Contents
- 1 Seborrheic Dermatitis
- 1.0.1 Seborrheic dermatitis vs. psoriasis
- 1.0.2 Seborrheic dermatitis vs. dandruff
- 1.0.3 Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.4 Risk factors for seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.5 Symptoms and signs of seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.6 Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.7 Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.8 Home remedies for seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.9 Prognosis and complications of seborrheic dermatitis
- 1.0.10 Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that is highly treatable but incurable.
Seborrheic dermatitis (seborrhea) is a chronic inflammation of the skin that waxes and wanes. It produces a red scaling, occasionally weepy, eruption.
Seborrheic dermatitis commonly involves the scalp, brows, mid-face, ears, mid-chest, and mid-back. It can affect infants and young children, often involving the scalp (cradle cap) and diaper area.
Seborrheic dermatitis vs. psoriasis
Both conditions can cause itchy scaling dermatitis on the scalp, making it difficult to distinguish between them. However, psoriasis typically affects different areas of skin than seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis produces an eczematous dermatitis with a weepy, oozing appearance.
Psoriasis causes scaling red skin with papules and plaques. A skin biopsy is rarely necessary to distinguish between the two.
Seborrheic dermatitis vs. dandruff
Dandruff flakes are scales from the scalp that can be seen in several inflammatory skin diseases, including seborrhea and psoriasis.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis are poorly understood, but genetic influences have been recognized. Gene mutations or protein deficiencies are more common in individuals with seborrheic dermatitis, with many genes playing a role in the immune response or epidermal differentiation.
Oily skin and an overgrowth of normal skin yeast (Pityrosporum or Malassezia) in affected areas may also contribute to seborrheic dermatitis. The role of fungi in causing this disease is still being determined.
Seborrheic dermatitis may be more prevalent in patients with severe central nervous system diseases (dementia and traumatic brain injuries). The involvement of the nervous system in causing seborrhea is unclear.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
Seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious.
Risk factors for seborrheic dermatitis
Although seborrheic dermatitis generally affects healthy individuals, there seems to be an association with central nervous system diseases and AIDS (HIV).
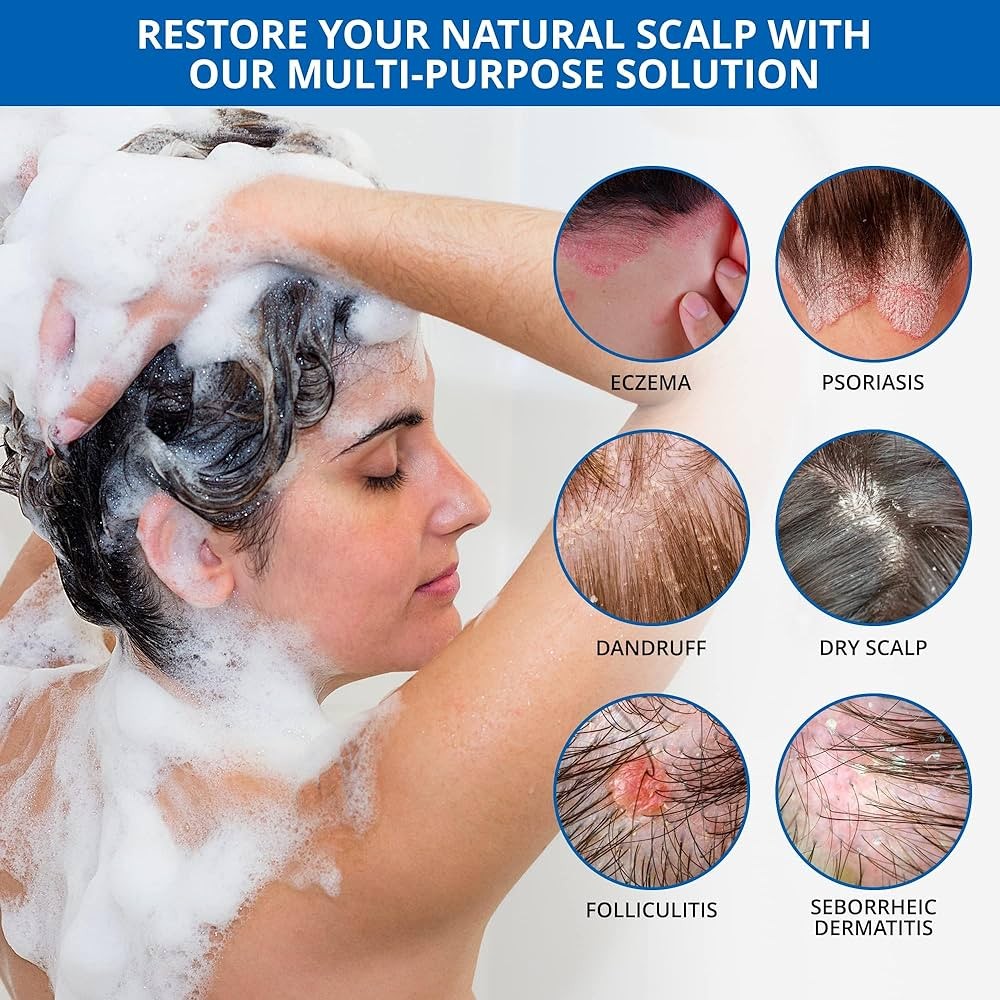
Symptoms and signs of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by spontaneous remissions and flare-ups. The rash is red and scaling, occasionally weepy and oozy. It can cause significant dandruff.
The distribution of the rash helps with diagnosis. Commonly involved areas include the scalp, ears, forehead, eyebrows, eyelids, cheeks, armpits, mid-chest, and mid-back. In infants, it causes "cradle cap" on the scalp and can extend to the diaper area.
