Contents
- 1 What Does It Mean to Have Squamous Epithelial Cells in Urine?
- 1.0.1 What is the normal range of squamous epithelial cells in urine?
- 1.0.2 Does the presence of excess squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate cancer?
- 1.0.3 What are the treatment options for excess squamous epithelial cells in urine?
- 1.0.4 Can I have a high epithelial cell count in urine in the absence of a kidney condition?
- 1.0.5 What is a clean catch method?
- 1.0.6 From
What Does It Mean to Have Squamous Epithelial Cells in Urine?
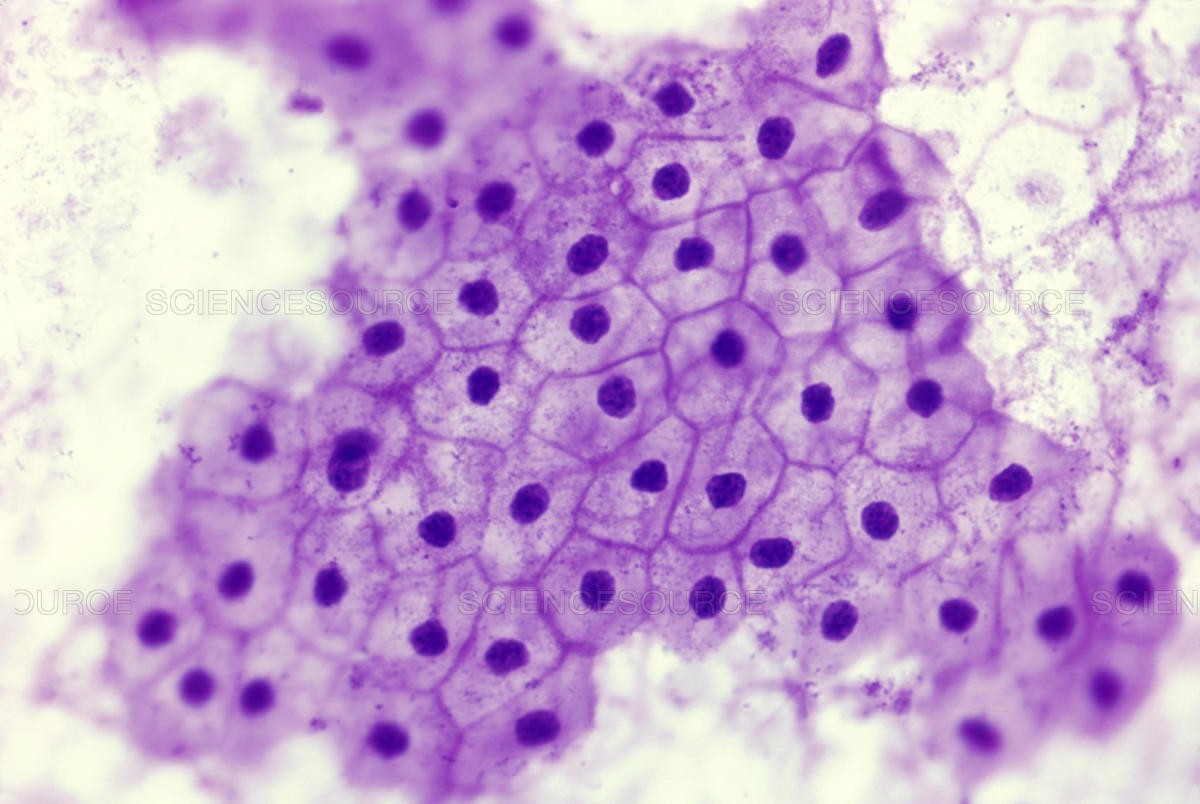
The normal range of squamous epithelial cells in urine is typically zero to five per high-power field (HPF).
The presence of squamous epithelial cells in your urine sample may indicate contamination from the urethra or vaginal opening. Improper urine sample collection is the main cause. Your doctor may ask you to take another urine test.
Squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate shedding of cells that line the bladder or urethra. This can be due to:
- Normal epithelial shedding: A small amount is normal and happens when the bladder and/or urethra cells shed.
- Urinary tract infection: Inflammation and irritation of the urinary tract can lead to increased shedding of squamous cells.
- Physical trauma or irritation: Vigorous sex, catheterization, or injury to the urinary tract can cause increased shedding of squamous cells.
- Bladder or urethral diseases: Diseases like urethritis, bladder cancer, or urethral cancer can cause increased shedding of squamous cells.
Squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate the presence of flat, scale-like cells that typically line the outer layer of skin and other surfaces in the body. They can be a sign of damage or irritation to the urethra or other parts of the urinary tract. Further diagnostic tests such as a urine culture or biopsy may be necessary to determine the cause.
What is the normal range of squamous epithelial cells in urine?
The normal range is typically zero to five per high-power field (HPF). A higher number indicates contamination in the urine sample.
More than five cells in a single field of view may indicate an infection or other health condition. Consult a doctor if the cell count is outside the normal range.
The normal range may vary between laboratories and can be influenced by age, sex, and overall health. It is best to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate interpretation of urine test results.
A moderate amount of squamous epithelial cells in the urine is not necessarily a cause for concern. However, consistently high numbers or other signs of a urinary tract infection may require further investigation and treatment.
Does the presence of excess squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate cancer?
Squamous epithelial cells in urine may indicate an underlying health condition, but not necessarily cancer. They are normally found in the skin and lining of certain organs. When present in urine, they may indicate shedding from abnormal sites like the bladder or urethra.
In some cases, the presence of squamous epithelial cells in urine may signify an infection, irritation, or injury. However, other conditions like bladder or urethral cancer can also cause their presence.
A cancer diagnosis cannot be made based on the presence of squamous epithelial cells in urine alone. Additional tests may be necessary. Consult a healthcare provider if concerned.
What are the treatment options for excess squamous epithelial cells in urine?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: For infection.
- Hydration: Increasing fluid intake to flush out excess cells.
- Avoiding irritants: Not using harsh soaps, bubble baths, or spermicidal products.
- Medical procedures: Bladder wash or irrigation to remove excess cells.
- Surgery: For severe cases or underlying conditions.
If a tumor is causing the blockage, treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Seek medical advice for diagnosis and treatment.
Can I have a high epithelial cell count in urine in the absence of a kidney condition?
In certain systemic conditions, a high epithelial cell count in urine is possible.
Risk factors include liver disease, weak immune system, diabetes, high blood pressure, enlarged prostate, family history of kidney disease, pregnancy, and certain ethnicities.
Treatment Options
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Lifestyle modifications may be advised for chronic conditions. Consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is a clean catch method?
The clean catch method is used to ensure urine sample collection is not contaminated with epithelial cells.
Steps include washing hands, using tissue paper to clean the genital area, collecting a midstream sample, and avoiding contact between the container and genitals to reduce contamination.
From
Medical Test Resources
- What Is Polycythemia Vera?
- Symptoms of Neuromyelitis Optica
- When Should You Consider Genomic Testing?
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew


