Contents
Indian Gooseberry: Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
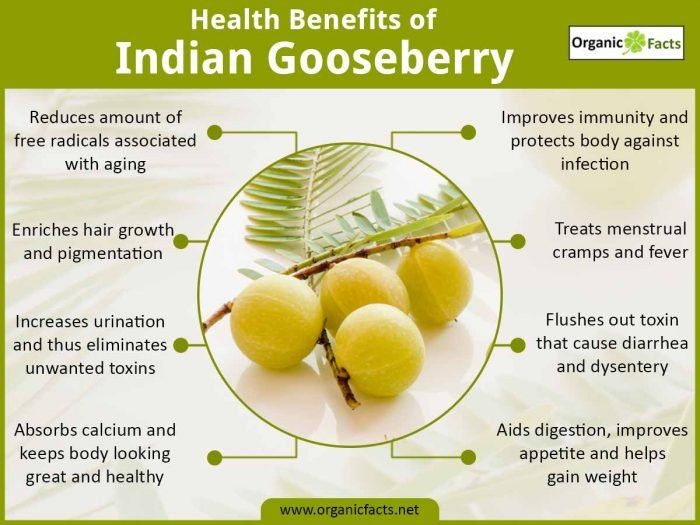
Indian gooseberry, also known as amla, is a significant plant in Ayurveda. The fruit is essential for treating various illnesses.
- Amla treats the common cold, fever, acts as a diuretic, laxative, liver tonic, anti-inflammatory, and hair tonic. It also prevents peptic ulcers and dyspepsia.
- Amla has numerous therapeutic effects, including antipyretic, analgesic, antitussive, cardioprotective, gastroprotective properties, and more.
- Amla and its phytochemicals have anticancer properties.
- Amla has multiple benefits, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities. It may be effective in the treatment and prevention of cancer.
8 Benefits and Uses of Indian Gooseberry
Indian gooseberry offers the following benefits:
- Effective antioxidant: Amla is rich in vitamin C, quercetin, kaempferol, polyphenols, alkaloids, and vitamin A, which boost the immune system, prevent allergies, infections, and toxins.
- Aids in hair care: Amla improves hair color, growth, root strength, and prevents hair loss and balding.
- Possible antiaging agent: Amla’s antioxidants reduce the risk of aging symptoms like wrinkles and age spots.
- Improves digestion: Amla’s fiber content maintains bowel regularity and enhances digestion.
- Controls blood sugar: Amla helps lower blood sugar levels and has cholesterol-lowering properties.
- Helpful for eye care: Amla juice, rich in vitamin A, can improve vision and protect against eye disorders.
- Diuretic effects: Amla has a mild diuretic effect, promoting urination and detoxification.
- Potentially beneficial for hypertension: Regular consumption of amla lowers blood pressure due to its antioxidants and potassium content.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of Indian gooseberry?
While amla has many advantages, it has some side effects:
- Amla’s high fiber content may cause gastrointestinal problems.
- Consult a physician before consuming amla during pregnancy.
- Excessive amla intake can lower blood sugar levels too much.
- Caution should be exercised to avoid overconsumption of fiber.
- Further evidence is required to determine if excess fiber causes constipation.
- Excessive fiber can harm colonic transit and cause bloating and stomach cramps.


