Contents
Can HIV Be Cured?
No cure or vaccine currently exists for HIV infection, but early treatment can prolong the lives of those infected.
While a cure for HIV does not yet exist, treatment options allow most infected individuals to live long, healthy lives.
- Antiretrovirals can suppress the virus in people living with HIV.
- Treatment can reduce HIV levels in the blood to undetectable levels.
Before the late 1980s, HIV infection was often fatal, resulting in AIDS within a few years or even months. AIDS is a disease that compromises the immune system’s ability to protect the body from threats, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and certain types of cancer cells.
However, individuals with HIV can now expect to live as long as anyone else, thanks to early detection and prompt antiretroviral therapy initiation that prevents immune system damage.
Treatment for a Lifetime
- Without treatment, newly infected individuals can expect to live for about 10 more years, during which they will likely be sick and weak.
- HIV treatments, like highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), have transformed the infection into a manageable chronic illness.
- A 25-year-old with a new HIV diagnosis can expect nearly 40 additional years of life with these treatments.
- Communicate closely with your doctor about severe side effects of HIV medications. They can adjust dosages or change medications if necessary.
Living Well and Staying Healthy
- A healthy diet is essential for maintaining a strong immune system. Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- If medications cause appetite loss or stomach issues, consult a doctor or dietitian for guidance.
- Avoid recreational drugs, smoking, and heavy drinking, as they weaken the immune system and impair judgment.
- To prevent other infections, avoid unsafe foods like raw seafood, unpasteurized milk, and undercooked meats.
- Regular handwashing minimizes the risk of common illnesses like colds.
- Stay up to date on immunizations, including the annual flu shot.
- Regular exercise improves mental and physical well-being, while adequate sleep provides energy to fight illness.
Healthy Mind, Healthy Body
- If anxiety and depression interfere with your ability to fight illness, seek help from a mental health professional.
- Counseling and medication can provide relief from mental health challenges.
- Engage in hobbies that relieve stress and divert your attention from the disease.
5 Potential HIV Cures
Scientists are exploring these 5 potential cures for HIV:
- A Vaccine
- A vaccine would be a powerful tool against HIV infection. Some studies have shown promise in developing a vaccine.
- Ongoing projects bring researchers closer to a vaccine than ever before.
- Vaccination has eliminated many other diseases in the past.
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) as a Cure
- Treating HIV within 48 hours of exposure reduces the size of the hidden HIV reservoir.
- This method suits some individuals, but it is not effective for everyone.
- Timely HIV testing is crucial to initiate treatment promptly.
- ARTs are part of a treatment plan, not a cure strategy.
- Stem Cell Transplants
- Transplanting healthy stem cells can rebuild the immune system.
- This procedure is commonly used to treat leukemia.
- Stem cell transplants are complex and require precise donors to prevent rejection.
- Shock and Kill Technique
- HIV hides in the body’s reservoir cells and becomes dormant during antiretroviral therapy.
- Discontinuing therapy causes the virus to replicate throughout the body.
- The goal is to awaken all dormant viruses and eliminate them.
- Scientists have identified drugs that awaken latent reservoir cells.
- Finding a drug or method to selectively destroy infected cells while preserving healthy cells poses a challenge.
- Lock and Block Technique
- This method aims to trap HIV in reservoir cells, preventing reactivation.
- By constraining the virus, it cannot escape its host cell or replicate.
- Current research focuses on drugs that can effectively trap HIV without harming uninfected cells.
- Ideally, a drug would lock HIV away and deplete the reservoir, preventing future reemergence.
HIV patients can live at home and maintain a normal social life. The virus cannot be transmitted through casual, nonsexual household contact, meaning family members, roommates, and visitors are not at risk of infection.
Being infected with HIV is life-altering, but it doesn’t have to be life-ending. With proper treatment and self-care, individuals can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
What is HIV?
HIV weakens the body’s immune system.
- The immune system protects the body from illness and is vital for good health.
- HIV attacks T-cells, important white blood cells that detect and eliminate invading organisms and cancerous cells.
- HIV multiplies and destroys T-cells, compromising the immune system.
- A weakened immune system makes the body susceptible to infections that a healthy person can fight off.
Some individuals experience flu-like symptoms within two weeks of HIV exposure, including:
Not everyone exhibits all symptoms, and the virus may not be detectable for several weeks.
Untreated HIV infection progresses to AIDS, characterized by severe symptoms like:
- Rapid weight loss
- Extreme tiredness
- Recurring fever and infections
- Swelling of the lymph glands
- Long bouts of diarrhea
- Blotchy skin
- Mouth sores
- Memory loss
HIV is present in infected individuals’ body fluids, such as blood, semen, vaginal and anal fluids, and breast milk. Transmission requires one of these fluids to enter another person’s bloodstream.
