Contents
9 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Vitamin B6 plays a key role in processing carbs, fat, and protein. It also helps produce red blood cells and neurotransmitters.
A deficiency in vitamin B6 can cause fatigue, weakness, and other unpleasant symptoms. Here are 9 common signs:
9 signs of vitamin B6 deficiency
1. Skin rashes
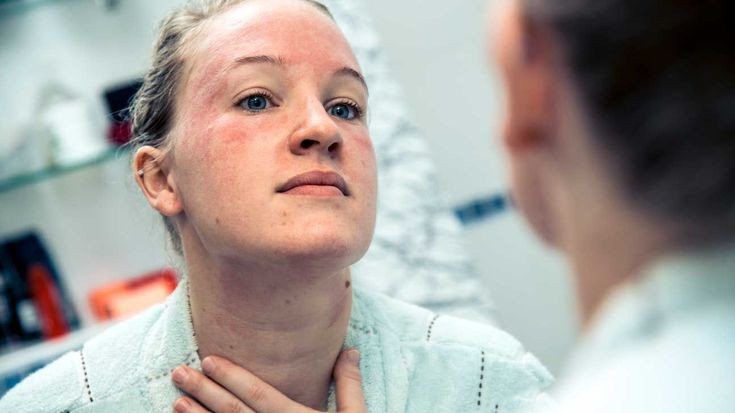
A deficiency in vitamin B6 can cause rashes on the skin, which may appear over time.
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to a red, itchy rash called seborrheic dermatitis. Rashes may appear on the scalp, neck, face, and upper chest, and are known for their flaky, oily appearance.
Skin irritation can occur because vitamin B6 helps synthesize collagen for healthy skin. Taking B6 supplements might help clear the rash.
Those with seborrheic dermatitis may need additional B6, and a face cream with B6 can help alleviate symptoms.
2. Cracked and dry lips
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to scaly, chapped lips with cracked mouth corners. Other causes include deficiencies in riboflavin, folate, and iron, as well as external factors like dry weather.
3. Sore and glossy tongue
Low levels of vitamin B6 can cause glossitis, which leads to a swollen, sore, red, or inflamed tongue.
Glossitis is caused by a loss of small bumps on the tongue surface and can affect chewing, swallowing, and talking.
4. Weak immune system
A deficient vitamin B6 intake can weaken the immune system by reducing the production of antibodies and white blood cells that fight infections. It can also decrease the production of a protein called interleukin-2, which helps regulate the immune system.
Autoimmune disorders and cancer can lower vitamin B6 levels, increasing the need for supplements.
5. Tingling in the hands or feet
Vitamin B6 deficiency can cause peripheral neuropathy, which leads to nerve damage and symptoms like tingling, burning, and shooting pain in the arms, legs, hands, and feet.
Other symptoms may include clumsiness, balance problems, and difficulty walking.
6. Low energy
Vitamin B6 deficiency is associated with tiredness, often due to anemia. B6 is responsible for producing hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body. Inadequate levels of hemoglobin can lead to tiredness and fatigue.
Vitamin B6 is also responsible for producing melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep. Inadequate melatonin levels can cause sleep disturbances and related fatigue.
7. Seizures
Vitamin B6 is needed to produce gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which calms excited neurons and prevents seizures. Seizures can cause muscle spasms, shaking, and loss of consciousness.
8. Brain fog
Vitamin B6 is essential for memory function, and a deficiency can lead to age-related cognitive impairment, including memory loss.
A deficiency in B6 can increase levels of homocysteine, which is associated with stroke, Alzheimer’s, and other nervous system conditions.
9. Mood changes
Vitamin B6 deficiency can cause mood changes, including depression, anxiety, irritability, and feelings of pain.
B6 is needed to produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA, which help reduce anxiety, depression, and mood swings.
Studies have shown that taking 50-80 mg of vitamin B6 supplements can alleviate premenstrual syndrome symptoms like moodiness, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
How to prevent vitamin B6 deficiency
You can prevent B6 deficiency by consuming foods rich in vitamin B6 or using supplements. The recommended daily dosage is less than 100 mg per day.
| 1.1 | 65% |
| 0.9 | 53% |
| 0.9 | 53% |
| 0.6 | 35% |
| 0.5 | 29% |
| 0.4 | 25% |
| 0.4 | 25% |
| 0.4 | 25% |
| 0.4 | 25% |
| 0.4 | 25% |
| 0.3 | 18% |
| 0.3 | 18% |
| 0.2 | 12% |
| 0.2 | 12% |
| 0.2 | 12% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
| 0.1 | 6% |
QUESTION
What is the daily recommended intake of vitamin B6?
| 0.1 mg per day |
| 0.3 mg per day |
| 0.5 mg per day |
| 0.6 mg per day |
| 1.0 mg per day |
| 1.3 mg per day |
| 1.7 mg per day |
| 1.2 mg per day |
| 1.3 mg per day |
| 1.5 mg per day |
| 1.9 mg per day during pregnancy and 2.0 mg per day during lactation |