (tachycardia), confusion, disorientation, depression, memory impairment, nervousness, visual hallucinations, worsening of psychotic symptoms, toxic psychosis, lethargy, numbness of fingers, absence of sweating (anhidrosis), high body temperature (hyperthermia), and others. Safety of use in pregnancy is not established, avoid use. Anticholinergic medications may suppress lactation, and it is not known if they are excreted in breast milk, avoid use.


