Contents
Bronchoscopy
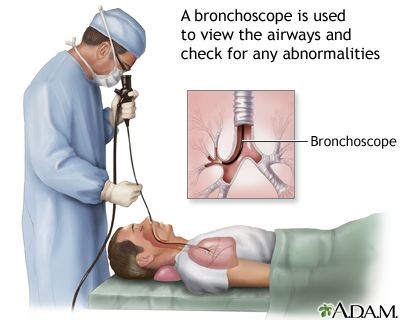
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that uses a viewing tube to evaluate a patient’s lungs and airways for the diagnosis or treatment of lung conditions.
- A bronchoscopy is a procedure in which an examiner uses a viewing tube to evaluate a patient’s lungs and airways, including the voice box, vocal cord, trachea, and bronchi.
- Bronchoscopy is typically performed by a pulmonologist or a thoracic surgeon.
- Although a bronchoscope does not allow for direct viewing of lung tissue, samples can be biopsied through the bronchoscope for laboratory examination.
There are two types of bronchoscopes:
- A flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope
- A rigid bronchoscope
Since the 1960s, the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope has increasingly replaced the rigid bronchoscope due to its ease of use. In some cases, flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy can be performed without anesthesia, but conscious sedation (twilight sleep) is usually used.
On the other hand, rigid bronchoscopy requires general anesthesia and the presence of an anesthesiologist. During bronchoscopy, the examiner can view the tissues of the airways directly through the instrument or on a TV monitor.
The choice between the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope and the rigid bronchoscope depends on the specific indication. For example, a rigid bronchoscope is used when a patient is coughing up large amounts of blood because it has a large suction channel and allows for better control of bleeding.
The majority of bronchoscopies are performed using the flexible fiberoptic scope due to improved patient comfort and reduced need for anesthesia.
Why is bronchoscopy done?
Bronchoscopy can be used for diagnosis or treatment. The following lists provide a greater awareness of the indications for bronchoscopy.
Bronchoscopy is used for diagnosis in the following conditions:
- Persistent or unexplained cough
- Blood in the sputum
- Abnormal chest x-ray findings
- Evaluation of a possible lung infection
Bronchoscopy is used for treatment:
- Foreign body removal from the airway
- Placement of a stent to open a collapsed airway
- Removal of a blockage in the airway
How should patients prepare for bronchoscopy?
Patients undergoing bronchoscopy should not consume anything orally after midnight before the procedure.
Routine medications can be taken with sips of water, except for medications that can increase the risk of bleeding. These medications include aspirin, blood thinners, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and should be discontinued according to the doctor’s instructions.
Patients should inform their doctor of any drug allergies or major drug reactions they have experienced.
What should patients expect during bronchoscopy?
Upon arrival in the bronchoscopy suite or hospital, an intravenous catheter (IV) will be started for medication and fluid administration. The patient will be connected to a monitor for continuous monitoring of vital signs. Supplemental oxygen may be provided through a cannula or facemask.
Medication will be given through the IV to induce relaxation and sleepiness for flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy. For rigid bronchoscopy, anesthesia will be induced and monitored by an anesthesiologist. Patients will lie on their backs with supplemental oxygen. Before inserting the bronchoscope, local anesthesia with lidocaine will be administered in the nose and throat. The bronchoscope can be inserted through the mouth or nose. Some patients may require an endotracheal tube to secure the airway.
Once the bronchoscope is in the airway, additional topical anesthetic will be sprayed to minimize discomfort. The rigid bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth only and is usually performed under general anesthesia.
Flexible bronchoscopy is generally comfortable. Patients may feel the urge to cough due to the foreign object sensation in the airway. Pre-procedural medication and local anesthesia help minimize this feeling. The procedure typically takes 15 to 60 minutes.
If further evaluation is needed or an abnormality is found, samples can be collected using various methods:
- Washing – Saline is injected into the area of interest and then suctioned back for analysis.
- Brushing – A soft brush is used to collect cells around the airway for analysis.
- Needle aspiration – A small needle is used to obtain samples outside of the airway.
- Forceps biopsy – Forceps are used to biopsy visible or lung lesions.
What is the recovery like after bronchoscopy?
After the bronchoscopy procedure, patients are monitored for one to two hours in an observation area until the effects of the medication wear off and they can safely swallow.
- A family member or friend must accompany the patient home.
- Patients should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery for the rest of the day due to possible impairment of reflexes and judgment.
- Some patients may experience dark-brown sputum for the next one to two days, which is normal.
- If there is persistent bright red blood in the sputum, the doctor must be consulted immediately.
- A follow-up visit is scheduled to review the laboratory results.
What are the potential complications of bronchoscopy?
Complications of bronchoscopy are relatively rare, but can occur. All procedures involve some risk or complications due to individual variations. Some potential complications include:
- Nose bleeding
- Vocal cord injury
- Irregular heartbeats
- Lack of oxygen to the body’s tissues
- Heart injury
- Bleeding from the biopsy site
- Punctured lung
- Damage to teeth
- Complications from medications or anesthesia
What is new in bronchoscopy?
- Lasers are now being used with the bronchoscope to remove and destroy lung tumors.
- Probes can be passed through the scope to freeze bleeding sites or shrink tumors.
- Newer technologies are being developed for the management of asthma and emphysema, such as warming the airway linings to reduce asthma attacks.
- Studies are investigating the use of one-way valves in the upper lobe airways of emphysema patients.
- This therapy aims to provide benefits similar to lung volume reduction surgery.


