Contents
- 1 Gonorrhea
- 1.0.1 How is gonorrhea transmitted?
- 1.0.2 What are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
- 1.0.3 How long does it take for gonorrhea symptoms to show up?
- 1.0.4 How is gonorrhea diagnosed?
- 1.0.5 What are the treatments for gonorrhea? Can it be cured?
- 1.0.6 What are the complications of gonorrhea? What happens if it is left untreated?
- 1.0.7 What is the prognosis for gonorrhea?
- 1.0.8 Is it possible to prevent gonorrhea?
- 1.0.9 From
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an STD caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. It is transmitted through unprotected sexual contact – oral, vaginal, or anal intercourse.
Chlamydia is often found concomitantly with gonorrhea.
- Women with gonorrhea have a 40% chance of having chlamydia.
- Men with gonorrhea have a 25% chance of having chlamydia.
- Young adults with gonorrhea have a 50% chance of having chlamydia.
How is gonorrhea transmitted?
Gonorrhea is transmitted through unprotected oral, vaginal, or anal sex.
- Gonorrhea bacteria cannot survive outside the body for long and cannot live on the skin, arms, hands, or legs. It cannot be transmitted from toilet seats, countertops, or sinks.
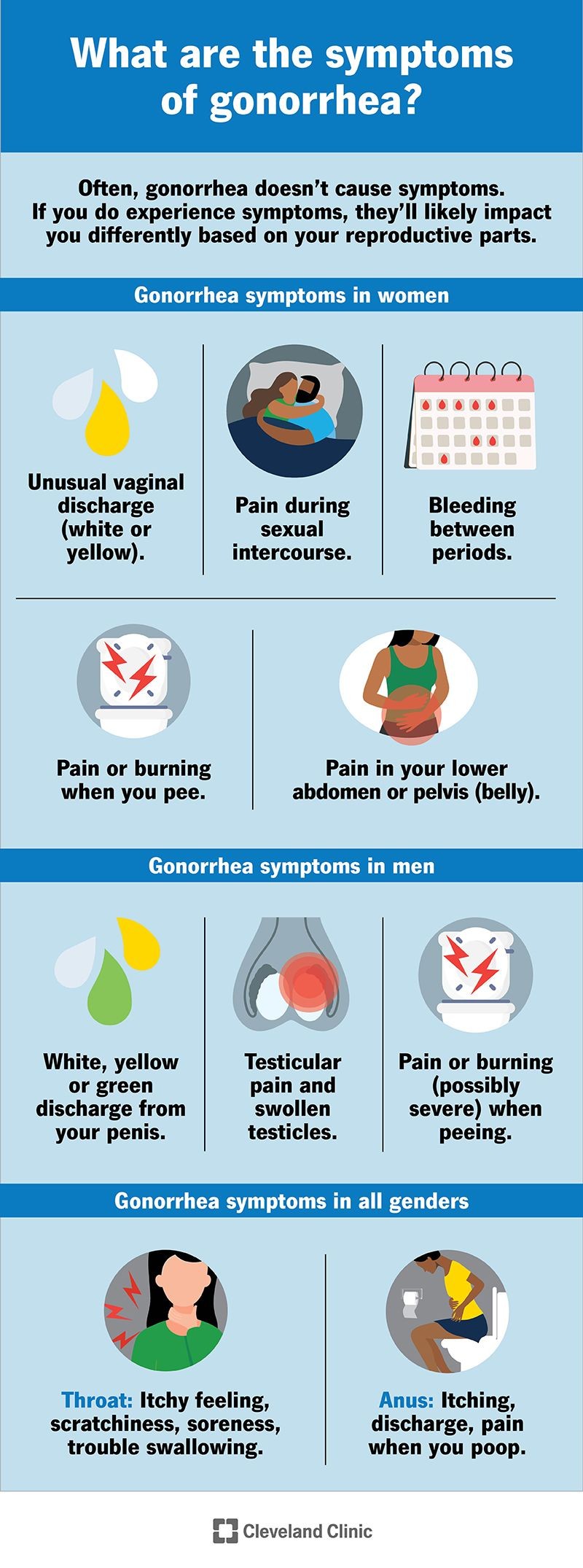
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
Symptoms of gonorrhea depend on the site of infection – throat, urethra, anus, or vagina.
Many infected individuals are asymptomatic and unaware of the infection.
Below are the symptoms that may occur based on the infection location.
Genital gonorrhea symptoms
- Urethritis (inflammation of the urethra)
- In males, there may be a pus discharge, burning with urination, increased urge to urinate, and swelling of the penis.
- In females, symptoms are often absent, but may include burning with urination and increased urge to urinate.
Gonorrhea of the throat
- Infections of the throat are usually asymptomatic.
- Symptoms may include sore throat, pus in the back of the throat, and swollen glands.
Gonorrhea of the anus
- In males, infection of the anus and rectum usually occurs through anal intercourse.
