Contents
- 1 Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
- 1.0.1 What if I drank heavily before I knew I was pregnant?
- 1.0.2 What causes fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.3 What are risk factors for fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.4 What are symptoms and signs of fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.5 How do physicians diagnose fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.6 Do all alcoholics have babies with FAS?
- 1.0.7 What is the treatment for fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.8 What are the complications and long-term effects of fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.9 Does FASD get worse with age?
- 1.0.10 Is it possible to prevent fetal alcohol syndrome?
- 1.0.11 Is it safe to consume alcohol and breastfeed?
- 1.0.12 Where can people find more information about fetal alcohol syndrome?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
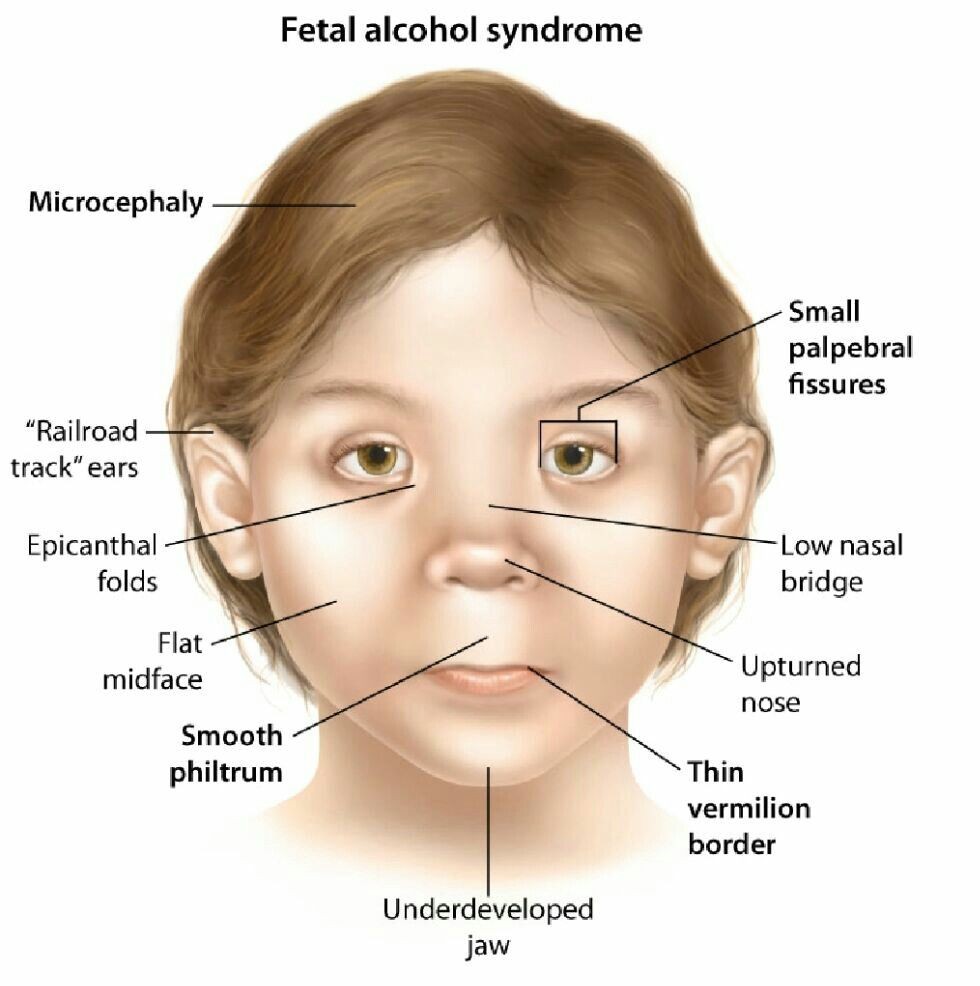
The Institute of Medicine defined fetal alcohol syndrome as "a pattern of physical, behavioral, and cognitive abnormalities in individuals exposed to alcohol during pregnancy. To diagnose fetal alcohol syndrome, specific criteria must be met. These include documenting three facial abnormalities, smaller than expected growth parameters, and central nervous system abnormalities. Other congenital malformations may also be present.
What if I drank heavily before I knew I was pregnant?
Most alcohol use during pregnancy occurs in the first trimester. Alcohol use decreases in the second and third trimesters. Many pregnant women stop drinking alcohol once they become aware of their pregnancy.
What causes fetal alcohol syndrome?
Alcohol rapidly passes from the mother to the fetus and can cause miscarriage and birth defects. There is no established relationship between the amount of alcohol consumed and the infant’s side effects. Alcohol consumed at any time during pregnancy can have severe and permanent consequences. First trimester alcohol ingestion is linked to facial abnormalities and reduced growth rate. Second and third trimester alcohol consumption is associated with lower IQ, growth retardation, and cognitive deficits.
What are risk factors for fetal alcohol syndrome?
The Surgeon General and the Secretary for Health and Human Services recommend abstaining from alcohol during pregnancy. Binge drinking is more problematic than consuming alcohol over time. Other risk factors include older maternal age and various background elements such as lower socioeconomic status, smoking, and substance abuse.
What are symptoms and signs of fetal alcohol syndrome?
Infants with fetal alcohol syndrome have unique facial characteristics, growth delay, central nervous system abnormalities, and congenital malformations.
How do physicians diagnose fetal alcohol syndrome?
Pregnant women are asked about their alcohol consumption and other behavioral risk factors. Several screening questionnaires and laboratory blood studies may be used to indicate alcohol use. Physical indicators and developmental delays may also lead to a diagnosis.
Do all alcoholics have babies with FAS?
In addition to fetal alcohol syndrome, there are three other conditions associated with fetal alcohol exposure. These include partial FAS, alcohol-related birth defects, and alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder.
What is the treatment for fetal alcohol syndrome?
While there is no cure for fetal alcohol syndrome, early intervention programs can help with language, motor, and cognitive impairments. Therapy programs can also address academic, legal, and psychiatric problems.
What are the complications and long-term effects of fetal alcohol syndrome?
Infants and children with FAS may face issues with regulation, learning, vision, hearing, and cognitive abilities. Adolescents and adults may experience difficulties with sexual behavior, legal problems, and substance abuse.
Does FASD get worse with age?
Individuals with FAS may face physical and intellectual challenges throughout their lives. Early intervention programs and multi-therapy programs can help mitigate the impact of the condition.
Is it possible to prevent fetal alcohol syndrome?
Avoiding alcohol consumption while planning for conception and during pregnancy can prevent fetal alcohol syndrome.
Is it safe to consume alcohol and breastfeed?
The concentration of alcohol in breast milk is similar to blood levels. Alcohol consumption while breastfeeding can have negative effects on newborns.
Where can people find more information about fetal alcohol syndrome?
For more information about fetal alcohol syndrome, visit reputable sources such as the Institute of Medicine or consult with healthcare professionals.
Sources:
- Institute of Medicine. Stratton, K., C. Howe, and F. Battaglia, eds. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Diagnosis, Epidemiology, Prevention, and Treatment Institute of Medicine. Washington, DC; National Academy Press, 1966.
- Lyons Jones, Kenneth, et al. Smith’s Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation, 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders Co, 1997.
- Thachray, H. and C. Fifft. "Fetal Alcohol Syndrome." Pediatrics in Review 22.2 February 2001.