Contents
- 1 Salmonella Food Poisoning
- 1.0.1 What are symptoms and signs of Salmonella poisoning?
- 1.0.2 What causes (eggs, chicken) Salmonella outbreaks? How does Salmonella spread?
- 1.0.3 What are risk factors for Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.4 Is Salmonella contagious?
- 1.0.5 What is the incubation period for a Salmonella infection?
- 1.0.6 What is the contagious period for salmonellosis?
- 1.0.7 Which types of doctors treat Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.8 What tests diagnose Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.9 What is the treatment for Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.10 What is the prognosis of Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.11 What are the complications of Salmonella food poisoning?
- 1.0.12 7 Tips to prevent Salmonella food poisoning
Salmonella Food Poisoning
Salmonella infection, or salmonellosis, is another name for Salmonella food poisoning. Salmonella is a bacteria known to cause food-borne illness for over 125 years. The organism is named after scientist Daniel Elmer Salmon, who discovered it. Salmonellosis is a food-borne infection caused by consuming contaminated foods. Salmonella causes an estimated 1 million food-borne illnesses and about 19,000 hospitalizations annually in the U.S.
Different types of Salmonella bacteria can cause the illness. The two most common types in the U.S. are S. typhimurium and S. enteritidis. Some strains have become resistant to many drugs traditionally used for treatment, posing a risk to public health.
Some types of Salmonella bacteria (S. typhi) cause typhoid fever, a serious illness occurring in nonindustrialized areas of the world.
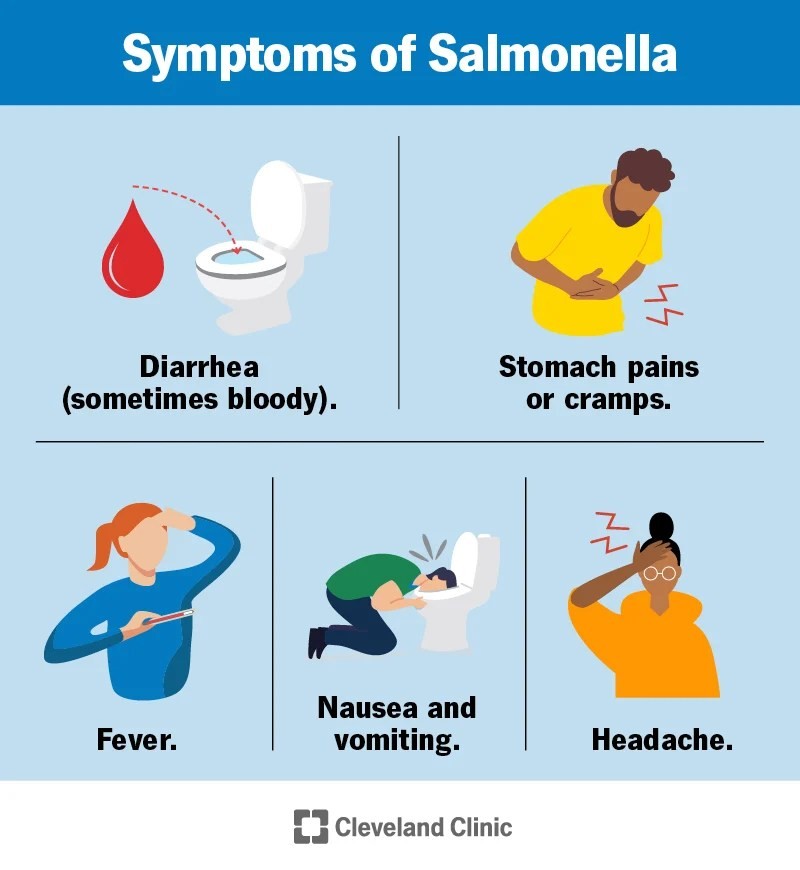
What are symptoms and signs of Salmonella poisoning?
Salmonella illness causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, known as gastroenteritis.
- Symptoms usually begin 12-72 hours after infection.
- Common symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever.
- Diarrhea is typically loose and not bloody.
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Muscle aches
The symptoms usually go away on their own after four to seven days.
What causes (eggs, chicken) Salmonella outbreaks? How does Salmonella spread?
Poultry, beef, milk, and eggs may contain Salmonella bacteria as they live in the intestines of humans and animals. Thorough cooking destroys the bacteria.
