Contents
Is GERD Curable?
GERD occurs when stomach acid, fluids, or food flow back up into the esophagus. While there is no cure for GERD, it is a treatable ongoing digestive disorder.
Although there is no cure for GERD, some individuals can manage symptoms through diet and lifestyle changes, while others require additional treatment.
Although GERD is a common disorder, its symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions. So what exactly are the symptoms of GERD in adults? Let’s find out.
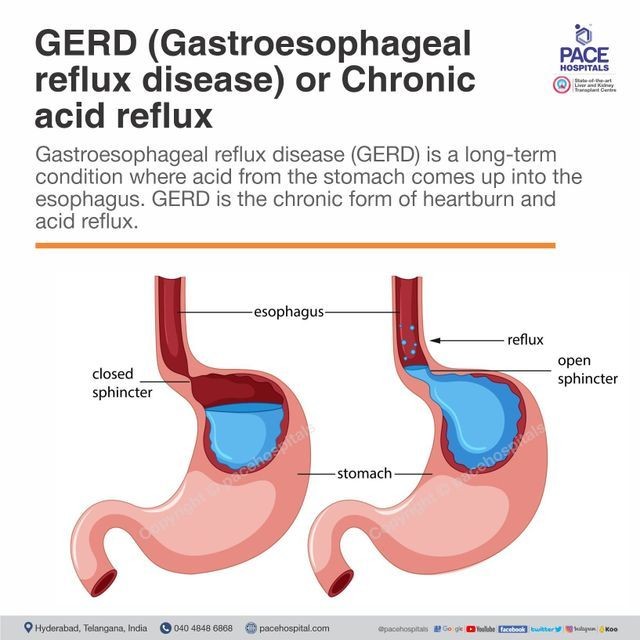
GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease, is characterized by stomach acid, fluids, or food flowing back into the esophagus, resulting in inflammation and symptoms such as heartburn. If left untreated, GERD can cause damage to the esophagus, including sores, scarring, and other problems.
Some individuals have a form of GERD known as non-erosive esophageal reflux disease (NERD). Despite acid reflux, these individuals have a normal esophagus lining. Although NERD can cause symptoms, there is debate among experts about whether it is an early stage of GERD or a distinct variation of the condition.
GERD vs. acid reflux
While GERD is sometimes referred to as acid reflux, it is a more severe form of the condition that significantly impacts daily life.
Stages of GERD
GERD can be categorized into different stages based on the severity and frequency of symptoms:
- Stage 1: mild GERD with symptoms less than once a week
- Stage 2: moderate GERD with symptoms a few times a week
- Stage 3: severe GERD with daily symptoms
- Stage 4: GERD with complications
If left untreated or if it worsens over time, GERD can lead to complications and more severe diseases such as erosive esophagitis (ulcers or open sores in the esophagus lining), esophageal strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), Barrett’s esophagus (pre-cancerous changes to the esophageal lining), and esophageal cancer.
What are the symptoms of GERD in adults?
The most common symptom of GERD is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest that occurs after meals or when lying down. Other symptoms of GERD in adults include regurgitation, sour or bitter taste in the mouth, chest pain, trouble swallowing, nausea, hoarseness, throat clearing, coughing or wheezing, sore throat, cavities or tooth enamel breakdown, bad breath, and feeling a lump in the throat.
In some cases, acid can remain in the throat and be inhaled into the lungs, leading to lung-related symptoms. GERD can also result in food impaction, causing food to get stuck in the esophagus.
What causes GERD?
The underlying cause of GERD is a weak or irregular lower esophageal sphincter. This muscle at the bottom of the esophagus acts as a valve to the stomach. For individuals with GERD, the muscle relaxes too often or for too long, allowing fluid to flow back in the wrong direction.
Factors that can weaken the esophageal muscle and contribute to GERD include obesity or being overweight, pregnancy (due to higher progesterone levels), caffeine and alcohol intake, and smoking. Additionally, a hiatal hernia, in which the stomach pushes through a small opening in the diaphragm, can interfere with the esophageal muscle.
What are the treatment options for GERD?
Treating GERD usually involves making lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments. If these are not sufficient, medication and surgical procedures may be necessary.
Lifestyle changes
Managing GERD begins with lifestyle modifications. Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, eating smaller meals, avoiding eating close to bedtime, staying upright after meals, losing weight, cutting back on caffeine, and elevating the head of the bed are all recommended strategies.
Exercising can aid in weight loss, but it is advisable to wait a few hours after eating before engaging in physical activity to prevent aggravating symptoms.
Diet changes
In individuals with GERD, certain foods can relax the esophageal muscle and exacerbate acid reflux. High-fat foods, acidic foods, and certain chemicals found in foods or drinks can affect esophageal muscle movements and slow down stomach emptying. Avoiding fast food, pizza, fried foods, tomatoes/tomato-based products, coffee, alcohol, peppermint, milk, citrus fruits, garlic, onion, chocolate, and carbonated drinks may alleviate symptoms.
Medications
If lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments are insufficient, medication may be prescribed. Antacids, over-the-counter or prescription H-2 receptor blockers, prescription proton pump inhibitors, and prescription baclofen are among the medications that can help reduce stomach acid production, neutralize acid, or strengthen the esophageal sphincter.
Surgery
In rare cases or when medications are not effective or desirable, surgery to tighten the esophageal muscle may be considered.
Outlook
GERD is a chronic disease without a cure, but it can be managed through lifestyle changes, medication, and dietary modifications. Ongoing treatment is typically necessary, but serious complications are rare.