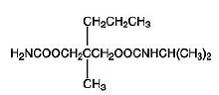
Carisoprodol/Aspirin – Oral, Soma Compound
Medication Uses How To Use Side Effects Precautions Drug Interactions Overdose Notes Missed Dose Storage USES: This product is used short-term to treat muscle pain and discomfort. It is usually used along with rest, physical therapy, and other treatments. Carisoprodol helps relax the muscles. Aspirin helps decrease pain and swelling. HOW TO USE: Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually 4 times a day. Take this medication with a full glass of water (8 ounces/240 milliliters) unless directed otherwise. Do not lie down for at least 10 minutes after taking this medication. If you have stomach upset while taking this medication, take it with food or milk. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. This medication should only be used short-term (for 3 weeks or less) unless directed by your doctor. Do not increase your dose or use this drug more often or for longer than prescribed. Your condition will not improve any faster, and your risk of side effects will increase. Use the smallest effective dose. Pain medications work best if used at the first signs of pain. If you wait until the symptoms have worsened, the medication may not work as well. This medication may cause withdrawal reactions, especially if it has been used regularly for a long time or in high doses. In such cases, withdrawal symptoms such as stomach cramps, trouble sleeping, headache, and nausea may occur if you suddenly stop using this medication. To prevent withdrawal reactions, your doctor may reduce your dose gradually. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more details, and report any withdrawal reactions immediately. Along with its benefits, this medication may rarely cause abnormal drug-seeking behavior (addiction). This risk may be increased if you have abused alcohol or drugs in the past. Take this medication exactly as prescribed to lessen the risk of addiction. Tell your doctor if your condition persists after 2 to 3 weeks or if it worsens. SIDE EFFECTS: Drowsiness, dizziness, headache, stomach upset, nausea/vomiting, or heartburn may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Remember your doctor has prescribed this medication because the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects. Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: easy bruising/bleeding, dark urine, yellowing eyes/skin, persistent nausea/vomiting, hearing problems like ringing in the ears or hearing loss, change in amount of urine, fast/pounding heartbeat, unusual tiredness, confusion. This drug may infrequently cause serious (rarely fatal) bleeding from the stomach or intestines. If you notice any of the following unlikely but serious side effects, stop taking this medication, and consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately: black stool, vomit that looks like coffee grounds, persistent stomach/abdominal pain. A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, seek medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to carisoprodol or aspirin; or to meprobamate, tybamate, or mebutamate; or to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: a certain blood disorder (acute intermittent porphyria), asthma (including a history of worsening breathing with runny/stuffy nose after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs), growths in the nose (nasal polyps), stomach/intestine/esophagus problems (such as bleeding, heartburn, ulcers), bleeding/clotting disorders (such as hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia), personal or family history of regular use/abuse of drugs/alcohol, kidney disease, liver disease, seizure, certain enzyme deficiencies (such as G6PD or pyruvate kinase deficiency), gout. Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products). This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do any activity that requires alertness until you are sure you can perform such activities safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. This medicine may cause stomach bleeding. Daily use of alcohol and tobacco, especially when combined with this medicine, may increase your risk for stomach bleeding. Avoid alcohol and stop smoking. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more information. This medication contains aspirin. Children and teenagers less than 18 years old should not take aspirin if they have chickenpox, flu, or any undiagnosed illness or if they have recently received a vaccine. In these cases, taking aspirin increases the risk of Reye’s syndrome, a rare but serious illness. Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially drowsiness, confusion, stomach/intestinal bleeding, and ulcers. Drowsiness and confusion can increase the risk of falling. This medication is not recommended for use during pregnancy. If you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant, tell your doctor immediately. Do not use this medication during the last 3 months of pregnancy because of possible harm to the unborn baby or problems during delivery. Consult your doctor for more details. This medication passes into breast milk and may have undesirable effects on a nursing infant. Therefore, breastfeeding while using this drug is not recommended. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding. DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval. Some products that may interact with this drug include: corticosteroids (such as prednisone), mifepristone. This medication may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with other drugs that also may cause bleeding. Examples include anti-platelet drugs such as clopidogrel/ticagrelor, "blood thinners" such as dabigatran/enoxaparin/warfarin, among others. Check all prescription and nonprescription medicine labels carefully since many medications contain pain relievers/fever reducers (aspirin, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen). These drugs if taken together with this medication may increase your risk of side effects. However, if your doctor has directed you to take low-dose aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke (usually at dosages of 81-325 milligrams a day), you should continue taking the aspirin unless your doctor instructs you otherwise. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more details. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness including alcohol, antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine), drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, diazepam, meprobamate, zolpidem), other muscle relaxants, and narcotic pain relievers (such as codeine). Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain ingredients that cause drowsiness. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.
QUESTION
OVERDOSE: If overdose is suspected, contact a poison control center or emergency room immediately. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: ringing in ears, severe drowsiness/dizziness, seizures, slow/shallow breathing, mental/mood changes (such as confusion, hallucinations), inability to move legs/arms, shaky/unsteady movement, vision changes (such as blurred vision). NOTES: Do not share this medication with others. It is against the law. This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later for another condition unless your doctor directs you to do so. A different medication may be necessary in that case. MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your usual dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up. STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets. Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company. Information last revised November 2013. Copyright(c) 2013 First Databank, Inc.
Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Selected from data included with permission and copyrighted by First Databank, Inc. This copyrighted material has been downloaded from a licensed data provider and is not for distribution, except as may be authorized by the applicable terms of use.
CONDITIONS OF USE: The information in this database is intended to supplement the expertise and judgment of healthcare professionals. The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that the use of a particular drug is safe, appropriate, or effective for you or anyone else. A healthcare professional should be consulted before any drug is taken, any diet is changed, or any course of treatment is started or stopped.


