Contents
- 1 tolmetin
- 1.0.1 What are the uses for tolmetin?
- 1.0.2 What are the side effects of tolmetin?
- 1.0.3 What is the dosage for tolmetin?
- 1.0.4 Which drugs or supplements interact with tolmetin?
- 1.0.5 Is tolmetin safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
- 1.0.6 What else should I know about tolmetin?
- 1.0.7 Summary
- 1.0.8 Related Disease Conditions
- 1.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- 1.2 Osteoarthritis (OA)
- 1.3 Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
- 1.4 Pain Management
- 1.5 Ankylosing Spondylitis
- 1.6 Ankle Pain (Tendonitis)
- 1.7 Psoriatic Arthritis
- 1.8 Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Ulcers
- 1.9 Reactive Arthritis
- 1.10 SAPHO Syndrome
- 1.11 Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
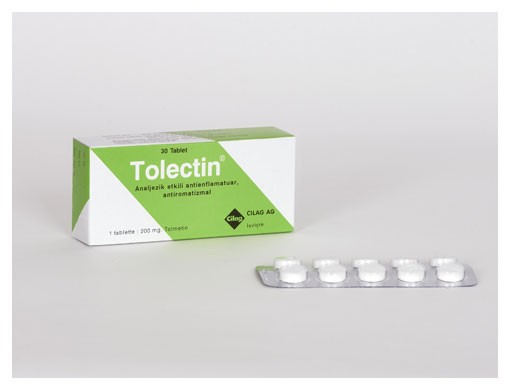
tolmetin
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) effective in treating fever, pain, and inflammation in the body. It is similar to ibuprofen (Motrin or Advil), naproxen (Naprosyn), and others. NSAIDs are non-narcotic relievers of mild to moderate pain, including injury, menstrual cramps, arthritis, and musculoskeletal conditions. They work by reducing the levels of prostaglandins, chemicals responsible for pain, fever, and inflammation. Tolmetin blocks the enzyme that makes prostaglandins (cyclooxygenase), resulting in lower concentrations. This reduces inflammation, pain, and fever. The FDA approved Tolectin in March 1976.
Is tolmetin available as a generic drug?
GENERIC AVAILABLE: Yes
Do I need a prescription for tolmetin?
What are the uses for tolmetin?
Tolmetin is used for inflammation and pain from rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile arthritis, or osteoarthritis.
What are the side effects of tolmetin?
Most patients benefit from tolmetin and other NSAIDs with few side effects. However, serious side effects can occur, and generally tend to be dose related. Therefore, it is advisable to use the lowest effective dose to minimize side effects. Common side effects of tolmetin involve the gastrointestinal system, and these include:
- ulcerations,
- abdominal pain,
- cramping,
- nausea,
- gastritis,
- serious gastrointestinal bleeding,
- liver toxicity,
- stomach ulceration,
- black tarry stools,
- weakness.
Tolmetin should be avoided by patients with a history of asthma, hives, or other allergic reactions to aspirin or other NSAIDs. Rare but severe allergic reactions have been reported in such individuals. It should also be avoided by patients with peptic ulcer disease or poor kidney function, since this medication can aggravate both conditions.
Other important side effects include:
- heart attacks,
- strokes,
- accumulation of fluid,
- increased chance of heart failure.
Tolmetin may cause or worsen high blood pressure and kidney failure.
What is the dosage for tolmetin?
The recommended dose is 200-600 mg three times daily. The maximum daily dose is 1800 mg. Tolmetin should be taken with food and 8-12 ounces of water to avoid stomach upset.
Which drugs or supplements interact with tolmetin?
Tolmetin should be used with caution in patients taking blood thinning medications (anticoagulants), such as warfarin (Coumadin), due to the increased risk of bleeding. Patients taking lithium (Eskalith, Lithobid) or methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall) may develop toxic blood levels of either drug, as tolmetin may inhibit their elimination by the kidney. Side effects from cyclosporine may also be increased by tolmetin. Tolmetin may reduce the effectiveness of antihypertensives and NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors.
