Contents
Deafness (Hearing Loss)
Hearing loss, or deafness, can be present at birth (congenital) or become evident later in life (acquired). The distinction between acquired and congenital deafness specifies the time of appearance, not the cause.
Acquired deafness may or may not be genetic. It can be a delayed-onset form of genetic deafness or a result of ear damage from noise or other conditions.
Congenital deafness may or may not be genetic. Non-genetic causes include conditions or infections that the mother is exposed to during pregnancy, like the rubella virus. Another condition is Waardenburg syndrome, which is identified by a white forelock and includes congenital deafness. Over half of congenital hearing loss is inherited.
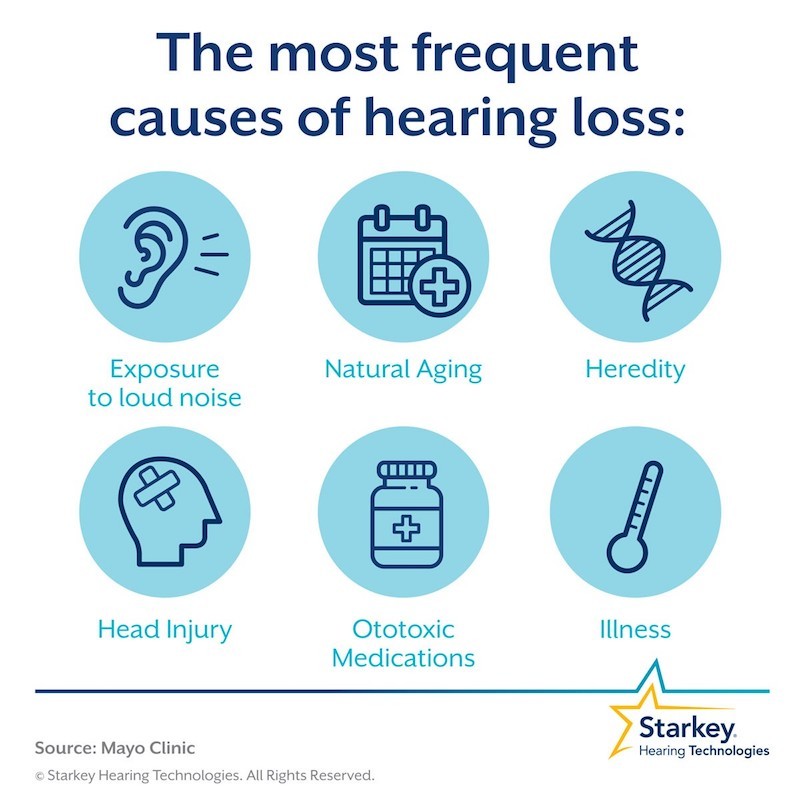
Types of hearing loss and causes
Hearing loss can be categorized as sensorineural or conductive, depending on which parts of the auditory system are affected.
Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by conditions affecting the cochlea, eighth cranial nerve, spinal cord, or brain, such as Meniere’s disease, noise-induced hearing loss, presbycusis, syphilis-induced nerve injury, idiopathic hearing loss, nerve tumors, and drug toxicity.
Conductive hearing loss is caused by conditions affecting the ear canal, eardrum, and middle ear, such as ear wax blockage, otitis media, and otosclerosis.
Other causes of hearing loss include fluid buildup in the middle ear, head injury, and autoimmune disorders.
QUESTION
Symptoms of hearing loss
Symptoms of hearing loss include mild high-frequency hearing loss, tinnitus, and complete deafness. People with hearing loss may withdraw from conversations, increase the volume of media, and ask others to repeat themselves frequently.
Treatment for hearing loss
Treatment for hearing loss depends on the cause:
- Ear wax can be removed.
- Ear infections can be treated with medications.
- Ear inflammation can be treated with medication.
- Avoid medications toxic to the ear.
- In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary.
Assisted hearing devices
Hearing aids and cochlear or brainstem implants are examples of assisted hearing devices that enable people, including those born deaf, to hear and develop speech and language.
Hearing aids are small electronic devices worn in or behind the ear to improve hearing. They benefit those with moderate hearing loss. Severe to profound deafness may require other options like bone-anchored hearing aids, cochlear implants, or auditory brainstem implants.
Bone-anchored hearing aids are implanted behind the ear and help individuals with conductive hearing loss. They allow sound to be transferred directly to the cochlea, bypassing the middle ear.
Choosing the right hearing aid
When selecting a hearing aid, consider individual listening needs, budget, and lifestyle for optimal improvement in hearing and quality of life.
- Telecoil: Boosts sound signals through a magnet.
- Digital feedback suppression: Suppresses secondary interfering sounds.
- Digital noise reduction: Reduces unwanted background noise.
- Directional mic: Receives sound from a specific direction.
- Low battery indicator: Indicates when to change the battery.
- Volume control: Adjusts volume according to hearing ability.
- Wax guard: Protects the device from ear wax buildup.
- Data logging: Keeps track of usage statistics like time.
- Memory: Remembers user’s ideal configurations.
- Audio input: Receives sound from the surroundings.
- Wireless connectivity: Facilitates freedom of movement.
- Frequency shifting: Adapts to varying sound wavelengths.
- Remote control: Allows easy and accurate device control.
Analog vs. digital hearing aids
Analog hearing aids:
- Make continuous sound waves louder.
- Amplify all sounds equally (some analog aids are programmable).
- Can have multiple programs for different environments.
Digital hearing aids:
- Convert sound waves into digital signals for precise replication.
- Analyze speech and environmental sounds.
- Provide more complex sound processing, improving performance in certain situations.
- Allow for customized programming based on the user’s specific hearing loss pattern.
- Have multiple program memories.
Hearing aid coverage by health insurance
Medicare does not cover hearing tests, evaluations, or hearing aids. Private insurance coverage varies, with some covering tests and evaluations. Check with your insurance company to determine coverage.
Learning to speak with hearing loss
Deaf individuals can learn to communicate through various methods. Normally, children learn to respond to auditory cues and imitate sounds from their surroundings. People born deaf or deaf at a young age may find learning to speak challenging. However, those who acquired speech skills before hearing loss can regain speech and language abilities with appropriate training.
Strategies for learning speech with hearing loss
A speech and language therapist can help individuals with hearing loss learn speech. Strategies include speech training, assistive hearing devices, auditory training, and lip reading. Parents and caregivers play an important role in the process.
Untreated hearing loss consequences
Untreated hearing loss can lead to anger, irritability, depression, fatigue, dementia, difficulty concentrating, self-isolation, loneliness, safety risks, learning difficulties, reduced job performance, and decreased mental and physical health.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Why Do Hearing Aids Cost So Much? https://www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-2016/hearing-aid-costs-prices-cs.html
Hearing Aids: https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hearing-aids
Hearing Aids: https://betterhearing.org/hearing-aids/the-price-of-hearing-aids/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. How People with Hearing Loss Learn Language. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/language.html
Deaf Education. Learning to Talk. https://deafeducation.org.uk/home/family-support/learning-to-talk/
Hearing Loss Association of America. Assistive Listening Systems.
Hearing Loss Association of America. Assistive Listening Systems.


