Contents
Aspirin vs. Eliquis (apixaban)
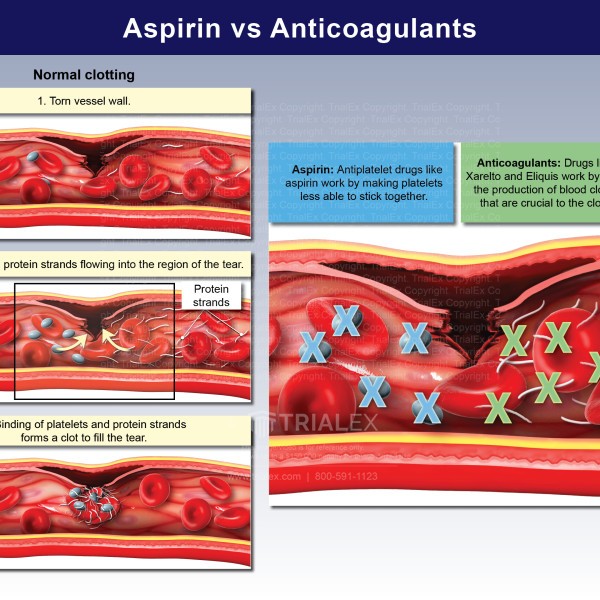
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat fever, pain, and inflammation. It is also used to prevent blood clots (antithrombotic).
Aspirin inhibits platelet function for prolonged periods, reducing the risk of another heart attack or stroke in individuals who have already experienced one.
Other NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Motrin), indomethacin (Indocin), and nabumetone (Relafen). NSAIDs reduce levels of prostaglandins, chemicals released during inflammation that cause pain and fever. NSAIDs block the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which produces prostaglandins, resulting in lower levels of prostaglandins and a reduction in inflammation, pain, and fever. Suppression of prostaglandins also reduces platelet function and blood clotting ability.
Eliquis (apixaban) is a blood thinner (anticoagulant) used to reduce the risk of blood clots in the heart and strokes in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. It is also used to treat and prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in patients who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of aspirin and Eliquis?
Aspirin side effects
Most patients benefit from aspirin and other NSAIDs with few side effects. However, serious side effects can occur, usually dose-related. Therefore, it is advisable to use the lowest effective dose to minimize side effects.
The most common side effects of aspirin involve the gastrointestinal system and ringing in the ears.
Gastrointestinal side effects include ulcerations, abdominal burning, pain, cramping, nausea, gastritis, and serious gastrointestinal bleeding. Liver toxicity can also occur.
Sometimes, ulceration and bleeding can occur without abdominal pain. Black tarry stools, weakness, and dizziness when standing may be the only signs of internal bleeding.
If ringing in the ears occurs, the daily dose of aspirin should be reduced.
Other side effects include:
Aspirin should be avoided by patients with peptic ulcer disease or poor kidney function, as it can worsen both conditions. It may also worsen asthma and raise blood uric acid levels in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. Children and teenagers should avoid aspirin for flu or chickenpox symptoms due to the risk of Reye’s Syndrome. Aspirin can increase the effects of diabetes medications, resulting in low blood sugar levels if not monitored. NSAIDs should be stopped before elective surgery due to their mild interference with blood clotting. Aspirin, with its prolonged effect on platelets, should be discontinued at least ten to fourteen days before the procedure.
Eliquis side effects
The most common side effects of apixaban are bleeding.
Bleeding caused by apixaban can be fatal.
Major bleeding events occurred less frequently in patients who received apixaban compared to those who received warfarin, another commonly used drug for preventing blood clots.
Rash and serious allergic reactions may also occur.
What is the dosage of aspirin vs. Eliquis?
Aspirin dosage
Aspirin should be taken with food. Doses range from 50 mg to 6000 mg daily depending on the use.
Usual doses for mild to moderate pain are 350 or 650 mg every 4 hours or 500 mg every 6 hours. Doses for rheumatoid arthritis range from 500 mg every 4-6 hours to 1950 mg twice daily. Heart attack prevention doses range from 75-325 mg daily. Non-enteric coated aspirin should be chewed immediately when experiencing heart attack symptoms. The dose for preventing another stroke is 75-100 mg daily.
Eliquis dosage
The usual dose for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is 5 mg twice daily. For individuals 80 years or older, weighing less than or equal to 60 kg, or with reduced kidney function, the usual dose is 2.5 mg twice daily. The recommended dose for treating DVT or pulmonary embolism is 10 mg twice daily for the first 7 days, then 5 mg twice daily. After six months of treatment, the dose may be reduced to 2.5 mg daily for prevention. When used to prevent DVT after hip or knee replacement surgery, the suggested dose is 2.5 mg daily, starting 12 to 24 hours after surgery.
What drugs interact with aspirin vs. Eliquis?
Aspirin drug interactions
Aspirin is associated with several suspected or probable interactions that affect the action of other drugs. Examples include:
NSAIDs may increase blood levels of lithium, leading to toxicity. Aspirin may reduce the blood pressure-lowering effects of blood pressure medications. Combining aspirin with methotrexate or aminoglycoside antibiotics may increase blood levels of these drugs, potentially causing side effects. Individuals taking oral blood thinners should avoid aspirin to avoid excessive blood thinning and serious bleeding.
Eliquis drug interactions
Apixaban is metabolized by CYP3A4 and P-gp. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp increase exposure to apixaban and raise the risk of bleeding. Inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp decrease exposure to apixaban and increase the risk of stroke and other thromboembolic events.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Are aspirin and Eliquis safe to take while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Aspirin
Aspirin is generally avoided during pregnancy due to potential adverse effects on the fetus. However, low doses may be safely used for preventing pregnancy complications. It is excreted in breast milk and may cause adverse effects in infants.
Eliquis
No adequate studies have been conducted in pregnant women. Use during pregnancy may increase the risk of bleeding. Apixaban should be avoided during pregnancy. It is unknown if apixaban is excreted in human milk, so nursing mothers should discontinue either apixaban or breastfeeding.
From
Pain Management Resources
- Managing a Sickle Cell Pain Crisis
- Take Control of Your Migraine, Now
- Side Effects From aHUS Treatment
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Summary
Aspirin and Eliquis (apixaban) are anticoagulants used to prevent blood clots. Aspirin also treats fever, pain, and inflammation. Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), while Eliquis is an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Common side effects of both drugs include gastrointestinal bleeding and rash.