Bronchiectasis (Acquired, Congenital)
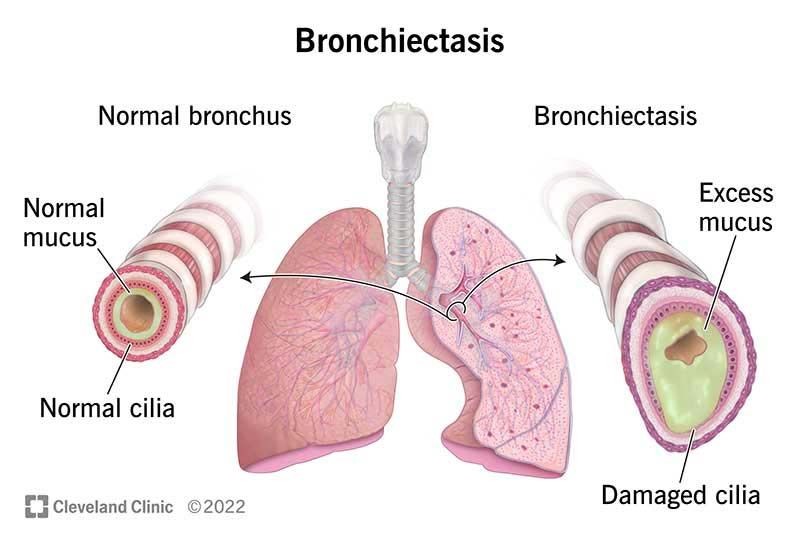
Bronchiectasis is the abnormal widening of the bronchi in the lungs, which increases the risk for infection.
It occurs when the bronchial tubes in the lung become damaged from inflammation or other causes and lose their elasticity.
There are two types of bronchiectasis: acquired and congenital.
Some researchers have identified three types of bronchiectasis based on their appearance: cylindrical, saccular or varicose, and cystic.
Bronchiectasis is caused by damage to the bronchial walls, resulting in decreased mucus removal and increased susceptibility to infections.
Acquired causes include infections, environmental exposure, and substance abuse, while congenital causes include genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis.
People at risk for bronchiectasis include those with alpha-1 antiproteinase deficiency, cystic fibrosis, and lung infections or lung tissue destruction.
Symptoms of bronchiectasis include coughing, sputum production, fatigue, shortness of breath, wheezing, and weight loss.
Medical care should be sought for chronic cough, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, repeated pneumonia, increased sputum production, and exposure to lung-damaging substances.
Diagnosis involves a history and physical exam, sputum analysis, chest X-ray, and high-resolution CT of the chest. Additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment aims to control symptoms, prevent infections, and slow disease progression. This includes immunizations, lifestyle changes, good nutrition, fluid intake, expectorants, chest physical therapy, antibiotics, bronchodilators, and surgical therapy if necessary.
The prognosis for bronchiectasis varies depending on the cause and timing of treatment. If properly managed, the prognosis can be fair to good. Complications include permanent lung damage, respiratory and heart failure.
Bronchiectasis due to genetic defects cannot be prevented, but the risk of progression can be reduced by avoiding environmental factors and situations that increase the risk of developing bronchiectasis.
Immunization can also prevent bronchiectasis caused by pertussis (whooping cough) in children.