Contents
Coumadin vs. Plavix: Differences and Similarities
Coumadin (warfarin) is an oral anticoagulant that inhibits blood clotting. It helps prevent the formation and extension of blood clots, reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism and stroke. Coumadin is used in various conditions, such as deep vein thrombosis, atrial fibrillation, and after orthopedic surgeries.
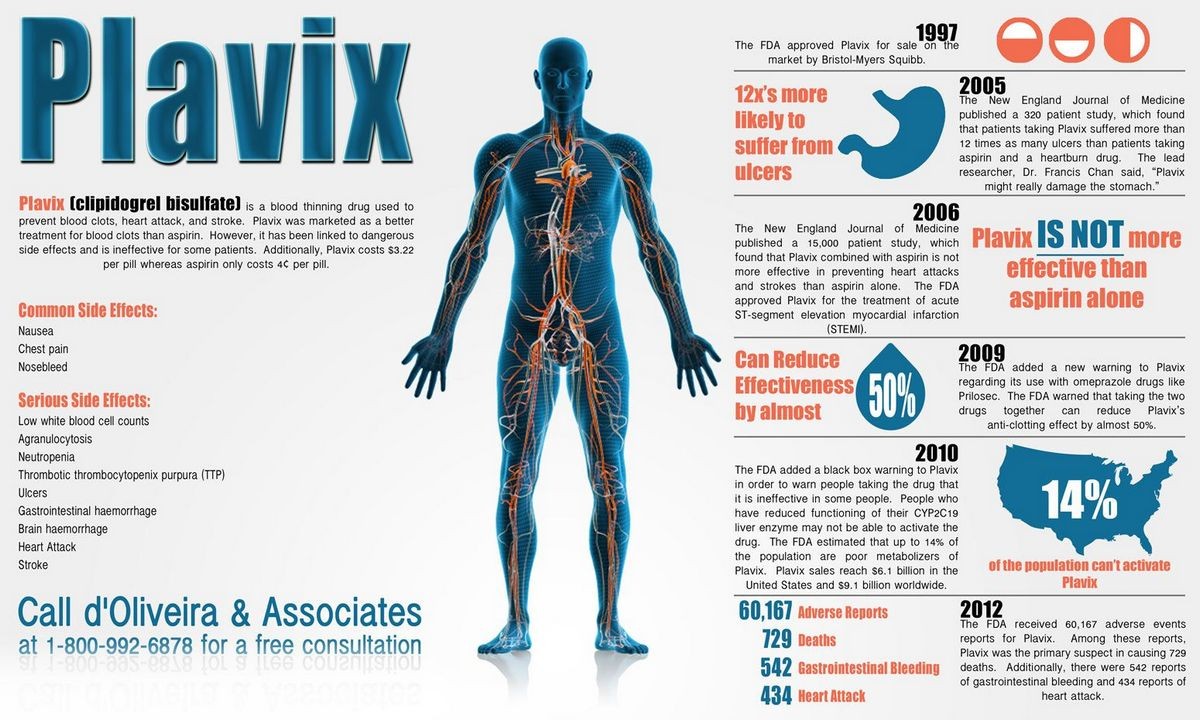
Plavix (clopidogrel bisulfate) is an antiplatelet drug that prevents blood clots. It is used to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and death in individuals with a history of stroke, unstable angina, heart attack, or peripheral arterial disease. Plavix belongs to a class of drugs called P2Y12 inhibitors.
QUESTION
What are the uses for Coumadin vs. Plavix?
Coumadin uses
- Coumadin is used to prevent the extension of blood clots and reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism.
- It is also used in people with atrial fibrillation or artificial heart valves to prevent strokes, as well as after a heart attack.
- Certain orthopedic surgeries, such as knee or hip replacements, benefit from Coumadin to prevent blood clot formation.
- Warfarin is used to prevent closure of coronary artery stents due to clotting.
Plavix uses
- Plavix is used to prevent strokes, heart attacks, and death in individuals with previous stroke, unstable angina, heart attack, or peripheral arterial disease.
- Combining clopidogrel with aspirin is more effective than using either drug alone in preventing another heart attack, although it increases the risk of bleeding.
What are the side effects of Coumadin vs. Plavix?
Coumadin side effects
The two most serious side effects of warfarin are bleeding and skin necrosis (gangrene).
- Bleeding can occur in any organ or tissue, leading to symptoms such as severe headache, paralysis, joint pain, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Other side effects may include purple, painful toes, rash, hair loss, bloating, diarrhea, and jaundice.
- Signs of overdose include bleeding gums, bruising, nosebleeds, heavy menstrual bleeding, and prolonged bleeding from cuts.
Plavix side effects
The tolerability of clopidogrel is similar to that of aspirin.
- Common side effects include diarrhea, rash, itching, abdominal pain, headache, chest pain, muscle aches, and dizziness.
- Severe bleeding, allergic reactions, pancreatitis, and liver failure are rare but possible side effects.
- Compared to the related drug ticlopidine, clopidogrel has a lower risk of severe reduction in white blood cell count and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
What is the dosage of Coumadin vs. Plavix?
Coumadin dosage
- Warfarin may be taken with or without food.
- Treatment usually starts at 2 to 5 mg once daily and is adjusted based on INR tests.
- Patient dosage typically ranges from 2 to 10 mg of warfarin daily.
Frequent blood tests (INR tests) are performed to measure the effect of warfarin and adjust dosing. Dosages need to be lowered in patients with liver and kidney dysfunction.
Plavix dosage
- Clopidogrel bisulfate is usually taken once daily, with or without food.
- Treating unstable angina or heart attack starts with a 300 mg initial dose followed by 75 mg daily in combination with 75-325 mg of aspirin.
- Peripheral arterial disease or recent stroke is treated with 75 mg daily.
Patients with reduced liver enzyme activity may have an inadequate response to clopidogrel. Alternative treatments should be used.
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet, and I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.
What are the drug interactions for Coumadin vs. Plavix?
Coumadin drug interactions
Many drugs, both prescription and nonprescription (OTC), can affect warfarin’s anticoagulant action or increase bleeding risk. Patients on warfarin should consult their doctor before taking any medications. Carrying identification alerting others to anticoagulation use is advisable.
Drugs that increase warfarin’s effect include amiodarone, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, fluconazole, and various others.
Bleeding is increased by anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and certain SSRIs. Garlic and ginkgo supplements also increase bleeding risk.
Foods high in vitamin K can reduce the effect of warfarin.
Plavix drug interactions
Clopidogrel combined with NSAIDs may increase the risk of bleeding. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac.
Drug interactions that reduce clopidogrel’s activity involve enzymes in the liver. These can occur with omeprazole, fluoxetine, cimetidine, and various other drugs.


