Contents
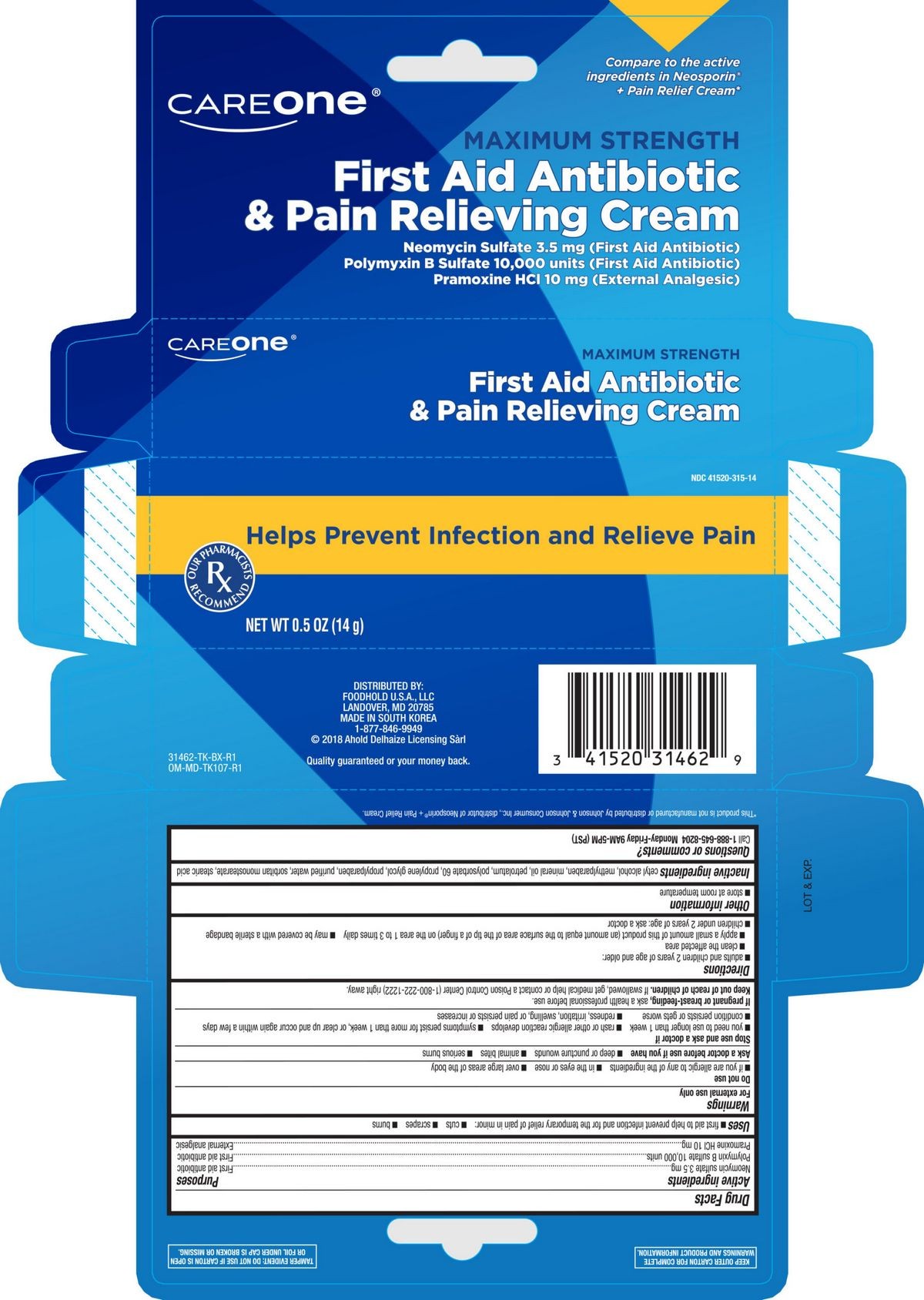
Neomycin Sulfate
Neomycin Sulfate is an antibiotic used to reduce the risk of infection during bowel surgery and hepatic coma. It is available in generic form.
Warnings
- Systemic absorption of Neomycin occurs after oral administration and may cause toxic reactions. Close clinical observation is necessary for patients treated with neomycin due to potential toxicity.
- Neurotoxicity (including ototoxicity) and nephrotoxicity have been reported with oral use of Neomycin Sulfate even at recommended doses.
