Contents
- 1 Atorvastatin (Lipitor) vs. Simvastatin (Zocor)
- 1.0.1 What are atorvastatin and simvastatin?
- 1.0.2 What are the uses for atorvastatin and simvastatin?
- 1.0.3 What are the side effects of atorvastatin and simvastatin?
- 1.0.4 How should atorvastatin and simvastatin be taken (dosage)?
- 1.0.5 Which drugs interact with atorvastatin and simvastatin?
- 1.0.6 Are atorvastatin and simvastatin safe during pregnancy or while breastfeeding?
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) vs. Simvastatin (Zocor)
Atorvastatin and simvastatin target the same chemical in the body to drastically reduce levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad cholesterol") in the bloodstream. This reduces the risk of clogged arteries, a key cause of cardiovascular problems.
Both drugs also slightly increase levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or "good cholesterol".
While both Lipitor and Zocor effectively lower LDL, Zocor is better at raising HDL and tends to have fewer gastrointestinal side effects, according to a study.
Atorvastatin and simvastatin share possible side effects such as diarrhea, liver damage, muscle inflammation and damage, and increased blood sugar levels seen in diabetes.
There are other less serious side effects that differ between Lipitor and Zocor.
Many drugs interact with both atorvastatin and simvastatin, so it’s important to inform your doctor about all other medications if they prescribe these cholesterol drugs to you.
What are atorvastatin and simvastatin?
Atorvastatin and simvastatin are chemicals that interfere with liver cells’ cholesterol production. They belong to a family of statins which also includes lovastatin (Mevacor), fluvastatin (Lescol), and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
These medications target an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the process cells use to produce cholesterol. Statins are known as "HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors."
Cholesterol is essential for many body functions, but an excess of LDL in the bloodstream can lead to cardiovascular diseases. Statins like atorvastatin and simvastatin disrupt the liver cells’ cholesterol-making process, reducing cardiovascular disease risk.
Statins also modestly increase HDL (good cholesterol), which helps remove LDL from the bloodstream.
Researchers are still studying how statins increase HDL.
What are the uses for atorvastatin and simvastatin?
Lipitor and Zocor are used to treat elevated total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides, as well as to elevate HDL cholesterol. They can help prevent angina, stroke, heart attack, hospitalization for congestive heart failure, and revascularization procedures in individuals with coronary artery disease. They also reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, angina, and revascularization procedures in adults with multiple risk factors for coronary artery disease.
What are the side effects of atorvastatin and simvastatin?
Common side effects of both Lipitor and Zocor include:
Simvastatin can also cause nausea, vomiting, gas, and allergic reactions.
The most serious possible side effect of both Lipitor and Zocor is liver damage. Doctors should discontinue atorvastatin or simvastatin if liver tests show abnormal concentrations for an extended period.
Muscle inflammation caused by Lipitor and Zocor can lead to serious damage, including rhabdomyolysis, a potentially fatal condition that can cause kidney failure.
Atorvastatin and simvastatin can also raise blood sugar and HbA1c levels, mimicking conditions seen in diabetes.
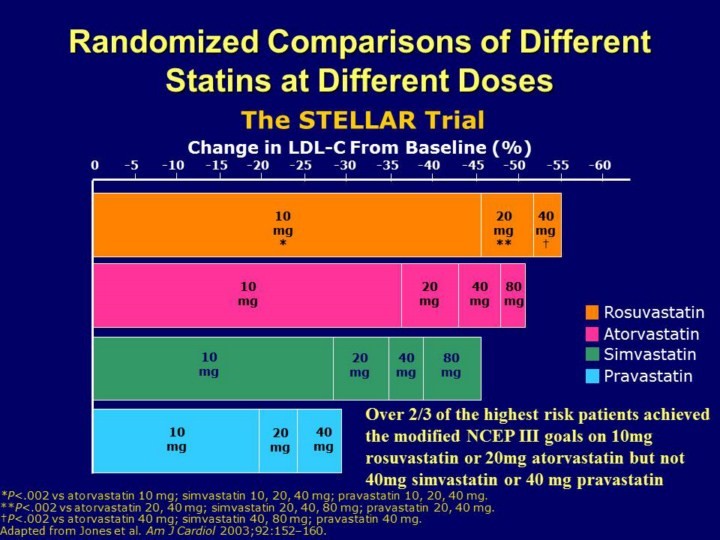
How should atorvastatin and simvastatin be taken (dosage)?
Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Lipitor is prescribed once daily, with a usual starting dose of 10-20 mg per day and a maximum dose of 80 mg per day. Adults requiring more than a 45% reduction in LDL cholesterol may be started at 40 mg daily.
- Pediatric patients should receive 10 mg once daily up to a maximum dose of 20 mg daily. Lipitor can be taken with or without food at any time of day.
Simvastatin (Zocor)
- The recommended dose range of simvastatin is 10 mg to 40 mg, taken once daily in the evening with or without food. High-risk patients can start with 40 mg daily.
- Simvastatin 80 mg is only for patients who have been taking 40 mg for an extended period without muscle toxicity. Patients requiring more than 80 mg should switch to an alternative drug.
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet and understand that I may opt out of subscriptions at any time.
Which drugs interact with atorvastatin and simvastatin?
A number of drugs can reduce the body’s ability to metabolize Lipitor and Zocor, including erythromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, telithromycin, cyclosporine, nefazodone, and HIV protease inhibitors such as indinavir and ritonavir.
Large quantities of grapefruit juice can also increase blood levels of atorvastatin and simvastatin.
Other drugs, such as amiodarone, verapamil, cyclosporine, niacin, gemfibrozil, and fenofibrate, can increase the risk of muscle toxicity when combined with Lipitor or Zocor.
There are additional drugs that can interact with these statins. It is important to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking if they prescribe atorvastatin or simvastatin.
Are atorvastatin and simvastatin safe during pregnancy or while breastfeeding?
Pregnant and nursing mothers should not take atorvastatin, simvastatin, or any other statin due to the risk they pose to the fetus and infants. Statins are only prescribed to women of childbearing age if they are unlikely to become pregnant.
Lipitor and Zocor are passed through breast milk, so alternative methods of feeding, like formula, should be considered if taking these medications.


