Contents
What Is Rose Hip Good for and Are There Side Effect Risks?
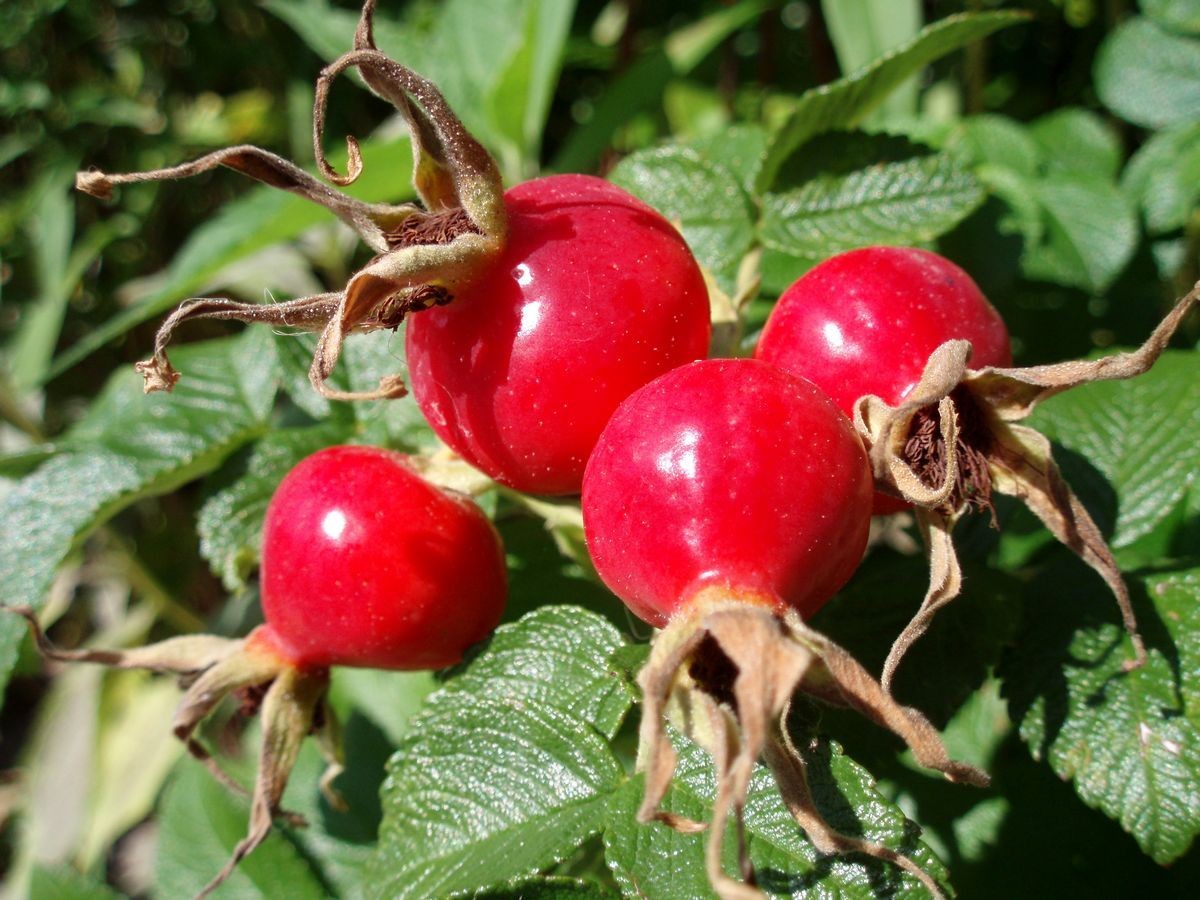
Rose hips are fleshy, red berries of the rose plant and they are rich in vitamins and may have health benefits. Rose hips help heal wounds, lower inflammation, alleviate arthritis, and have other benefits.
Rose hip is an edible fruit used in skincare products and supplements. People have used rose hips as medicine for a long time, and modern research shows potential benefits.
Rose hips are fleshy, red berries found just under the blooms of the rose plant. They hold the plant’s seeds and are ripe by the end of summer or early fall. Rose hips usually come from the dog rose, Rosa canina, also known as rose haw or rose heps.
People have used rose hips as food and medicine for centuries. The fruit is commonly made into jams, jellies, syrups, yogurt, alcoholic drinks, and herbal tea. Today, you can also buy rose hip extracts and supplements.
What is rose hip good for?
Rose hips are rich in vitamins and may have health benefits. Research on rose hip supplements has produced conflicting results, so more research is needed.
Rich in vitamin C
Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is essential for the skin, joints, bones, immune system, and nervous system. It aids in wound healing, neutralizes free radicals, and combats infections. Rose hips are a good source of vitamin C, especially when consumed as herbal tea or fresh.
Might lower inflammation
Rose hip contains a compound called galactolipid, which can fight inflammation. It is unclear how it works, but studies suggest a mixture of rose hip compounds contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects.
Youthful skin
Rose hip powder can improve skin elasticity, moisture content, and reduce wrinkles. It contains quercetin, which can help brighten the skin by blocking pigment production.
Heart health
Rose hip powder has shown potential in lowering blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and preventing plaque formation in animal studies, suggesting it may benefit heart health.
May help arthritis
Rose hip extract might ease symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis by reducing inflammation. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Might help with weight and visceral fat loss
Rose hip extract may assist in weight loss and reducing visceral fat. In a study, participants taking rose hip extract experienced significant weight loss and a decrease in visceral fat.
Side effects of rose hip
Rose hips from Rosa canina are safe to consume, even in higher doses. The most common side effects include digestive upset. There is a theoretical risk of kidney stones due to the high vitamin C content, but studies suggest rose hips may actually help prevent kidney stones.
Rose hip supplements may interact with certain medications, so it’s essential to consult with a doctor before taking them.
The bottom line on rose hips
Rose hips are nutritious and rich in vitamin C. They are commonly used in supplements for various reasons, but more research is needed to fully understand their benefits. Consult with a doctor before taking rose hip supplements.
QUESTION
American Journal of Kidney Diseases; "Total, Dietary, and Supplemental Vitamin C Intake and Risk of Incident Kidney Stones.
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies: "Rose hip and its constituent galactolipids confer cartilage protection by modulating cytokine, and chemokine expression."
Clinical Interventions in Aging: "The effectiveness of a standardized rose hip powder, containing seeds and shells of Rosa canina, on cell longevity, skin wrinkles, moisture, and elasticity."
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy: "Daily intake of rosehip extract decreases abdominal visceral fat in preobese subjects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial."
Harvard Medical School Harvard Health Publishing: "Abdominal fat and what to do about it."
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: "Vitamin C."
Inflammopharmacology: "The anti-inflammatory properties of rosehip."
International Journal of Molecular Sciences: "Therapeutic Applications of Rose Hips from Different Rosa Species."
Iowa State University: "Roses have hips too!"
Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry: "Dietary rose hip exerts antiatherosclerotic effects and increases nitric oxide-mediated dilation in ApoE-null mice."
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture: "Effect of rosehip (Rosa canina L.) phytochemicals on stable free radicals and human cancer cells."
Mayo Clinic: "Arteriosclerosis / atherosclerosis."
Molecules: "Rose Hips, a Valuable Source of Antioxidants to Improve Gingerbread Characteristics."
National Library of Medicine MedlinePlus: "Rose Hip."
Phytomedicine: "The effects of rose hip (Rosa canina) on plasma antioxidative activity and C-reactive protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal controls: a prospective cohort study."
Recent Patents on Food, Nutrition, and Agriculture: "Galactolipids as potential health promoting compounds in vegetable foods."