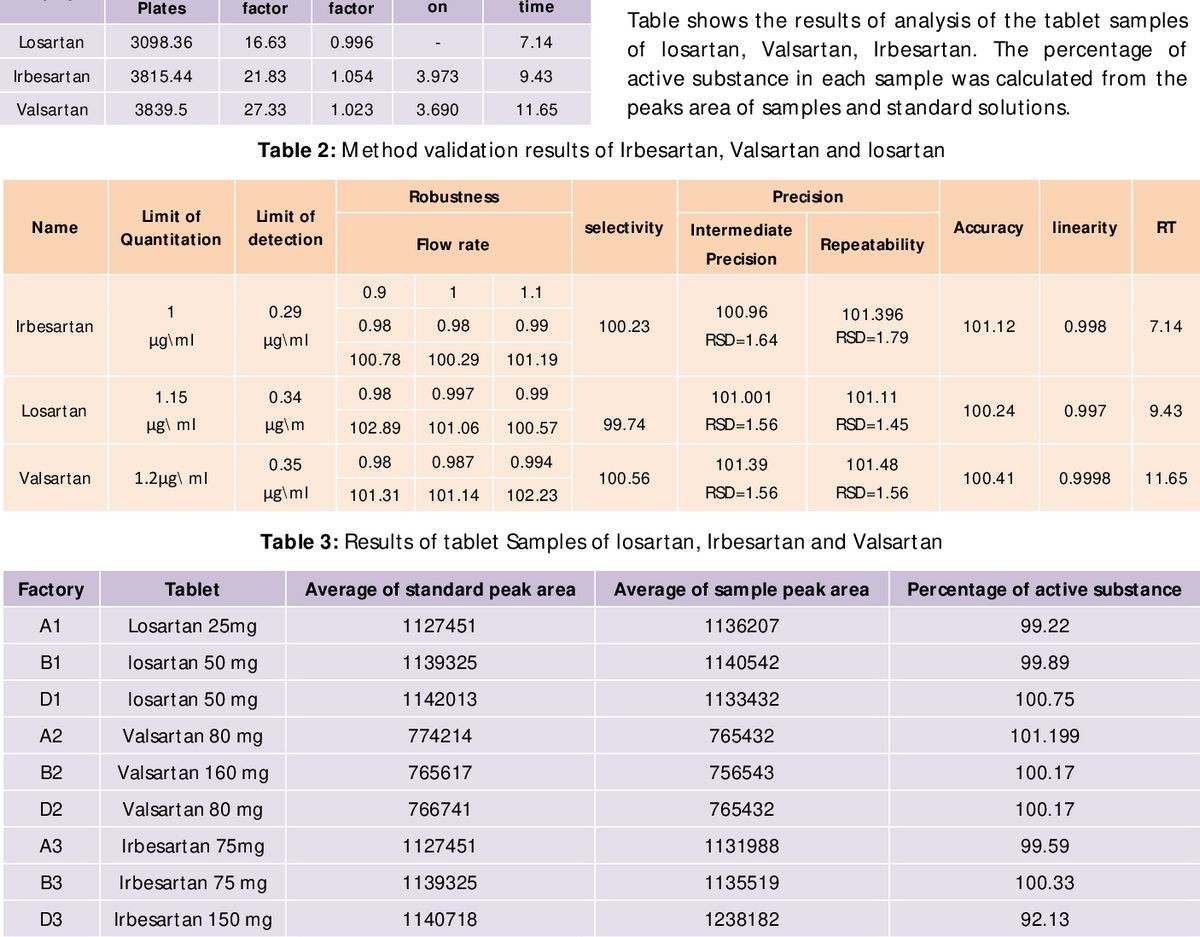
Contents
- 1 Losartan vs. Valsartan: Differences in Side Effects and Uses
Losartan vs. Valsartan: Differences in Side Effects and Uses
Losartan is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) that prevents the binding of angiotensin II to its receptors, resulting in the relaxation and dilation of blood vessels. This effectively reduces blood pressure and eases the heart’s pumping.
Valsartan
Valsartan, also an ARB, works similarly to losartan by inhibiting the binding of angiotensin II to its receptors. This leads to the relaxation and dilation of blood vessels, effectively lowering blood pressure and reducing strain on the heart.