Combining NSAIDs with angiotensin receptor blockers (e.g., valsartan [Diovan], losartan [Cozaar], irbesartan [Avapro]) or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (e.g., enalapril [Vasotec], captopril [Capoten]) in elderly patients, those with poor kidney function, or who are volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy) may result in reduced kidney function, including kidney failure. These effects are usually reversible.
Persons who consume more than three alcoholic beverages per day are at an increased risk of developing stomach ulcers when taking tolmetin or other NSAIDs.
Is tolmetin safe to take if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
Tolmetin is generally avoided during pregnancy.
Tolmetin is excreted in breast milk. Nursing mothers should decide whether to stop nursing or stop tolmetin to avoid adverse effects in the infant.
What else should I know about tolmetin?
What preparations of tolmetin are available?
Tablets or capsules: 200, 400, and 600 mg
How should I keep tolmetin stored?
Tolmetin should be stored at room temperature in a sealed container and protected from moisture.
Summary
Tolmetin (Tolectin [Discontinued Brand]) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) prescribed for inflammation and pain from rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile arthritis, or osteoarthritis. Review side effects, drug interactions, dosage, and pregnancy safety information before taking this medication.
Related Disease Conditions
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease causing chronic inflammation of the joints, surrounding tissues, and other organs in the body. Early RA signs and symptoms include anemia, symmetric joint inflammation, depression, fatigue, fever, joint deformity, joint pain, joint redness, joint stiffness, joint swelling, joint tenderness, joint warmth, limping, loss of joint function and range of motion, and polyarthritis.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis caused by inflammation, breakdown, and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. Also known as degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis can be caused by aging, heredity, trauma, or disease.
Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in stiffness, warmth, swelling, redness, and pain. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, gout, and pseudogout.
Pain Management
Pain management and treatment can be simple or complex, depending on the cause. There are two basic types of pain: nociceptive pain and neuropathic pain. Some causes of neuropathic pain include complex regional pain syndrome, interstitial cystitis, and irritable bowel syndrome. Chronic pain can be treated using various methods based on the type experienced.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that causes chronic inflammation of the spine. The tendency to develop ankylosing spondylitis is genetically inherited. Treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and exercise.
Ankle Pain (Tendonitis)
Ankle pain is commonly due to a sprain or tendinitis. The severity of ankle sprains ranges from mild (which can resolve within 24 hours) to severe (which may require surgical repair). Tendinitis of the ankle can be caused by trauma or inflammation.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a disease that causes skin and joint inflammation. Symptoms and signs include painful, stiff, and swollen joints, tendinitis, and organ inflammation. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory medications and exercise.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Ulcers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed medications for the treatment of inflammatory conditions. Examples of NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and more. One common side effect of NSAIDs is peptic ulcer (ulcers of the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum). Side effects, drug interactions, warnings and precautions, and patient safety information should be reviewed prior to taking NSAIDs.
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a chronic, systemic rheumatic disease characterized by three conditions: conjunctivitis, joint inflammation, and inflammation of the genital, urinary, or gastrointestinal systems. Inflammation leads to pain, swelling, warmth, redness, and stiffness of the affected joints. Non-joint areas may experience irritation and pain. Treatment depends on which area of the body is affected and may include anti-inflammatory medications.
SAPHO Syndrome
SAPHO syndrome is a chronic disorder affecting the skin, bone, and joints. It is related to arthritic conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis and reactive arthritis. Treatment is directed towards the specific symptoms present and may include medications such as NSAIDs and cortisone.
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) affects approximately one child in every thousand annually. There are six types of JRA. Treatment depends on the type and focuses on managing the symptoms that occur.
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) affects approximately one child in every thousand annually. There are six types of JRA. Treatment depends on the type and focuses on managing the symptoms that occur.