The rash may be asymptomatic, but itching is common, especially on the scalp.
IMAGES
Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
Most primary care physicians can diagnose and treat seborrheic dermatitis. In some cases, a referral to a dermatologist may be necessary.
The diagnosis is usually made based on the appearance of the rash. Sometimes, a skin scraping treated with potassium hydroxide is examined under a microscope to rule out fungal infection. A skin biopsy is rarely needed.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
Treatment of the scalp and hair-bearing areas often involves using over-the-counter shampoos containing tar, ketoconazole, ciclopirox, zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, salicylic acid, or sodium sulfacetamide and sulfur solution. Prescription-strength topical steroid lotions or solutions may also be used.
Non-hair-bearing areas can be treated with weak to moderately potent topical steroids or topical antifungal creams. Topical calcineurin inhibitors can also be effective but are expensive.
It should be noted that seborrheic dermatitis is incurable but easily controlled. Treatment may need to be continued to prevent recurrence, but excessive treatment of normal skin is unnecessary and potentially risky.
Home remedies for seborrheic dermatitis
There is little evidence supporting the effectiveness of home remedies such as coconut oil, apple cider vinegar, tea tree oil, aloe vera, fish oil supplements, or biotin. However, 1% hydrocortisone, available without a prescription, can be effective. Applying olive oil or fluocinolone topical oil to the scalp can help soften and loosen flaky patches.
Prognosis and complications of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is generally not associated with serious problems, but it is an incurable condition. Treatment can result in an excellent response, but the disease is likely to recur if treatment is stopped. Complications may arise from misdiagnosis or mistreatment, such as fungal infections, skin thinning from the overuse of potent topical steroids, or temporary hair loss.
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis cannot be prevented.
References:
Borda, Luis J., M. Perper, and J.E. Keri. "Treatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Dermatological Treatment. 2018 DOI: 10.1080/09546634.2018.1473554.
Clark, Gary W., Sara M. Pope, and Khalid A. Jaboori. "Diagnosis and Treatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis." Am Fam Physician 91.3 (2015): 185-190.
Ijaz, N., and D. Fitzgerald. "Seborrheic Dermatitis." British Journal of Hospital Medicine 78.6 June 2017: C88-C91.
Okokon, E.O., J.H. Verbeek, J.H. Ruotsalainen, O.A. Ojo, and V.N. Bakhoya. "Topical Antifungals for Seborrheic Dermatitis (Review)." Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 5 May 2, 2015.
Stefanaki, I., and A. Katsambas. "Therapeutic Update on Seborrheic Dermatitis." Skin Therapy Lett. 15.5 May 2010: 1-4.