Contents
- 1 Labyrinthitis (Inner Ear Inflammation)
- 1.0.1 Causes of labyrinthitis
- 1.0.2 Symptoms of labyrinthitis
- 1.0.3 Duration of labyrinthitis
- 1.0.4 Diagnosing labyrinthitis
- 1.0.5 Treatment for labyrinthitis
- 1.0.6 Medications for labyrinthitis
- 1.0.7 Home remedies for labyrinthitis
- 1.0.8 Prognosis and complications of labyrinthitis
- 1.0.9 Preventing labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis (Inner Ear Inflammation)
Labyrinthitis is a type of inner ear condition that causes dizziness, vertigo, and balance problems. The inflammation of the nerves in the inner ear can be caused by an ear infection and has similar symptoms.
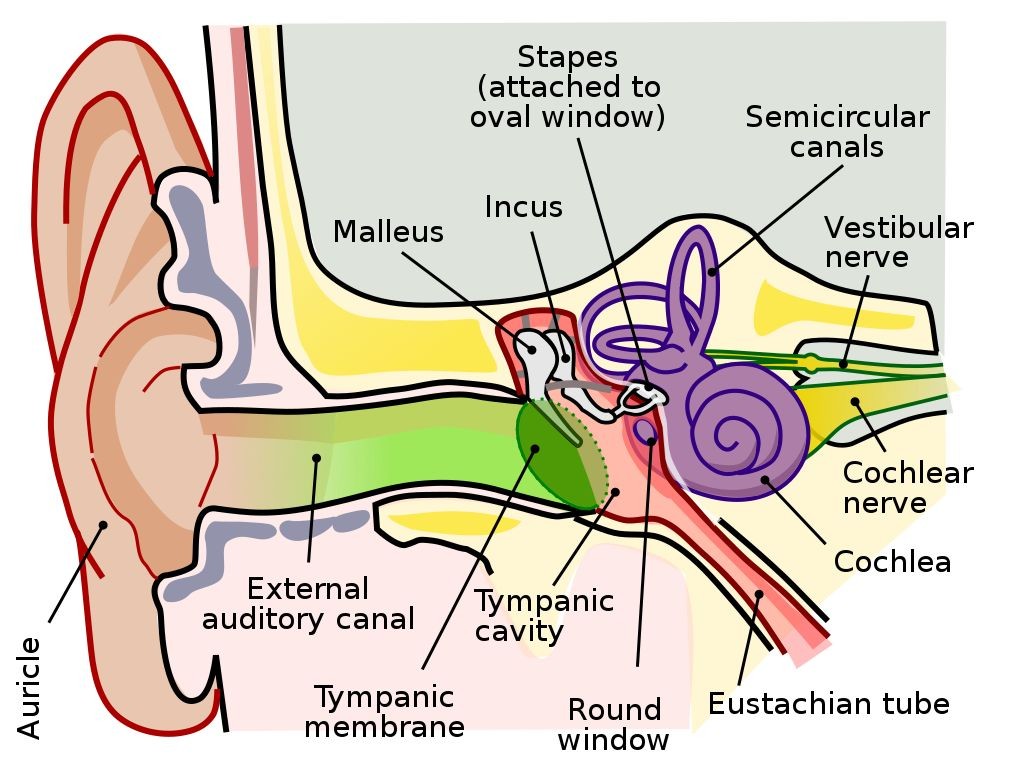
The ear is divided into three parts:
The outer ear, which consists of the auricle (pinna), earlobe, and ear canal up to the eardrum. The middle ear, which consists of the eardrum and the auditory bones (incus, malleus, and stapes). The inner ear, which consists of the semicircular canals, cochlea, vestibular nerve, and auditory nerve.
Causes of labyrinthitis
The exact cause of labyrinthitis is unknown. It may be caused by problems with the nerve responsible for balance and hearing. Labyrinthitis can also occur during or after a viral infection.
Other ear problems like barotrauma or otosclerosis can rarely cause labyrinthitis.
Labyrinthitis itself is not contagious. However, the viral infections that can lead to labyrinthitis are contagious.
QUESTION
Symptoms of labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis causes dizziness, vertigo, and balance problems.
Signs and symptoms may include:
- Dizziness
- Vertigo
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Balance problems
- Difficulty walking
- Hearing loss in one ear
- Earache
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Ringing in the ear or abnormal sounds
- Discharge from the ear
These symptoms are similar to vestibular neuritis, but vestibular neuritis does not include hearing loss.
Duration of labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis symptoms usually last a few weeks. If symptoms persist after 3 weeks or are severe, immediate medical care is necessary.
Diagnosing labyrinthitis
The only way to know if you have labyrinthitis is to see a doctor. A doctor will rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
An otoscope exam and a tuning fork exam may be performed to check for abnormalities in the ear.
Treatment for labyrinthitis
Treatment depends on the cause, symptoms, and duration of labyrinthitis. Medications may be prescribed to treat infection, reduce swelling, and relieve symptoms.
Physical therapy can help with balance problems.
Medications for labyrinthitis
Medications such as diphenhydramine or meclizine may be recommended to relieve symptoms. Steroids, antibiotics, and antivirals may help with inflammation and associated infections.
Intravenous fluids may be administered if dehydration occurs due to severe vomiting.
Home remedies for labyrinthitis
Home remedies can help relieve symptoms but cannot cure labyrinthitis.
Some remedies include using a warm compress, standing or sitting upright, gargling saltwater, avoiding smoking and alcohol, managing stress, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
Consult a doctor before using any home remedies.
Prognosis and complications of labyrinthitis
When treated promptly, labyrinthitis resolves in days to 2 weeks with no permanent damage.
Complications include an increased risk of hearing loss, BPPV, and the development of Ménière’s disease.
Preventing labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis cannot be spread from person to person. To prevent ear infections, practice good hygiene, avoid sharing food and drinks, and avoid smoking and secondhand smoke. Children should be vaccinated against pneumococcal bacteria.
References:
Hain, TC, MD. "Vestibular Neuritis and Labyrinthitis." American Hearing Research Foundation. Reviewed: Oct 2012.