Contents
- 1 Bilirubin and Bilirubin Blood Test
- 1.0.1 What are other names for bilirubin?
- 1.0.2 What is the bilirubin test?
- 1.0.3 What are normal bilirubin levels in adults?
- 1.0.4 What do high bilirubin levels in a newborn mean?
- 1.0.5 What are symptoms of high bilirubin levels in adults?
- 1.0.6 What are the symptoms of high bilirubin levels in newborns?
- 1.0.7 How do I prepare for the bilirubin test?
- 1.0.8 How is the bilirubin test performed?
- 1.0.9 What is the treatment for elevated bilirubin in adults?
- 1.0.10 What is the prognosis for an adult with elevated bilirubin levels?
- 1.0.11 What is the prognosis for newborns?
- 1.0.12 What risks are associated with the bilirubin test?
- 1.0.13 Can high levels of bilirubin be prevented?
Bilirubin and Bilirubin Blood Test
Bilirubin is an orange-yellow bile pigment formed during the breakdown of red blood cells (hemoglobin). It is excreted in the bile. Bilirubin can be classified as indirect (free or unconjugated) while circulating and as direct after conjugation in the liver with glucuronic acid.
What are other names for bilirubin?
Bilirubin usually exists in two forms in the body. However, the two forms have multiple names that frequently appear in the literature. The term "bilirubin" is often used alone without distinguishing between the two forms, which can cause confusion. To clarify, below are listed the two forms and their names and synonyms:
Bilirubin – a yellowish pigment made in the liver when red blood cells break down. It is normally excreted with bile; also known as "total bilirubin."
- Indirect bilirubin – the form of bilirubin that circulates in the body. It may also be referred to as "free" or "unconjugated bilirubin."
- Direct bilirubin – the form of bilirubin after conjugation in the liver with glucuronic acid. It may also be called "conjugated bilirubin."
- Neonatal bilirubin – total bilirubin in neonates (conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin)
What is the bilirubin test?
The bilirubin test measures the total bilirubin level (unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin) spectrophotometrically. It can also estimate the two major forms of bilirubin, unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. The test can be performed on blood, amniotic fluid, or urine. There is also a non-invasive method to scan newborns transcutaneously to check their bilirubin levels.
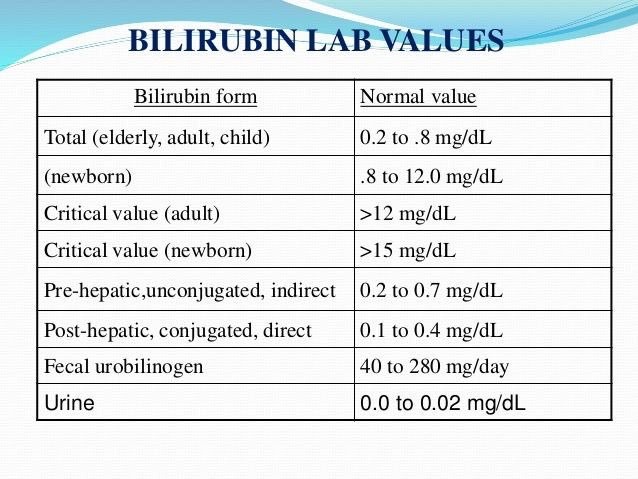
What are normal bilirubin levels in adults?
- Normal direct bilirubin values range from 0 to 0.4 mg/dL.
- Total bilirubin (direct and indirect) ranges from about 0.2 to 1.2 mg/dL (some lab values go as high as 1.9 mg/dL with minor variations in "normal" levels in medical literature).
- Low bilirubin levels may be due to certain medications such as theophylline (Elixophyllin, Theo-24), phenobarbital, and increased vitamin C levels.
What do high bilirubin levels in a newborn mean?
High bilirubin levels in newborns are usually caused by unconjugated bilirubin and are generally not a major problem as newborns quickly metabolize it. Neonates typically clear jaundice within a week. However, prolonged exposure to very high unconjugated bilirubin levels (over weeks) can be neurotoxic and may lead to death or lifelong neurological problems (kernicterus) in survivors.