Uses of Losartan and Valsartan
Losartan Uses
Losartan is prescribed for hypertension, stroke risk reduction in patients with hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy (enlarged heart muscle), type 2 diabetes, and hypertensive patients with diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease). It can be used alone or in combination with other medications.
Valsartan Uses
Valsartan is used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and post-heart attack patients with congestive heart failure. It may also reduce hospitalizations in patients with congestive heart failure.
QUESTION
Side Effects of Losartan vs. Valsartan
Losartan
Side effects of losartan may include:
- Persistent cough
- Increase in serum potassium (hyperkalemia)
- Impotence (erectile dysfunction, ED)
Losartan may also decrease kidney function in some patients and should not be used by those with bilateral renal artery stenosis (narrowing of both arteries going to the kidneys). Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown) have been reported.
Valsartan
Valsartan is generally well-tolerated. The most common side effects include:
- Hyperkalemia
- Impotence
- Reduced renal function
- Allergic reactions
Rare but serious side effects of valsartan include rhabdomyolysis (inflammation and destruction of muscle) and angioedema (swelling of soft tissues, including the throat and larynx).
Dosage of Losartan vs. Valsartan
Losartan Dosage
- The starting dose of losartan for adults is 25-50 mg daily.
- The maximum dose is 100 mg daily. The total daily dose may be divided into two administrations.
- The starting dose for pediatric patients (6 years of age and older) is 0.7 mg/kg up to 50 mg once daily. Doses exceeding 1.4 mg/kg or 100 mg daily have not been evaluated in pediatric patients.
- Losartan can be taken with or without food.
The usual dose of valsartan for adults with high blood pressure is 80-160 mg once daily, with a maximum dose of 320 mg daily. For congestive heart failure, the usual dose is 40 mg twice daily, which can be increased to 80-160 mg twice daily. After a heart attack, the initial dose is 20 mg twice daily, which can be increased to 160 mg twice daily if tolerated without side effects.
Valsartan Dosage
The usual dose of valsartan for adults with high blood pressure is 80-160 mg once daily, with a maximum dose of 320 mg daily. For congestive heart failure, the usual dose is 40 mg twice daily, which can be increased to 80-160 mg twice daily. After a heart attack, the initial dose is 20 mg twice daily, which can be increased to 160 mg twice daily if tolerated without side effects.
Drug Interactions with Losartan vs. Valsartan
Losartan
Losartan may increase potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia), which can lead to serious heart problems. Therefore, combining losartan with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium may cause dangerous increases in serum potassium.
Combining losartan or other ARBs with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in certain patients may result in reduced kidney function, including kidney failure. The antihypertensive effect of losartan may be reduced when combined with aspirin and other NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen.
Combining ARBs, ACE inhibitors, or aliskiren increases the risk of hypotension (low blood pressure), hyperkalemia, and reduces kidney function. Aliskiren and losartan should not be combined in patients with diabetes or renal impairment. Increases in blood lithium levels and toxicity have occurred when lithium and ARBs or hydrochlorothiazide were combined.
Valsartan
Combining valsartan with potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium may lead to hyperkalemia and increased serum creatinine levels, especially in heart failure patients.
Combining valsartan or other ARBs with certain NSAIDs may result in reduced kidney function, including kidney failure. Aspirin and other NSAIDs may also reduce the effects of ARBs.
Safety of Losartan vs. Valsartan during Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Losartan Safety
During the second or third trimester of pregnancy, ARBs can cause harm and even death to the fetus. Therefore, losartan should not be used during pregnancy, and it should be discontinued as soon as pregnancy is detected. It is unknown whether losartan is excreted in breast milk, but caution should be exercised in nursing females due to the potential harm to the infant.
Valsartan Safety
Similar to losartan, the use of valsartan and similar drugs during the second or third trimester of pregnancy can harm and even cause death to the fetus. Therefore, valsartan should be stopped as soon as pregnancy is detected. It is unknown whether valsartan is secreted into human milk, but it is excreted in the milk of rats.
Summary
Losartan and valsartan are both angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) that effectively lower blood pressure by blocking the effects of angiotensin II on blood vessels. The main uses of these medications include the treatment of high blood pressure. Losartan also has additional uses, such as reducing stroke risk, managing left ventricular hypertrophy, treating type 2 diabetes, and diabetic nephropathy. Valsartan, on the other hand, is also used to treat heart failure and reduce deaths in patients who developed congestive heart failure after a heart attack.