HIV is most commonly transmitted through unprotected vaginal or anal sex. Other transmission routes include:
- Sharing contaminated needles, syringes, or drug paraphernalia
- Spread from an HIV-positive mother to her child before, during, or after birth
- Engaging in oral sex or sharing sex toys
Although anyone can contract HIV, certain factors increase the risk, such as:
- Engaging in unprotected sex
- Using injected drugs
- Having another sexually transmitted infection
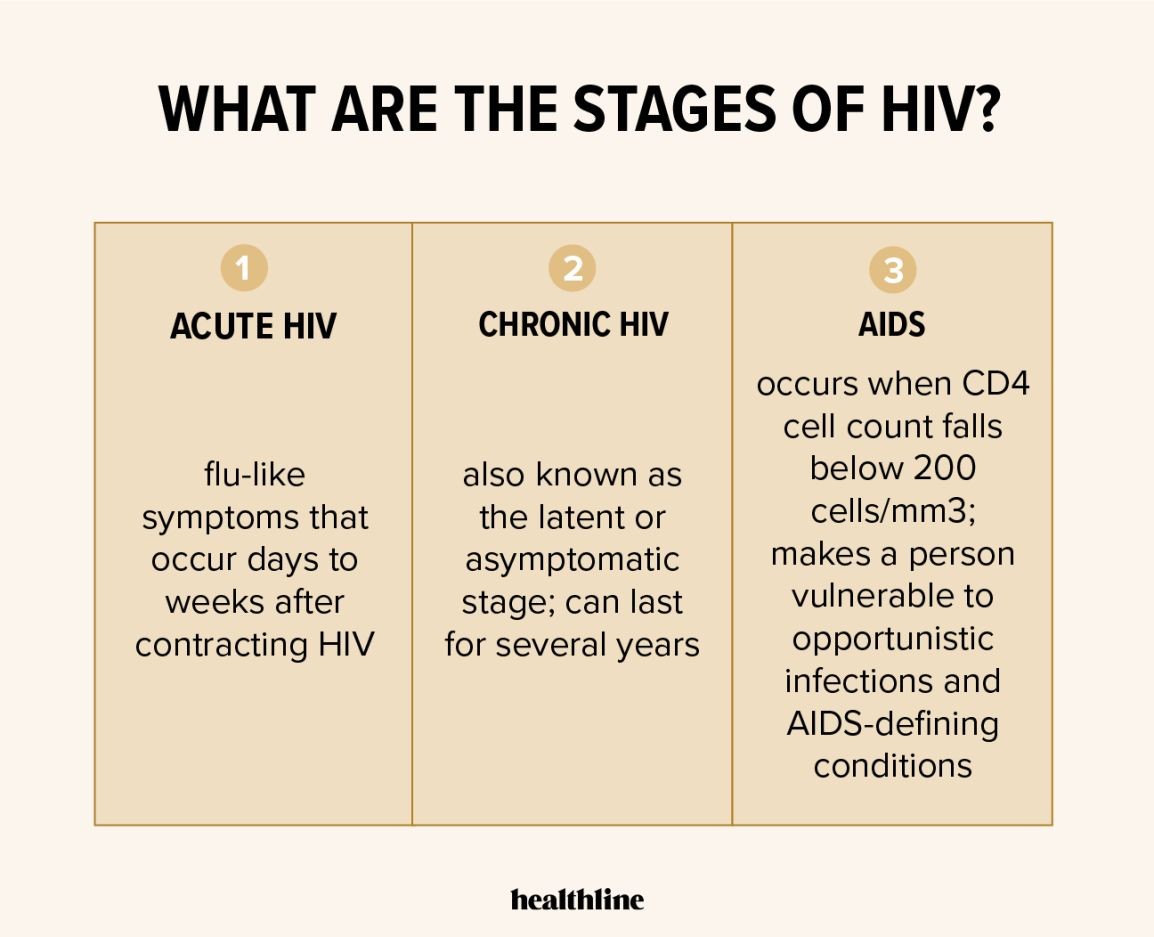
What are the Different HIV Stages?
World Health Organization (WHO) classifies HIV infection into four stages:
- Stage I (HIV Infection): CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage II (HIV Infection): CD4+ cell count is between 350 and 499.
- Stage III (Advanced HIV Disease or AHD): CD4+ cell count is between 200 and 349.
- Stage IV (AIDS): CD4+ cell count is less than 200 or the percentage of CD4+ cells is below 15% of all lymphocytes.
A higher CD4+ count signifies a lower risk of opportunistic diseases. Without treatment, most people with HIV experience a gradual decline in CD4+ cell count.
HIV deteriorates the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to diseases and infections. AIDS refers to the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by over 20 opportunistic infections or HIV-related cancers.
Over 1.1 million people in the United States live with HIV, with an estimated 162,500 unaware of their status. While medications can prevent the spread of HIV and its progression to AIDS, a cure or vaccine for the virus does not yet exist.
Over 1.1 million people in the United States live with HIV, with an estimated 162,500 unaware of their status. While medications can prevent the spread of HIV and its progression to AIDS, a cure or vaccine for the virus does not yet exist.


