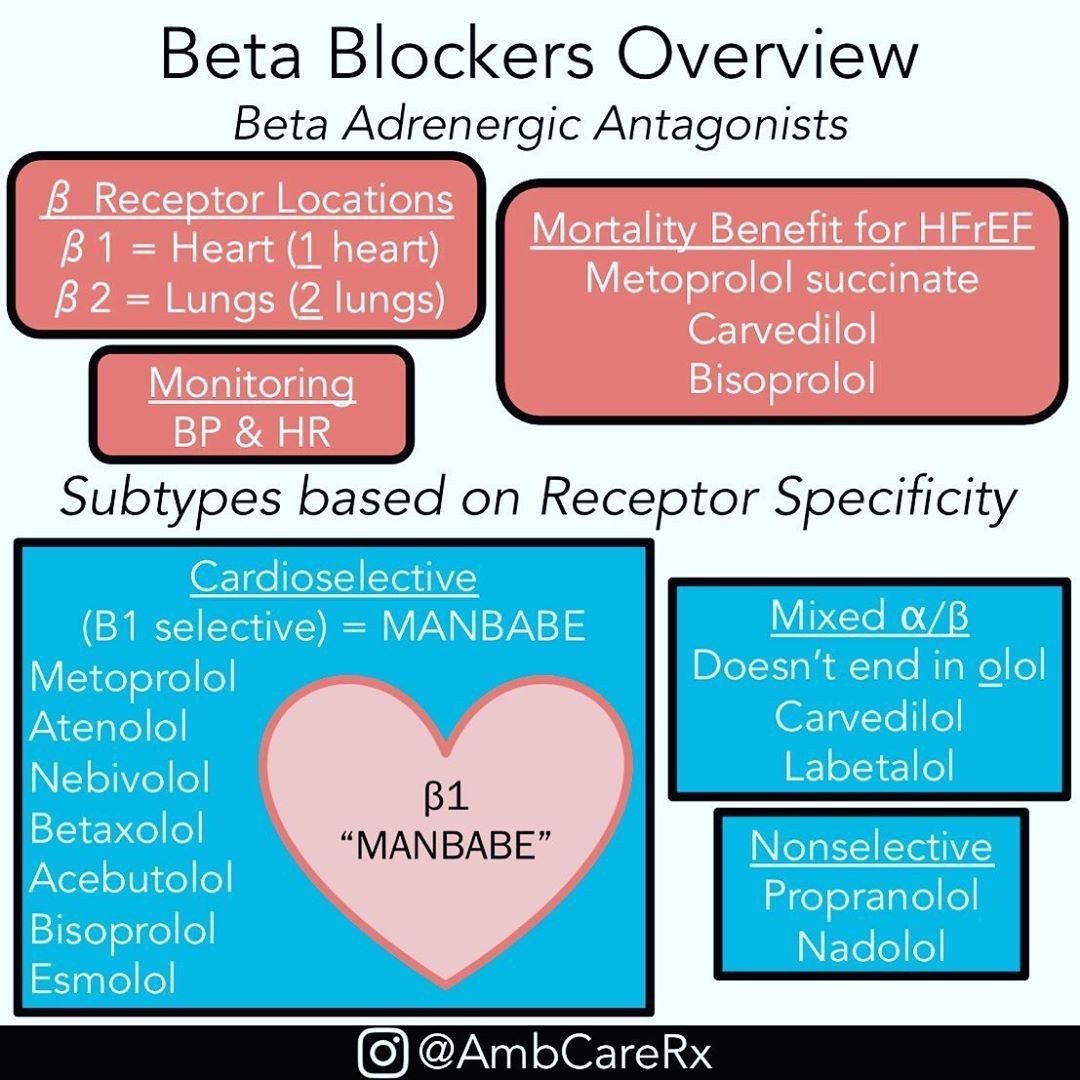
Contents
- 1 Metoprolol vs. propranolol
Metoprolol vs. propranolol
Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that treats high blood pressure, heart pain, congestive heart failure, abnormal heart rhythms, hyperthyroidism, and some neurologic conditions. It is also used to prevent migraines.
Propranolol is another beta-blocker used to treat high blood pressure, heart pain, abnormal heart rhythms, and some neurologic conditions. It reduces heart rate, lowers blood pressure, and helps with heart pain.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of metoprolol and propranolol?
Metoprolol side effects
Metoprolol may cause abdominal cramps, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, insomnia, indigestion, nausea, depression, dreaming, memory loss, fever, impotence, lightheadedness, low blood pressure, decreased exercise tolerance, increased triglycerides, bronchospasm, cold extremities, sore throat, and shortness of breath or wheezing.
Possible serious adverse effects include slow heart rate, Raynaud’s phenomenon, hepatitis, and increased insulin resistance. Metoprolol can worsen breathing difficulties in patients with asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema.
WARNING: Metoprolol can cause slow heart rates and worsen symptoms of heart failure especially in patients with existing heart conditions. Abruptly stopping metoprolol can worsen heart pain and sometimes cause heart attacks. Gradual dosage reduction is recommended.
Propranolol side effects
Common side effects include abdominal cramps, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, insomnia, nausea, depression, dreaming, memory loss, fever, impotence, lightheadedness, slow heart rate, low blood pressure, cold extremities, sore throat, and shortness of breath or wheezing. Propranolol can worsen breathing difficulties in patients with asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema. It can also worsen symptoms of heart failure.
In patients with coronary artery disease, abrupt discontinuation of propranolol can worsen heart pain and occasionally cause heart attacks. Gradual dosage reduction is recommended.
What is the dosage of metoprolol vs. propranolol?
Metoprolol dosage
Metoprolol dosage varies depending on the condition being treated:
- Hypertension: 100 to 450 mg daily
- Angina: 100 to 400 mg daily
- Heart attack: Initial injections followed by 100 mg orally twice daily
- Congestive heart failure: Up to 200 mg daily
- Hyperthyroidism: 25 to 30 mg every 6 hours
Propranolol dosage
The dosage of propranolol depends on the condition:
- Hypertension: 80 to 240 mg twice daily or 80 to 160 mg daily
- Chest pain: 80 to 320 mg daily or 80 to 160 mg daily
- Abnormal heart rhythms: 10 to 30 mg 3 to 4 times daily
- Migraines: 80 to 240 mg daily
What drugs interact with metoprolol and propranolol?
Metoprolol drug interactions
- Calcium channel blockers and digoxin can have dangerous effects when combined with metoprolol.
- Metoprolol can mask low blood sugar symptoms in diabetic patients.
- Fluoxetine can increase blood levels of metoprolol and its side effects.
Propranolol drug interactions
- Calcium channel blockers and digoxin can have dangerous effects when combined with propranolol.
- Propranolol can mask low blood sugar symptoms in diabetic patients.
- Propranolol increases the concentration of thioridazine in the body, which can cause abnormal heartbeats.
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet and I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.
Are metoprolol and propranolol safe to use while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Metoprolol
- Safe use during pregnancy has not been established.
- Metoprolol is excreted in breast milk and may cause adverse effects in infants.
Propranolol
- Safe use during pregnancy has not been established and can cause growth retardation and congenital abnormalities in infants.
- Propranolol is secreted in breast milk and should be used with caution in nursing women.
From
Heart Health Resources
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Summary
Metoprolol and propranolol are beta-blockers used to treat high blood pressure, heart pain, abnormal heart rhythms, and some neurologic conditions. Metoprolol is also used to treat congestive heart failure, hyperthyroidism, and prevent migraines.