Contents
What Are the First Signs of Cirrhosis?
Ten early signs of liver cirrhosis, as well as symptoms that may worsen.
10 early signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis
- Tiredness and weakness
- Fluid builds up in the legs and abdomen (swelling)
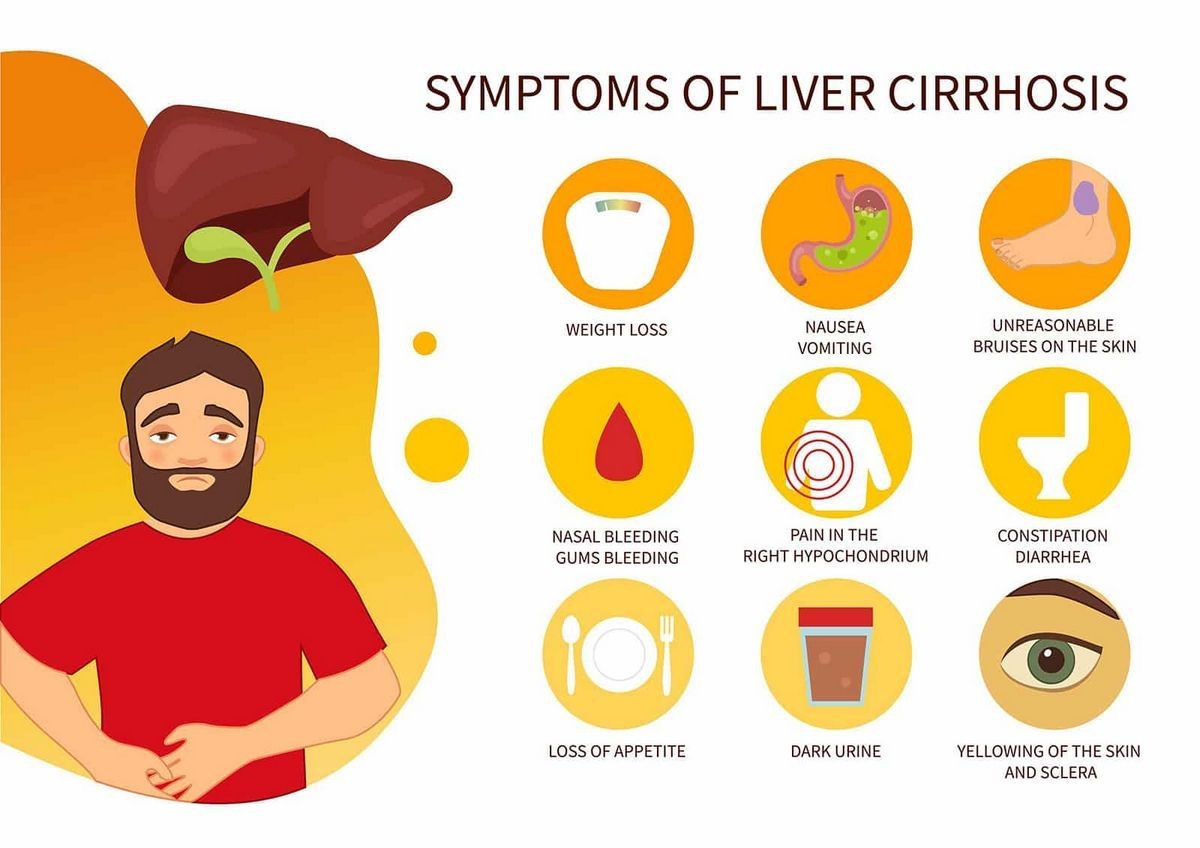
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling sick (nausea) and being sick (vomiting)
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss (although you may put on weight if you retain fluid)
- Visible spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- Sleep disturbances
- Getting sick often
- Redness in the palms of the hands
The following symptoms may present as the condition worsens:
- Tending to bleed and bruise more easily
- Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Gallstones
- Itchy skin
- Changes in behavior (confusion, forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating)
- Blood vomiting
- Passing blood with your stools
- Dark urine
- Blood from nose
- Painful swollen stomach from a buildup of fluid (ascites)
- Irregular periods
- Decrease in sexual libido
- Gynecomastia in men
- Swollen scrotum or shrunken testicles
- Drowsiness
- Slurred speech
- Muscle tremors
- Shortness of breath
- Some may develop liver cancer
A dull discomfort in the upper right abdomen may be felt in the early stages. As the illness worsens, the pain becomes more intense, progressing from mild to painful and stabbing under the ribcage followed by abdominal edema and spleen enlargement.