Foods, including vegetables and fruits, may also be contaminated during handling or processing, and this is another common source of outbreaks. For example, food may be contaminated by the feces of infected people or animals or from the unwashed hands of a person handling or preparing the food.
Small rodents such as hamsters, as well as baby chicks and ducklings, may also carry the bacteria, and contamination of food after handling these animals may also result in salmonellosis. Reptiles may also harbor Salmonella bacteria. In the 1970s, outbreaks were associated with baby turtles kept as pets. Further, the infection may be spread by contaminated surfaces (such as cutting boards) that have had contact with contaminated foods.
Contaminated foods usually look and smell normal. Over the past years, outbreaks of salmonellosis have been associated with a number of different foods, including chicken, cucumbers, alfalfa sprouts, bean sprouts, ground beef, mangoes, peanut butter, and cantaloupe. These are just a few examples. An outbreak in February 2016 caused by the strain Salmonella muenchen was linked to contaminated alfalfa sprouts. In 2017, an outbreak was linked to papayas from Mexico. A breakfast cereal known as Honey Smacks caused an outbreak in 2018.
What are risk factors for Salmonella food poisoning?
Foods contaminated with Salmonella are not obvious, so anyone may consume them. Owning pets such as rodents, chicks, ducklings, turtles, reptiles, or birds may increase the risk of coming in contact with Salmonella bacteria.
- People who are exposed to many people, such as those living in group housing, may have an increased risk.
- Young children (under 5 years of age) have the highest reported incidence of infection.
- People with medical conditions that lead to immune suppression are at risk for a more severe illness when infected.
Is Salmonella contagious?
- Many of the bacteria in the Salmonella genus are contagious.
- Salmonella food poisoning is usually acquired from eating contaminated foods. It is possible to spread the infection from person to person through fecal-oral cross-contamination, meaning that fecal material contaminates the hands of an infected person who then contaminates foods consumed by others.
What is the incubation period for a Salmonella infection?
Symptoms usually begin 12-72 hours after infection with salmonella.
What is the contagious period for salmonellosis?
Those with Salmonella infection can be contagious for days to weeks, even after symptoms have disappeared.
Which types of doctors treat Salmonella food poisoning?
Salmonellosis may be treated by
- primary care doctors,
- pediatricians,
- emergency medicine doctors, or
- internal medicine doctors.
In severe or complicated cases, other doctors may be consulted, including gastroenterologists or critical care specialists.
What tests diagnose Salmonella food poisoning?
The diagnosis of Salmonella infection requires identifying the organism in a stool sample from the affected person. Specific tests can identify the exact type of Salmonella responsible for an infection.
What is the treatment for Salmonella food poisoning?
In most cases, the symptoms resolve on their own within four to seven days.
- Taking plenty of fluids is essential to replace fluid lost by diarrhea and prevent dehydration.
- People with severe illness or who are unable to take oral liquids may need intravenous fluids.
- Antibiotics have been shown to prolong the presence of the bacteria in the stool and are not recommended for most cases.
- People with severe illness, those with risk factors for complications, or those with weakened immune function may require treatment with antibiotics.
What is the prognosis of Salmonella food poisoning?
Most cases of salmonellosis resolve completely without long-term complications, but bowel habits may be abnormal for months. About 380 people die from salmonellosis each year in the U.S.
What are the complications of Salmonella food poisoning?
Complications of Salmonella food poisoning can include dehydration from vomiting and diarrhea. The spread of the infection to the bloodstream is a further possible complication, most likely in people with suppressed immune function. The elderly and very young are also at increased risk for complications.
An uncommon complication called reactive arthritis involves joint pains, eye irritation, and pain during urination. Reactive arthritis may persist for months to years and can lead to chronic arthritis.
7 Tips to prevent Salmonella food poisoning
No vaccine is available to prevent Salmonella infection. However, the following steps can help ensure good hygiene and food safety, reducing the likelihood of infection:
- Wash hands thoroughly after using the bathroom.
- Cook meats and eggs thoroughly.
- Avoid consuming raw eggs or unpasteurized milk.
- Wash hands and kitchen surfaces with soap and water after contact with raw meat or eggs.
- Avoid exposing uncooked meats to other foods in the kitchen, including utensils and work surfaces.
- Wash hands thoroughly after contact with animal feces and after contact with reptiles, birds, and small rodents.
- Chill foods after serving and when transporting from place to place.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Salmonella." July 3, 2019. .
United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Salmonella." July 3, 2019. .


