Contents
Lyrica (pregabalin) vs. Cymbalta (duloxetine)
Lyrica (pregabalin) is an oral medication related to gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) used for pain caused by neurologic diseases like postherpetic neuralgia and seizures. It also treats fibromyalgia.
Cymbalta (duloxetine) is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) antidepressant used for depression, anxiety disorder, diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and chronic musculoskeletal pain. Other drugs in this category include milnacipran (Savella), venlafaxine (Effexor), and desvenlafaxine (Pristiq).
QUESTION
What are the side effects of Lyrica and Cymbalta?
Lyrica
WARNING
- Antiepileptic medications are associated with increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior. Patients must consider this risk when using antiepileptic drugs. Patients starting therapy should be closely observed for clinical worsening, suicidal thoughts, or changes in behavior.
The most common side effects of Lyrica are
- dizziness,
- drowsiness,
- dry mouth (xerostomia),
- edema (fluid accumulation),
- blurred vision,
- double vision (diplopia),
- weight gain,
- fatigue,
- abnormal gait (ataxia),
- tremor,
- difficulty concentrating.
Other side effects include
- constipation,
- increased appetite,
- nausea,
- flatulence,
- amnesia,
- disorientation,
- myoclonus (sudden, involuntary muscle jerking),
- heart failure,
- low blood pressure,
- vomiting,
- reduced blood platelet counts,
- increased blood creatinine kinase levels.
Increased creatinine kinase can indicate muscle injury. In clinical trials, three patients experienced severe muscle injury (rhabdomyolysis). Patients should report unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness to their doctors, especially if combined with fever and malaise. Lyrica has rarely been associated with angioedema (face, tongue, lips, gum, throat, and larynx swelling).
Cymbalta
The most common side effects of duloxetine are nausea, dry mouth, constipation, diarrhea, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and dizziness. Increased blood pressure can occur and should be monitored. Seizures have been reported. Sexual dysfunction (decreased sex drive, delayed orgasm and ejaculation) has been associated with duloxetine.
Some patients may experience withdrawal reactions upon stopping duloxetine. Symptoms of withdrawal include:
The dose of duloxetine should be gradually reduced when therapy is discontinued to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in short-term studies in children and adolescents with depression and other psychiatric disorders. Patients starting therapy should be closely observed for clinical worsening, suicidality, or changes in behavior.
What is the dosage of Lyrica vs. Cymbalta?
Lyrica
- Lyrica may be taken with or without food.
- Treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy: The initial dose is 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to a maximum of 100 mg three times daily (300 mg/day) after one week.
- Treating postherpetic neuralgia: The recommended dose is 75-150 mg twice daily or 50-100 mg three times daily. Dosing should begin at 75 mg two times a day or 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 100 mg three times daily (300 mg/day) after one week. If pain relief is inadequate after 2-4 weeks of treatment at 300 mg/day, the dose may be increased to 300 mg twice daily or 200 mg three times daily. Doses greater than 300 mg cause more side effects.
- Treating neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury: The dose is 150 to 600 mg daily. Start with 75 mg two times a day and increase to 150 mg two times daily after one week if response is inadequate. May increase to 300 mg twice daily if response is inadequate after 2 to 3 weeks.
- Treating seizures: The recommended dose is 150-600 mg/day divided into 2 or 3 doses, starting at 150 mg daily and increasing based on response. The maximum dose is 600 mg/day.
- Treating fibromyalgia: The dose is 300-450 mg/day in 2 or 3 divided doses.
Cymbalta
The recommended dose for depression is 20 or 30 mg twice daily or 60 mg once daily. Patients may be started with 30 mg once daily for one week before advancing to 60 mg daily.
The recommended dose for anxiety disorder, pain associated with diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia, or chronic musculoskeletal pain is 60 mg daily. Start with 30 mg daily for one week before increasing to 60 mg daily. Doses greater than 60 mg/day do not provide additional benefits. However, the maximum dose for depression or anxiety disorder is 120 mg/day.
What drugs interact with Lyrica and Cymbalta?
Lyrica
- Alcohol and sedative drugs may increase the sedative effects of pregabalin.
- Pioglitazone (Actos) and rosiglitazone (Avandia) cause weight gain, fluid retention, and possibly heart failure. Combining pregabalin with these drugs may increase weight gain and fluid retention.
Cymbalta
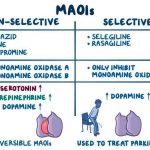
- Duloxetine should not be used with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) such as phenelzine (Nardil), tranylcypromine (Parnate), isocarboxazid (Marplan), and selegiline (Eldepryl), or within 14 days of discontinuing the MAOI. Allow at least 5 days after stopping duloxetine before starting an MAOI. Combinations of SNRIs and MAOIs may cause serious, sometimes fatal, reactions including high body temperature, muscle rigidity, rapid fluctuations of heart rate and blood pressure, extreme agitation progressing to delirium, and coma. Similar reactions may occur if duloxetine is combined with antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, or other drugs that affect serotonin in the brain. Examples include tryptophan, sumatriptan (Imitrex), lithium, linezolid (Zyvox), tramadol (Ultram), and St. John’s Wort.
- Fluoxetine (Prozac, Serafem), paroxetine (Paxil, Paxil CR, Pexeva), fluvoxamine (Luvox), and quinidine increase blood levels of duloxetine by reducing its metabolism in the liver. Such combinations may increase adverse effects of duloxetine.
- Combining duloxetine with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin (Coumadin), or other drugs associated with bleeding may increase the risk of bleeding, as duloxetine itself is associated with bleeding.
- Duloxetine has an enteric coating that prevents dissolution until it reaches a gastrointestinal segment with a pH higher than 5.5. Drugs that raise the pH in the gastrointestinal system (e.g., Prilosec) may cause early release of duloxetine, while conditions that slow gastric emptying (e.g., diabetes) may cause premature breakdown of duloxetine. Nevertheless, administration of duloxetine with an antacid or famotidine (Axid) did not significantly affect the absorption of duloxetine.
- Duloxetine may reduce the breakdown of desipramine (Norpramine), leading to increased blood concentrations of desipramine and potential side effects.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Are Lyrica and Cymbalta safe to use while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Lyrica
- There are no adequate studies of Lyrica in pregnant women.
- It is not known whether Lyrica is excreted in breast milk.
Cymbalta
Duloxetine is excreted into the milk of lactating women. The safety of duloxetine in infants is not known, so breastfeeding while on duloxetine is not recommended.
From
Pain Management Resources
- Managing a Sickle Cell Pain Crisis
- Take Control of Your Migraine, Now
- Side Effects From aHUS Treatment
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Summary
Lyrica (pregabalin) and Cymbalta (duloxetine) are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia. Lyrica is also used in combination with other drugs to treat partial onset seizures in adults. Cymbalta is also used to treat depression and anxiety disorder.