- Potential for nephrotoxicity, auditory ototoxicity, and vestibular toxicity exists in patients with normal renal function when treated with higher doses and/or for longer periods than recommended.
- Serial tests of renal function, vestibular and audiometric tests should be performed, especially in high-risk patients. Ototoxicity can occur even after discontinuation of neomycin.
- Neuromuscular blockage and respiratory paralysis have been reported with neomycin use. Caution should be exercised when administering neomycin to patients receiving certain anesthetics or neuromuscular blocking agents.
- Avoid concurrent use of other nephrotoxic or neurotoxic drugs with neomycin as it may increase toxicity.
- Advanced age and dehydration increase the risk of toxicity.
- Avoid concurrent use of neomycin with potent diuretics as it may cause ototoxicity. Diuretics administered intravenously may enhance neomycin toxicity.
Side Effects of Neomycin Sulfate
Common side effects include:
Notify your doctor if you experience serious side effects such as:
- drowsiness
- confusion
- mood changes
- increased thirst
- loss of appetite
- weight gain
- shortness of breath
- shallow breathing
- hearing problems
- spinning sensation
- feeling like you might pass out
- loss of balance or coordination
- trouble walking
- numbness or tingling under the skin
- muscle twitching
- seizures
- decreased urination or urinary retention
- swelling
- severe stomach cramps
- watery or bloody diarrhea
Dosage for Neomycin Sulfate
Use the lowest effective dose and shortest treatment period to control the condition. Treatment for longer than two weeks is not recommended.
Hepatic Coma
As an adjunct in the management of hepatic coma, the recommended dose is 4-12 grams per day given as follows:
- Withdraw protein from diet and avoid diuretic agents.
- Provide supportive therapy, including blood products, as needed.
- Give Neomycin Sulfate Tablets in divided doses of 4-12 grams per day (eight to 24 tablets) over a period of five to six days. Gradually reintroduce protein to the diet.
- For patients with chronic hepatic insufficiency who cannot tolerate less toxic drugs, neomycin in doses of up to four grams daily (eight tablets) may be necessary. Monitor patients regularly for drug toxicity. Consider the risks of nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade.
Preoperative Prophylaxis for Elective Colorectal Surgery
Below is an example of a recommended bowel preparation regimen for surgery scheduled at 8:00 a.m.:
- Pre-op Day 3: Minimum residue or clear liquid diet. Bisacodyl, 1 tablet orally at 6:00 p.m.
- Pre-op Day 2: Minimum residue or clear liquid diet. Magnesium sulfate, 30 mL (15 g) orally at 10:00 a.m., 2:00 p.m., and 6:00 p.m. Enema at 7:00 p.m. and 8:00 p.m.
- Pre-op Day 1: Clear liquid diet. Supplemental (IV) fluids as needed. Magnesium sulfate, 30 mL (15 g) orally at 10:00 a.m. and 2:00pm. Neomycin sulfate (1 g) and erythromycin base (1 g) orally at 1:00 p.m., 2:00 p.m., and 11:00 p.m. No enema.
Day of Operation: Patient evacuates rectum at 6:30 a.m. for scheduled operation at 8:00 a.m.
Drug Interactions
- Exercise caution when using neomycin with other neurotoxic or nephrotoxic drugs as it may enhance toxicity.
- Use neomycin with caution when other aminoglycosides or polymyxins are used to avoid increased nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neuromuscular blocking effects.
- Oral neomycin may interfere with gastrointestinal absorption of penicillin V, oral vitamin B-12, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, and digoxin. Monitor digoxin serum levels.
- Oral neomycin sulfate may enhance the effect of coumarin in anticoagulants by decreasing vitamin K availability.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Aminoglycosides can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women.
- Several reports have shown irreversible bilateral deafness in children whose mothers received streptomycin during pregnancy.
- The potential for harm exists when using other aminoglycosides in pregnant women, although serious side effects to the fetus or newborn have not been reported.
- Excretion of neomycin in human milk is unknown, but it has been found in cow milk after intramuscular injection.
- Other aminoglycosides have been detected in human milk.
- Consider the importance of the drug to the mother when deciding whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug due to potential adverse reactions in nursing infants.
Summary
Neomycin Sulfate is an antibiotic used to reduce the risk of infection during bowel surgery and hepatic coma. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.