Contents
- 1 Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
- 1.0.1 What is the anatomy of Eustachian tubes (pictures)?
- 1.0.2 What causes blocked Eustachian tubes?
- 1.0.3 What are the signs and symptoms of blocked Eustachian tubes?
- 1.0.4 What is the medical treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction?
- 1.0.5 What home remedies treat pain and help clear blocked Eustachian tubes?
- 1.0.6 Will surgery cure Eustachian tube dysfunction?
- 1.0.7 What changes can you make to avoid Eustachian tube dysfunction at altitudes?
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
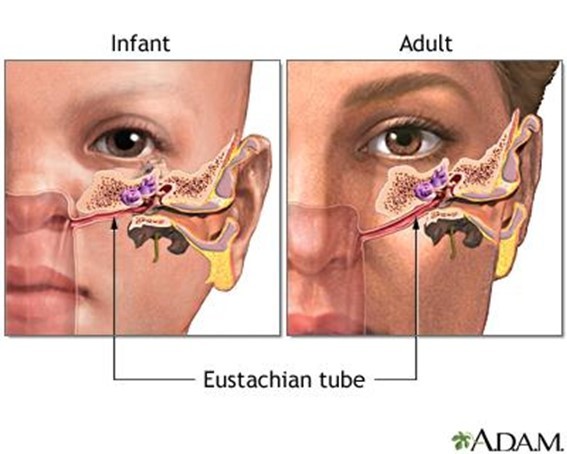
The Eustachian tube originates in the rear of the nose near the soft palate, runs uphill, and ends in the middle ear space. It connects the middle ear space to the rear of the nose. The middle ear space contains the hearing apparatus and is covered by the eardrum.
The first two-thirds of the Eustachian tube is made of cartilage, while the last third is made of bone.
How long are Eustachian tubes?
In adults, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm long and 3 mm in diameter.
Who discovered Eustachian tubes?
16th-century Italian anatomist Eustachius is credited with naming the Eustachian tube. Alcmaeon of Sparta is believed to have described the structure around 400 BC.
What is the anatomy of Eustachian tubes (pictures)?
Picture of the Structures of the Inner Ear and Eustachian Tubes.
The Eustachian tube has primary and secondary functions. Its primary function is to ventilate the middle ear space and maintain normal pressure. The secondary function is to drain secretions, infection, or debris from the middle ear space. Muscles in the throat and palate control the opening and closing of the Eustachian tube. Swallowing and yawning activate these muscles and regulate tube function. Without the Eustachian tube, the middle ear cavity would be isolated and vulnerable to changes in air pressure.
The nasal opening of the Eustachian tube is normally closed to prevent contamination from nasal secretions. A dysfunctional Eustachian tube that is always open is called a "patulous" Eustachian tube and can cause chronic ear infections. More commonly, Eustachian tube failure leads to ineffective air pressure regulation.
Partial or complete blockage of the Eustachian tube can cause sensations of popping, ear fullness, and occasional ear pain. Severe pain is usually experienced during air pressure changes, such as during airplane travel. Children may describe the popping sensation as "a tickle in my ear" or "my ears are itching."
If Eustachian tube function worsens, middle ear pressure decreases, causing ear fullness and muffled sounds. Eventually, a vacuum is created and fluid can be drawn into the middle ear space, leading to ear infections.
What causes blocked Eustachian tubes?
Healthcare professionals frequently encounter Eustachian tube problems and associated ear infections. Many people struggle to regulate middle ear pressure effectively.
Eustachian tube blockage or obstruction can be caused by various factors, including:
- Colds (upper respiratory infections) are the most common cause.
- Sinus infections and allergies can cause tissue swelling in the Eustachian tube, leading to blockage.
- Children are more prone to Eustachian tube blockage due to narrower tubes, more horizontal orientation, and proximity to the adenoids.
- Enlarged adenoids near the Eustachian tube can act as bacterial reservoirs and obstruct the tube opening. Adenoid removal (adenoidectomy) is common for children with chronic ear infections.
- Masses or tumors in the skull base or nasopharynx can obstruct the Eustachian tube but are rare.
- Children with Down Syndrome may have excessively small Eustachian tubes.
- Smoking damages the cilia that clear middle ear space via the Eustachian tube, leading to blockage.
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be caused by various factors, including allergies and narrow tubes in children with Down Syndrome.
What are the signs and symptoms of blocked Eustachian tubes?
Signs and symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction may include:
- Intermittent ear fullness
- Ear popping or cracking
- Pain
- Mild hearing loss
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Occasional poor balance
IMAGES
What is the medical treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Many people with Eustachian tube blockage or dysfunction use decongestants before air travel to shrink nasal and throat membranes, aiding ear pressure equalization. Aggressive control of allergies and acid reflux may also help. Allergy specialists or allergists can diagnose the cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction or blockage.
What home remedies treat pain and help clear blocked Eustachian tubes?
Several maneuvers can improve Eustachian tube function and aid in equalizing air pressure:
- Swallowing activates muscles in the throat, helping open the Eustachian tube. Chewing gum, drinking, and eating can promote swallowing and tube opening.
- Yawning is a stronger muscle activator.
- Forcibly opening the Eustachian tube can be done by taking a deep breath, pinching the nostrils, closing the mouth, and blowing. If a "pop" is felt, equalization is successful. Dizziness during this maneuver should be discussed with a doctor.
- People with colds, sinus infections, ear infections, or allergies may need to avoid air travel.
- Eustachian tube problems can make activities like scuba diving painful and dangerous.
- Babies cannot intentionally pop their ears, but sucking on a bottle or pacifier, or crying, can equalize air pressure.
Will surgery cure Eustachian tube dysfunction?
In severe cases, a pressure equalization tube (PET) can be surgically placed in the eardrum to ensure middle ear pressure equalization. This procedure is commonly performed in children with recurrent ear infections due to poor Eustachian tube function.
What changes can you make to avoid Eustachian tube dysfunction at altitudes?
A rapid change in altitude can cause unequal air pressure across the eardrum. A normally functioning Eustachian tube equalizes these pressure changes. During airplane descent, increasing air pressure pushes the eardrum inward and can cause symptoms in people with Eustachian tube blockage.
Poorly functioning Eustachian tubes can cause similar symptoms when riding elevators, driving through mountains, or swimming deep in pools. Scuba divers learn techniques to equalize ear pressure.
Reference: Middle Ear, Eustachian Tube, Inflammation/Infection Treatment & Management. Medscape. Updated: Apr 18, 2018.