Contents
HPA-1a negative platelets
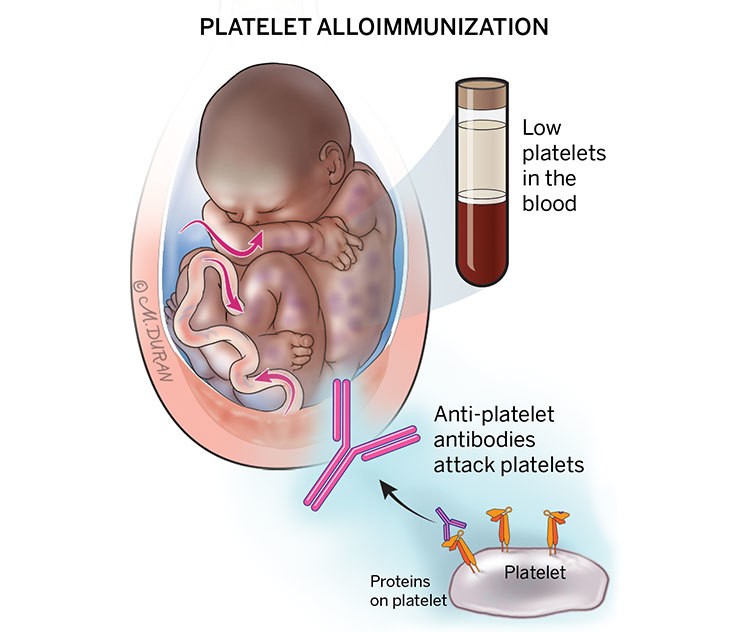
Platelets are fragments of bone marrow cells called megakaryocytes that form blood clots to stop bleeding and promote healing. Platelets are used to treat low platelet levels in people with thrombocytopenia. HPA-1a negative platelets are specifically used to treat neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAIT) in newborns.
Human platelet antigens (HPAs) are unique proteins on platelet surfaces. Antibodies to HPAs can cause NAIT if the mother has different HPA forms from those of the fetus. HPA-1a is the most common antigen associated with NAIT.
HPA-1a negative platelets are also used to treat alloimmune refractory thrombocytopenia due to antibodies against platelet specific antigens. These platelets are collected from donors who do not have HPA-1a antigen and are infused intravenously.
Warnings
- Do not use HPA-1a platelets for patients without anti-HPA-1a antibodies.
- HPA-1a negative platelets may not be readily available and can take days or weeks to acquire. Consult with a blood bank physician for recommendations on managing bleeding in patients with alloimmune thrombocytopenia.
- Consider alternative treatments for NAIT, such as washed maternal platelets or higher doses of untested platelets, in consultation with a blood bank physician.
- Monitor patients for signs of transfusion reaction and bacterial contamination.
- Platelet transfusion carries a risk of viral infections and transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD).
- CMV seronegative or unknown status patients should receive CMV reduced risk platelets.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of HPA-1a negative platelets?
Common side effects include transfusion-transmitted infections, hemolytic transfusion reactions, fever, transfusion-related lung injury, TA-GVHD, and allergic reactions. Seek medical attention for serious symptoms or side effects.
What are the dosages of HPA-1a negative platelets?
Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia:
- Use HPA-1a negative platelets for NAIT and alloimmune refractory thrombocytopenia.
- Dosing may vary, and consultation with a blood bank physician is recommended.
Adult:
- An adult may receive 6 whole blood derived (WBD) units or one unit of apheresis HPA-1a negative platelets to raise the platelet count by 30,000-60,000/uL.
Pediatric:
For neonates and small children, transfusion of 5-10 mL/kg is recommended. For children weighing more than 10 kg, a transfusion of 1 unit of whole blood derived platelets per 10 kg can be used.
Dosing considerations:
- Redosing may be required within 3-4 days if platelet transfusion is given for prophylaxis.
- The corrected count increment (CCI) can help determine if the platelet response is optimal.
What drugs interact with HPA-1a negative platelets?
Consult your doctor for information on drug interactions with HPA-1a negative platelets.
- No severe, serious, moderate, or mild interactions have been reported with other drugs.
For more information on drug interactions, consult the RxList Drug Interaction Checker. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Use CMV-seronegative or CMV reduced risk platelets in pregnant or breastfeeding women who are CMV-seronegative or of unknown status.
- Use Rh-compatible platelets in Rh-negative women to prevent anti-D formation.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Summary
HPA-1a negative platelets are used to treat neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Common side effects include transfusion-transmitted infections, hemolytic transfusion reactions, fever, transfusion-related lung injury, TA-GVHD, and allergic reactions.