9 causes of liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis of the liver can be caused by various diseases and ailments. It manifests gradually and can lead to liver failure if not effectively managed.
- Long-term hepatitis infections (chronic):
- Cirrhosis can develop from chronic liver infection.
- Cirrhosis is typically caused by hepatitis B and C virus infection.
- Chronic alcoholism:
- Alcohol consumption promotes inflammation in liver cells, poisoning them and resulting in scar tissue buildup in the liver.
- Cirrhosis is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, typically over a decade.
- The severity of the damage varies and is determined by familial susceptibility.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver (or steatohepatitis): Cirrhosis can develop from fat buildup in the liver over time. Scar tissue can develop due to various illnesses such as coronary artery disease, diabetes, obesity, corticosteroid drug treatment, excessive cholesterol, and protein deficiency.
- Toxic substances or medications: Some drugs, poisons, and environmental contaminants toxic to the liver can cause scarring and damage.
- Inherited (genetic) disorders: Genetic disorders can interfere with the liver’s metabolism and its ability to handle iron (hemochromatosis) and copper (Wilson’s disease) accumulation in the system.
- Autoimmune liver disease:
- Autoimmune infections occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues, including organs like the liver, instead of invasive organisms.
- Autoimmune hepatitis is an example where the body’s immune reaction malfunctions and attacks the liver, causing cell damage instead of battling an infection.
- Cardiac cirrhosis:
- The heart’s inability to pump blood adequately can cause blood to accumulate in the liver.
- This prolonged passive congestion produces liver cell destruction, edema, and pain.
- Infection of the heart muscle or the sac around the heart, heart valve failure, and smoking contribute to cardiac cirrhosis.
- Biliary cirrhosis: Various illnesses can affect the bile ducts, leading to a buildup of bile and inhibiting liver function.
- Poorly formed bile ducts (biliary atresia)
- Destruction of the bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis)
- Hardening and scarring of the bile ducts (primary sclerosing cholangitis)
- Injury: Cirrhosis of the liver is a dangerous disorder where scar tissue replaces healthy tissue due to long-term injury to the liver.
- Scarring develops as a result of ongoing injury from drinking too much alcohol, being infected with the hepatitis C virus, or having fatty liver disease.
- Scar tissue replaces healthy cells, causing the liver’s function to decline over time.
Your liver may eventually cease to function, which can be deadly.
Alcohol is a primary contributor to avoidable cirrhosis, with 5 to 15 percent of heavy drinkers acquiring it. Women who drink heavily appear to be more susceptible to cirrhosis than men.
QUESTION
What are the treatment options for cirrhosis?
The initial step to treat cirrhosis is to avoid and treat the cause of liver damage. The overall goal of treatments is to halt the disease’s progression and prevent liver failure.
- Weight loss is extremely important.
- If autoimmune hepatitis is the cause of liver damage, treating hepatitis is the choice.
- For alcohol-related liver damage, treatment begins with abstaining from alcohol.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver treatment targets metabolic risk factors like obesity, medication history, or diabetes.
- Hemochromatosis treatment aims to reduce iron levels in the blood.
In addition to treating the underlying cause, medication may be used to treat complications that can arise from cirrhosis.
- Lactulose may be recommended for patients with hepatic encephalopathy to reduce brain edema caused by liver failure.
- Diuretics or water pills may be prescribed to treat ascites or fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
- Antibiotics are sometimes used to prevent or cure infections.
- Blood pressure medications can lower pressure in the portal vein, reducing the risk of internal bleeding and spleen damage.
- Itching caused by cirrhosis may be relieved with prescribed drugs.
Liver transplantation
- When treatment no longer effectively controls the problems of cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be considered.
- A liver transplant is a major surgical procedure where a diseased liver is replaced with a whole, healthy liver from a deceased or living donor.
As mentioned, treatment for liver cirrhosis depends on the cause of the liver damage. Changing your lifestyle and diet can be one of the most effective ways to treat many liver problems.
- Nutrition, along with exercise, is significant for liver health.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol as they are extremely detrimental to your liver.
- If the liver injury has resulted in scarring, it is a lifelong condition that cannot be corrected.


