Contents
- 1 Placenta Previa: Symptoms, Types, Causes, Risks, & Treatment
- 1.0.1 What are the signs and symptoms of placenta previa?
- 1.0.2 What are the types of placenta previa?
- 1.0.3 What causes placenta previa?
- 1.0.4 What uterine factors contribute to the development of placenta previa?
- 1.0.5 What placental factors contribute to the development of placenta previa?
- 1.0.6 How many pregnant women have placenta previa? Who is at risk?
- 1.0.7 How is placenta previa diagnosed?
- 1.0.8 What is the treatment and management for placenta previa?
- 1.0.9 What are complications of placenta previa? Is it harmful to the fetus and baby?
- 1.0.10 What is the prognosis for a woman with placenta previa during pregnancy?
- 1.0.11 How can you prevent placenta previa during pregnancy?
Placenta Previa: Symptoms, Types, Causes, Risks, & Treatment
Placenta previa is the most common cause of painless bleeding in later stages of pregnancy (after the 20th week).
The placenta connects mother and fetus, transferring oxygen and nutrients. It is disk-shaped and measures about 7 inches in diameter at full term. The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus (womb).
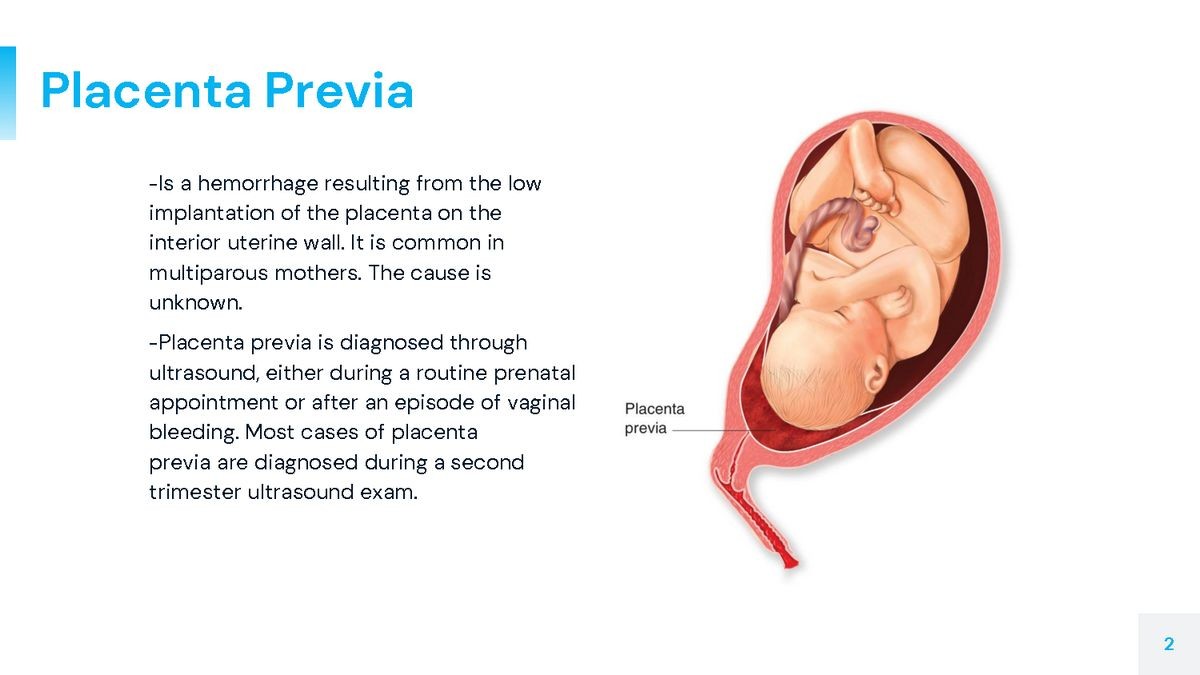
Placenta previa is a complication resulting from the placenta implanting near or overlying the uterus outlet (the cervix). Bleeding can occur when the cervix dilates or stretches due to the placenta’s rich blood vessels.
What are the signs and symptoms of placenta previa?
Bleeding is the primary symptom and occurs in the majority (70%-80%) of women with this condition.
- Vaginal bleeding after the 20th week of gestation characterizes placenta previa.
- Bleeding is usually painless but may be associated with uterine contractions and abdominal pain.
- Bleeding severity may vary from light to severe.
What are the types of placenta previa?
The types of placenta previa include:
- Complete placenta previa: placenta completely covers the cervix opening.
- Partial placenta previa: placenta partially covers the cervical opening.
- Marginal placenta previa: placenta is adjacent to but not covering the cervical opening.
The term low-lying placenta or low placenta is used to refer to both placenta previa and marginal placenta previa. Anterior placenta previa and posterior placenta previa are used to define the exact position of the placenta within the uterus using ultrasound examinations.
IMAGES
What causes placenta previa?
The placenta may be located in the lower part of the uterus due to various factors. The placenta typically migrates away from the cervical opening as the pregnancy progresses, reducing the occurrence of placenta previa. However, abnormalities of the uterus or increased placenta size can lead to persistent placenta previa.
What uterine factors contribute to the development of placenta previa?
Uterine factors that contribute to placenta previa include scarring of the upper lining tissues of the uterus due to prior Cesarean deliveries, prior instrumentation, or prior surgeries involving the uterus.
What placental factors contribute to the development of placenta previa?
Placenta previa risk increases when the placenta must grow larger to compensate for decreased function. Factors such as multiple gestation, maternal cigarette smoking, and living at high altitudes can increase the need for greater placenta function.
How many pregnant women have placenta previa? Who is at risk?
Approximately 4 out of every 1000 pregnancies beyond the 20th week of gestation have placenta previa. Risk factors include ethnicity (Asian women), carrying male fetuses, advanced maternal age, and a history of placenta previa in a previous pregnancy.
How is placenta previa diagnosed?
An ultrasound examination is used to diagnose placenta previa. Transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasound evaluations may be performed.
It is important to perform the ultrasound examination before a physical examination of the pelvis to prevent further bleeding.
What is the treatment and management for placenta previa?
Treatment depends on the extent and severity of bleeding, gestational age and condition of the fetus, position of the placenta and fetus, and whether the bleeding has stopped. Cesarean delivery is usually required for complete placenta previa and may be necessary for other types. Women with placenta previa may require blood transfusions, tocolytic drugs, or corticosteroids.
What are complications of placenta previa? Is it harmful to the fetus and baby?
- Placenta previa can be associated with other abnormalities of the placenta or umbilical cord. It may result in reduced fetal growth and increase the risk of breech or abnormal presentation of the fetus.
- Bleeding caused by placenta previa can increase the risk of preterm premature rupture of the membranes (PPROM) and premature labor.
- Placenta accreta is a serious complication occurring in 5% to 10% of women with placenta previa. It requires a hysterectomy at the time of Cesarean delivery.
- Placenta previa can have a significant emotional impact on pregnant women, similar to other complications of pregnancy.
What is the prognosis for a woman with placenta previa during pregnancy?
The majority of women with placenta previa in developed countries will deliver healthy babies, and the maternal mortality rate is less than 1%. Risks may be higher in developing countries.
How can you prevent placenta previa during pregnancy?
Placenta previa is typically not preventable. However, risk factors such as smoking can be eliminated to reduce the chances of developing placenta previa.