- In females, anal gonorrhea can occur without anal intercourse due to the proximity of the vagina and anus.
- Usually, anal gonorrhea has no symptoms.
- Proctitis may cause pain, rectal fullness, the urge to have a bowel movement, rectal bleeding, and rectal discharge.
How long does it take for gonorrhea symptoms to show up?
Symptoms can appear 2 to 14 days after exposure, usually within a week.
It is important to remember that many infected individuals are asymptomatic and unaware of the infection.
How is gonorrhea diagnosed?
Gonorrhea is diagnosed through laboratory testing.
Swabs from the throat, cervix, rectum, or urethra are tested for Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a type of nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT).
Swabs can be taken at a clinic or hospital, or collected at home and brought to the lab.
First-morning urine can also be tested for gonorrhea.
Treatment is often initiated before test results are available.
Testing for other STDs is also recommended, as co-infections are common. These include chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV.
Cultures, which involve growing the bacteria in the lab, were historically used to diagnose gonorrhea, but PCR/NAAT is now the preferred method.
What are the treatments for gonorrhea? Can it be cured?
Gonorrhea can be cured with antibiotics.
The recommended treatments are:
Uncomplicated gonorrhea
- A single injection of ceftriaxone.
- Alternative treatments for patients allergic to penicillin or ceftriaxone include a single dose of cefixime by mouth or a single dose of azithromycin by mouth with an injection of gentamicin. These alternatives have higher failure rates.
- Patients should also be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline by mouth for seven days.
- Sex partners should also be treated. Cefixime can be provided to the patient to give to their partners. Male patients with male partners should seek medical care for evaluation.
- Pregnant patients are treated with a single injection of ceftriaxone and should be retested in the third trimester before delivery to prevent transmission to the fetus.
Disseminated gonorrhea
Patients with an infected joint with pus may require joint drainage surgery followed by 1-2 weeks of intravenous antibiotics.
Patients with tenosynovitis, dermatitis, or polyarthralgia are treated with intravenous or intramuscular antibiotics for at least one week until symptoms resolve.
Does gonorrhea go away on its own?
No, antibiotics are necessary to eliminate the Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection. The body cannot heal itself.
What are the complications of gonorrhea? What happens if it is left untreated?
In women, untreated gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), tubo-ovarian abscesses, fallopian tube scarring, infertility, and the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, or perihepatitis, is a rare complication where the liver capsule becomes inflamed.
Gonorrhea can also cause complications during pregnancy and pose risks to the fetus and newborn.
Pregnancy complications
- Vaginal gonorrhea infection in pregnant women increases the risk of infecting the amniotic fluid, premature rupture of membranes, preterm labor, low birth weight, and spontaneous miscarriage.
- Untreated neonates are at risk of developing conjunctivitis, which can lead to corneal ulcers and blindness.
- Neonates are also susceptible to pharyngitis, joint infections, and bloodstream infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria.
Both men and women can develop disseminated gonorrhea.
Disseminated gonorrhea
- This refers to infections that extend beyond the primary sites (throat, vagina, urethra, or anus).
- Joint infections, tendon inflammation, skin inflammation, and eye infections can occur.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can lead to significant illness with fever, abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and pain during intercourse. PID can also be caused by other bacteria besides gonorrhea.
- Males may develop epididymitis and have an increased risk of prostate cancer.
What is the prognosis for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a curable infection, but seeking treatment is crucial. Routine STD screening is recommended.
Uncomplicated gonorrhea is effectively treated with a single intramuscular injection, and symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Patients with oral pharyngeal gonorrhea should be retested after 7 days due to potential treatment failures. No retesting is necessary for other gonorrhea infections.
Disseminated gonorrhea may require longer treatment, but the prognosis is excellent if patients complete the treatment course.
Is it possible to prevent gonorrhea?
Prevention involves using barrier methods, such as condoms, during oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for STDs can reduce the risk of contracting gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis. Taking doxycycline 200mg orally within 24-48 hours has been shown to be effective.
In monogamous relationships, the risk of gonorrhea infections is low. Ideally, both partners should undergo STD testing before engaging in sexual activity.
From
Healthy Resources
- HIV Medications
- HIV: How Complementary Therapies Help
- Your Guide to Understanding PrEP
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
References:
Forward KR. Risk of coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Nova Scotia. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. Summer;21(2):e84-6.
Barbee LA, Dombrowski JC, et al. Effect of nucleic acid amplification testing on detection of extragenital gonorrhea and chlamydial infections in men who have sex with men sexually transmitted disease clinic patients. Sex Transm Dis. 41(3):168-72.
Barbee LA, Dombrowski JC, et al. Effect of nucleic acid amplification testing on detection of extragenital gonorrhea and chlamydial infections in men who have sex with men sexually transmitted disease clinic patients. Sex Transm Dis. 41(3):168-72.