Contents
Haldol vs. Abilify
Haldol is an antipsychotic drug used to treat schizophrenia, acute psychosis, and Tourette’s syndrome. It interferes with neurotransmitters in the brain by blocking receptors for dopamine and serotonin on the nerves.
Abilify is an antipsychotic medicine used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, irritability associated with autistic disorder, and Tourette’s disorder. Its exact mechanism of action is unknown, but it is thought to affect dopamine and serotonin receptors.
Side effects of haloperidol and Abilify
Haloperidol
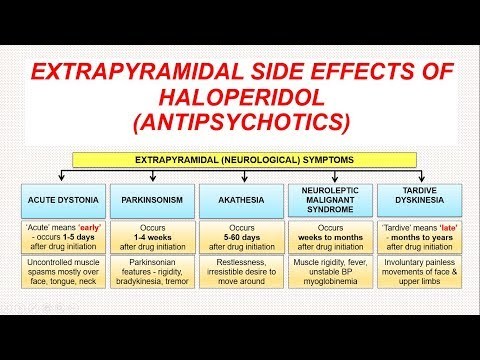
The most common side effects of Haldol are extrapyramidal effects, dizziness, hyperactivity, tiredness, and nausea. Other important side effects include sedation, weight gain, erectile dysfunction, menstrual irregularities, insomnia, gynecomastia, dry mouth, vomiting, and constipation. Haldol may cause orthostatic hypotension during the early phase of treatment. It can also cause abnormal heart beats, seizures, blood cell abnormalities, and withdrawal symptoms. Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with Haldol are at an increased risk of death.
Abilify
WARNINGS
- Long-term use of Abilify may lead to tardive dyskinesia.
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a potentially fatal condition, has been reported with Abilify. Symptoms include high fevers, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse or blood pressure, rapid heart rate, excessive sweating, heart arrhythmias.
The most common side effects of Abilify include anxiety, blurred vision, constipation, cough, headache, insomnia, lightheadedness, nausea, rash, restlessness, runny nose, sleepiness, tremors, vomiting, weakness, and weight gain.
Dosage for haloperidol vs. Abilify
Haloperidol
- The usual adult starting oral dose for patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder is 10 to 15 mg once daily, which may be increased over time to 30 mg daily. The recommended dose for Tourette’s disorder is 5 to 20 mg once daily.
Abilify
- The recommended oral dose for schizophrenia is 0.5-5 mg two or three times daily, with a maximum dose of 30 mg daily. The lactate solution dose is 2-5 mg every 4-8 hours. The decanoate solution dose is 10-20 times the daily oral dose once monthly.
- The recommended dose for Tourette’s syndrome is 0.5-5 mg orally two or three times daily.
Drug interactions
Haloperidol
Haldol may cause increased sedation when taken with alcohol or other sedating drugs. It may also interact with certain pain medications and antidepressants. Carbamazepine may decrease Haldol’s effectiveness, while rifampin may increase the risk of side effects.
Abilify
- Carbamazepine can decrease the amount of Abilify in the body, requiring a higher dose. Other drugs that can affect Abilify levels include phenytoin, rifampin, and phenobarbital.
- Ketoconazole can increase the amount of Abilify in the body. Other drugs that may have a similar effect include itraconazole, fluconazole, voriconazole, cimetidine, verapamil, diltiazem, erythromycinclarithromycin, nefazodone, ritonavir, saquinavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, and grapefruit juice.
Safety during pregnancy or breastfeeding
Haloperidol
- Neonates exposed to Haldol during the third trimester of pregnancy may experience withdrawal symptoms and extrapyramidal symptoms. It should not be used while breastfeeding.
Abilify
- Aripiprazole has not been adequately studied during pregnancy, but it may be used if the benefits outweigh the potential risks. It is not recommended during breastfeeding.
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
Summary
Haldol and Abilify are antipsychotic medications used to treat schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome. Haldol is also used for acute psychosis, while Abilify is used for bipolar disorder, irritability associated with autistic disorder, and major depression. Common side effects include nausea, weight gain, insomnia, vomiting, and constipation.


