multivitamins (includes prenatal vitamins) – oral
WARNING: Keep this product out of reach of children. Accidental overdose of iron-containing products can be fatal in children under 6 years old. If overdose occurs, seek immediate medical attention or call a poison control center. USES: This medication treats or prevents vitamin deficiency due to poor diet, certain illnesses, or during pregnancy. Vitamins are essential for a healthy body. HOW TO USE: Take this medication by mouth, once daily or as directed. Follow all directions on the product package or as directed by your doctor. Do not exceed the recommended dosage. If uncertain, consult your doctor or pharmacist. Take this medication regularly to maximize its benefits. Take it at the same time each day to help remember. SIDE EFFECTS: Constipation, diarrhea, or upset stomach may occur. These effects are usually temporary and may disappear as your body adjusts. If these effects persist or worsen, contact your doctor or pharmacist. Serious allergic reactions are rare. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience rash, itching/swelling, severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you notice other effects. PRECAUTIONS: Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to any ingredients, soy/peanut, or have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients that can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Consult your pharmacist for more details. Before taking this medication, inform your doctor or pharmacist of your medical history, especially alcohol use/abuse, liver problems, and stomach/intestinal problems. If the multivitamin contains folic acid, inform your doctor or pharmacist if you have vitamin B12 deficiency before taking it. Folic acid may affect certain laboratory tests for vitamin B12 deficiency without treating this anemia. Untreated vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to nerve problems. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. DRUG INTERACTIONS: Your doctor or pharmacist may be monitoring for possible drug interactions. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine without consulting them first. Inform your doctor or pharmacist of all prescription and nonprescription/herbal drugs you use, especially other vitamin/nutritional supplements. If the multivitamin contains iron, avoid taking it with antacids, bisphosphonates, levodopa, thyroid medications, or certain antibiotics. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about the dosing schedule. This document does not contain all possible interactions. Inform your doctor or pharmacist of all the products you use. OVERDOSE: If overdose is suspected, contact a poison control center or emergency room immediately. Symptoms of overdose may include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. NOTES: Do not share this medication with others. Keep all regular medical and laboratory appointments. This product is not a substitute for a proper diet. Get your vitamins from healthy foods and follow your doctor’s dietary guidelines. MISSED DOSE: If you are taking this product on a prescribed schedule and miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your usual schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up. STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medicines away from children and pets. Properly discard when expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for more details. Information last revised February 2014. Copyright(c) 2014 First Databank, Inc.
QUESTION
Related Disease Conditions
Osteoporosis
Learn about osteoporosis, a condition characterized by the loss of bone density, which leads to an increased risk of bone fracture. Unless one experiences a fracture, a person may have osteoporosis for decades without knowing it. Treatment for osteoporosis may involve medications that stop bone loss and increase bone strength and bone formation, as well as lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, regular exercise, cutting back on alcohol intake, and eating a calcium- and vitamin D-rich balanced diet.
Pregnancy Planning (Tips)
Pregnancy planning is an important step in preparation for starting or expanding a family. Planning for a pregnancy includes taking prenatal vitamins, eating healthy for you and your baby, disease prevention (for both parents and baby) to prevent birth defects and infections, avoiding certain medications that may be harmful to your baby, how much weight gain is healthy exercise safety during pregnancy, and travel considerations.
Stillbirth (Stillborn Baby)
About 1% of pregnancies result in stillbirth, meaning there are about 24,000 stillborn births each year in the U.S. Causes of stillbirth can include diseases, conditions, and problems with the pregnancy or the mother’s health. The most common symptom of stillbirth is not feeling the baby moving or kicking.
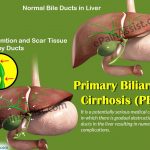
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) Treatment
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune disorder that involves the deterioration of the liver’s small bile ducts, which are important for transporting bile to the small intestine, digesting fats, and removing waste. Symptoms of PBC include edema, itching, elevated cholesterol, malabsorption of fat, liver cancer, gallstones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and hypothyroidism. Treatments for PBC include ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), colchicine (Colcrys), and immunosuppressive medications such as corticosteroids, obeticholic acid (Ocaliva), and medications that treat PBC symptoms. In extreme cases of PBC associated with cirrhosis of the liver, liver transplantation may be necessary.
What Are the 3 Prenatal Tests?
Prenatal tests are medical procedures performed during pregnancy to assess the health and development of the fetus and to help identify any potential problems or abnormalities. The three most common prenatal tests are ultrasound, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling (CVS). Other prenatal tests include pregnancy tests, first trimester screening, second trimester screening, noninvasive prenatal testing, fetal ultrasound, genetic counseling, biophysical profile, Group B streptococcus (GBS) test, glucose tolerance test, anomaly scan, and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test.
What Is a Good Family Multivitamin?
When choosing a multivitamin for your family, consider one that contains essential nutrients such as vitamin D, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, iron, zinc, and magnesium.
What Is the Best Vitamin Supplement to Take?
Dietary supplements include vitamins, minerals, botanicals, probiotics, and other products to supplement the diet. The best vitamin supplement varies for each individual based on factors such as gender, age, and any existing health conditions.