Newborn jaundice may be associated with underlying issues such as:
- A family history of Gilbert syndrome
- Genetic problems
- Birth trauma
- Maternal drug intake
- Viral infection or bleeding problems
- Liver and/or bile function disorders
What are symptoms of high bilirubin levels in adults?
In adults, elevated bilirubin levels in the blood manifest as jaundice (yellowish coloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes) and itching.
Some potential underlying causes of elevated bilirubin, along with their associated symptoms and signs, include:
Anemia (due to red blood cell destruction) symptoms and signs:
Viral hepatitis symptoms and signs:
Biliary obstruction symptoms and signs:
- Light-colored stools
- Dark urine
- Itching
- Pain in the right side of the abdomen
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Jaundice
Symptoms and signs of infections (e.g., malaria):
Symptoms and signs of genetic diseases (e.g., sickle-cell disease, hereditary spherocytosis):
- Abdominal pain
- Abnormal red blood cells
Symptoms and signs of liver (hepatic) causes (e.g., cirrhosis, liver cancers, drugs, toxins, Gilbert’s and Crigler-Najjar syndromes):
- Abnormal liver enzymes
- Liver masses
Elevated bilirubin levels in adults may indicate several types of problems such as:
- Excessive breakdown of red blood cells (e.g., blood transfusion reaction)
- Liver scarring
- Liver inflammation
- Other liver diseases including infections
- Dysfunction of the common bile duct
- Gallstones
- Pancreatic or gallbladder cancer
What are the symptoms of high bilirubin levels in newborns?
High bilirubin levels in newborns are primarily indicated by jaundice of the skin, starting on the face and forehead and spreading to the trunk and extremities. If high levels persist, newborns may experience changes like drowsiness, seizures, altered crying, and other complications such as petechiae, an enlarged spleen, anemia, and neurologic problems or death can occur.
How do I prepare for the bilirubin test?
Patients are often instructed to fast (only drink water) for several hours before the test.
- Avoid strenuous exercise prior to the test as it can elevate bilirubin levels.
- Avoid certain drugs such as caffeine, penicillin, salicylates, and others as they can lower bilirubin levels.
How is the bilirubin test performed?
A small blood sample is withdrawn from the individual to perform the test. The sample is then chemically screened for bilirubin levels. The test can determine levels of both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin.
What is the treatment for elevated bilirubin in adults?
The treatment for elevated bilirubin in adults involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. For example:
- Clot reabsorption
- Hemolytic anemia
- Liver and/or bile problems
Avoiding alcohol consumption is recommended to prevent further liver toxicity.
What is the prognosis for an adult with elevated bilirubin levels?
The prognosis for adults with high bilirubin levels can range from good to poor, depending on the underlying cause. For instance, most hepatitis A patients recover completely, while patients with liver cancer or cirrhosis may have a worse outcome.
What is the prognosis for newborns?
In general, newborns have a good outcome if their bilirubin levels decrease quickly (within a few days). However, the prognosis is not favorable if newborns have persistently high bilirubin levels.
What risks are associated with the bilirubin test?
The risks associated with this test are minor and consist of potential infection at the blood withdrawal site and possible bruising.
Can high levels of bilirubin be prevented?
High levels of bilirubin in neonates can be prevented through appropriate treatment. Phototherapy is the primary therapy for newborns, followed by exchange transfusions and intravenous immunoglobulin. Your newborn’s pediatrician will help manage their bilirubin levels.
The management of high bilirubin levels in adults varies depending on the underlying cause. Generally, adults with elevated bilirubin levels are advised to abstain from alcohol consumption and avoid compounds that may harm or stress the liver. Your healthcare professional can provide guidance based on your specific underlying problem.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Nazer, H. "Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia." Medscape. Updated May 02, 2016.
Weisinger, R. "Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia." Medscape. Updated Jan 05, 2016.
Weisinger, R. "Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia." Medscape. Updated Jan 05, 2016.