Contents
- 1 Moyamoya Disease
- 1.0.1 Is Moyamoya disease inherited?
- 1.0.2 What causes Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.3 What are the signs and symptoms of Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.4 Diagnosis of Moyamoya disease
- 1.0.5 What are the stages of Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.6 What is the treatment for Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.7 Is there a cure for Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.8 What types of surgery treat Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.9 How successful is surgery for Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.10 What are the complications of surgery for Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.11 What is the prognosis for Moyamoya disease?
- 1.0.12 Is Moyamoya disease fatal?
- 1.0.13 What types of surgery treat Moyamoya disease?
Moyamoya Disease
Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a rare cerebrovascular disease that causes stenosis or blockage of primary blood vessels in the brain.
Moyamoya disease was first noted in Japan in 1957 and is primarily seen in Asia. The disease is less common in Europe and North America. "Moyamoya" is a Japanese term that describes the hazy and tangled appearance of the small blood vessels that form to compensate for the blockage.
Is Moyamoya disease inherited?
The cause of Moyamoya disease is unknown. There may be a genetic factor, as up to 15 percent of Japanese people with Moyamoya have family members with the condition.
What causes Moyamoya disease?
The cause of Moyamoya disease is unknown. Possible factors include injuries, neurofibromatosis, X-rays of the skull, heart surgery, chemotherapy, infections, atherosclerosis, heart disease, vasculitis, blood disorders, autoimmune conditions, connective tissue disorders, chromosome disorders, metabolic diseases, head trauma, radiation therapy of the brain, brain tumors, Down syndrome, or Williams syndrome.
QUESTION
What are the signs and symptoms of Moyamoya disease?
Moyamoya disease can occur in children and adults. The most common symptoms in adults include bleeding in the brain, lightheadedness, visual disturbances, seizures, headaches, weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, and cognitive decline. In children, the symptoms may include headaches, developmental delays, speech problems, difficulty understanding others, involuntary movements, periods of inability to move limbs, and anemia.
Diagnosis of Moyamoya disease
Diagnosis may involve imaging tests such as CT or MRI scans, cerebral angiogram, SPECT, EEG, or transcranial Doppler ultrasound.
What are the stages of Moyamoya disease?
Moyamoya disease has six stages, each indicating different angiographic findings.
What is the treatment for Moyamoya disease?
Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve blood flow in the brain. Surgery is the preferred option, but medications can be used if surgery is not possible. Medications may include blood thinners, antiplatelet agents, calcium channel blockers, and seizure medications.
Is there a cure for Moyamoya disease?
Moyamoya itself is not curable, but revascularization surgery can prevent symptoms and reduce the risk of strokes by providing alternative blood supply to the brain.
What types of surgery treat Moyamoya disease?
Revascularization procedures, such as EDAS, pial synangiosis, EMS, EC-IC bypass, direct arterial bypass, omental transposition/transfer, and dural inversion, can be used to treat Moyamoya disease. Angioplasty and stenting may also be options.
How successful is surgery for Moyamoya disease?
Full recovery from surgery may take six to 12 months, but improvements in symptoms are noticeable immediately. Surgery is effective in preventing strokes, especially when performed before a stroke occurs.
What are the complications of surgery for Moyamoya disease?
Complications may include perioperative stroke, cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome, subdural hematoma, and wound healing disorders.
What is the prognosis for Moyamoya disease?
Early diagnosis and treatment lead to better outcomes. Patients who are diagnosed and treated promptly with surgery can have a normal life expectancy. Without treatment, cognitive and neurological decline is likely.
Is Moyamoya disease fatal?
Without surgery, Moyamoya disease can be fatal due to intracerebral hemorrhage. Prompt treatment can help prevent permanent damage.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
What types of surgery treat Moyamoya disease?
Revascularization is a type of surgical procedure used to treat Moyamoya disease. This procedure repairs the narrowed arteries, improves blood flow, and reduces the risk of stroke. Without surgery, Moyamoya is a progressive condition and patients will experience multiple strokes and a mental decline.
There are several types of revascularization procedures:
- EDAS (encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis): A scalp artery is rerouted onto the surface of the brain. Over time, new blood vessels form and ideally will provide a new blood supply to the ischemic area of the brain.
- A modification of EDAS is pial synangiosis: Reroutes healthy scalp blood vessels to the brain, bypassing the narrowed vessels.
- EMS (encephalomyosynangiosis): A muscle in the temple of the forehead is partially detached. A hole is drilled in the skull and the muscle is placed onto the surface of the brain, where it will eventually produce new blood vessels.
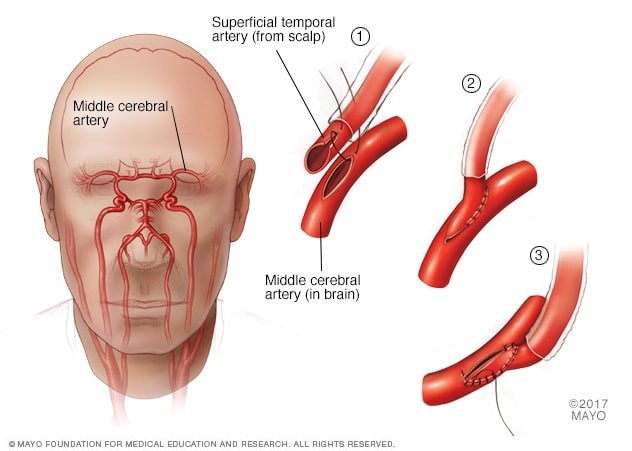
- External carotid to internal carotid (EC-IC) bypass: One of the arteries in the scalp (superficial temporal artery) is attached to one of the major arteries in the brain (middle cerebral artery).
- Direct arterial bypass, also called STA-MCA (superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery) bypass: A blood vessel from the scalp is joined directly to a brain surface artery to transport blood directly to where it is needed.
- Omental transposition/transfer: The omentum, a blood-rich lining surrounding the abdominal organs, is placed over the surface of the brain so new blood vessels can generate and grow into the brain.
- Dural inversion: The flaps of fibrous dural tissue on the meningeal vessel, a large artery within the skull, are inverted. The outer dural surface with a large number of blood vessels comes into direct contact with the parts of the brain that need blood flow.
In some cases, minimally invasive procedures such as angioplasty and stenting may be used to widen a narrowed artery.